* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ch. 17.1-17.2: War Changes Society
First Battle of Lexington wikipedia , lookup
First Battle of Bull Run wikipedia , lookup
Conclusion of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Capture of New Orleans wikipedia , lookup
Economy of the Confederate States of America wikipedia , lookup
Virginia in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Tennessee in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Commemoration of the American Civil War on postage stamps wikipedia , lookup
Baltimore riot of 1861 wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Fort Pillow wikipedia , lookup
Georgia in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
United States presidential election, 1860 wikipedia , lookup
South Carolina in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Hampton Roads Conference wikipedia , lookup
Alabama in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Border states (American Civil War) wikipedia , lookup
Issues of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
United Kingdom and the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Mississippi in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Opposition to the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Military history of African Americans in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
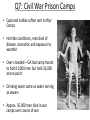
Ch. 17.1-17.2: War Changes Society Essential Question How does the Civil War change the lives of people in the North and South? Focus on differences in each region! Q1: Calls for Emancipation • Abolitionists continue to urge Lincoln to emancipate (free) slaves • Lincoln did not believe he had power under Constitution to abolish slavery where it already existed • Also afraid of angering 4 slave states still in Union FOR YOUR INFORMATION: • Although Lincoln disliked slavery, his first priority was to preserve the Union. • By summer of 1862 Lincoln finally decides in favor of emancipation Lincoln’s Opinion “If I could save the Union without freeing any slave I would do it. If I could save it by freeing all the slaves I would do it; and if I could save it by freeing some and leaving others alone, I would do that also.” Q2: Emancipation Proclamation • January 1, 1863 Lincoln issues Emancipation Proclamation • Document freed all slaves in Confederate territory • In reality, freed very few slaves as it was difficult for Union troops to enforce law in Confederate territory • Was important symbolic measure, making Civil War about liberation for North instead of preserving Union Q3: Why Only Southern Slaves? • Freeing Southern slaves weakened rebelling states in Confederacy, so it could be seen as a military tactic • As commander-in-chief Lincoln has this authority • Constitution did not give him power to free slaves in Union – however Lincoln asked Congress to abolish it gradually throughout land Q4: African-American Soldiers • Emancipation Proclamation also stated blacks now allowed to fight for Union • By war’s end 180,000 black soldiers served in Union Army • Organized in all-black regiments led by white officers • Given worst jobs/positions and paid less than whites • If captured usual shot or returned to slavery instead of being taken prisoner African-American Recruiting Poster FOR YOUR INFORMATION: 54th Massachusetts • Black regiment insisted on no pay • 2 sons of Frederick Douglass served in regiment • July 1863 led attack on Fort Wagner making 54th household name in North and increasing African – American enlistment The Famous 54th Massachusetts FOR YOUR INFORMATION: War Wears on Public NORTH (UNION) • “Copperheads” form – Lincoln’s main opponents, N Democrats wanted peace with S SOUTH (CONFEDERACY) • Growing weary of war and its sacrifices • By end of 1863 army lost 40% of men • Confederate states fell into disagreement • States’ rights hurting them from coordinating war effort FOR YOUR INFORMATION: More South (Confederacy) • Started drafting soldiers in spring 1862 • Wealthy could hire substitute to serve in their place (1863 = $6,000) • Southerners complained – “This is a rich man’s war, but a poor man’s fight” Men Needed North (Union) • Draft started in March 1863 • Allowed substitutes • Offered $300 payment for volunteering as result only small % of men needed to be drafted Q5: Economic Effects of War • Food shortages common in South • Inflation especially in South - Over course of war prices rose 9,000% in South • War production helped North industry and economy – giving advantage over South • In 1861 first income tax established and new currency called “greenbacks” issued – helping Union Q6: Women Aid War Effort • Women began doing traditional jobs of men, as men away fighting • 1000’s of women served on front lines as nurses • Relief agencies started washing clothes, cooking, and gathering supplies for soldiers • Women spies used by N and S Famous nurse, after war began the American Red Cross Q7: Civil War Prison Camps • Captured soldiers often sent to War Camps • Horrible conditions, men died of disease, starvation and exposure to weather • Over-crowded – GA had camp meant to hold 10,000 men but held 33,000 at one point • Drinking water same as water serving as sewers • Approx. 50,000 men died in war camps over course of war Summary • Write a 3-6 sentence summary answering the EQ questions. • Remember the EQ: How does the Civil War change the livesof people in the North and South? Focus on differences in each region!