* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Sexually Transmitted Infections
West Nile fever wikipedia , lookup
African trypanosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Middle East respiratory syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Leptospirosis wikipedia , lookup
Trichinosis wikipedia , lookup
Human cytomegalovirus wikipedia , lookup
Schistosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Marburg virus disease wikipedia , lookup
Diagnosis of HIV/AIDS wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis C wikipedia , lookup
Herpes simplex wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis B wikipedia , lookup
Herpes simplex virus wikipedia , lookup
Epidemiology of HIV/AIDS wikipedia , lookup
Hospital-acquired infection wikipedia , lookup
Candidiasis wikipedia , lookup
Neonatal infection wikipedia , lookup
Lymphocytic choriomeningitis wikipedia , lookup
Microbicides for sexually transmitted diseases wikipedia , lookup
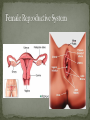
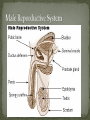
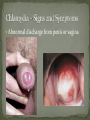
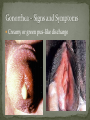
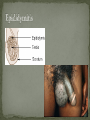
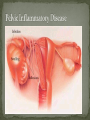
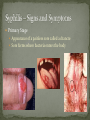
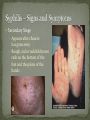
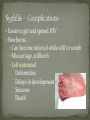
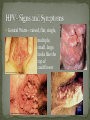
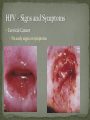
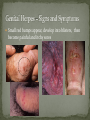
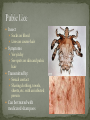
Nickee Palacios Future Method Weber-Morgan Health Department The media most often portrays the EMOTIONAL side of sexual activity. Hurt, rejection, pregnancy, destroyed reputation, and STIs Bacterial, viral, and parasitic infections that a person can ONLY get through sexual activity Bacterial and parasitic infections can be cured with medications Viral infections, such as AIDS and herpes, have NO known cure. More than 25 different STIs Over 95% of all STDs are contracted through sexual intercourse. Every time you have sexual contact with another person you run the risk of getting an STD. Mutual lifetime MONOGOMY is the most effective way to prevent getting STDs. Birth control pills DO NOT prevent STDs from being contracted. Most STDs can be TREATED. Even if the symptoms of the STD disappears, the disease may still be doing damage to the body. Once you are CURED of an STD, you can still be reinfected. Northern Utah Coalition : 393-4153 People with AIDS Coalition of Utah: 484-2205 Planned Parenthood: 479-7721 Weber-Morgan Health Dept.: 399-7180 Utah AIDS Foundation: 1-800-FON-AIDS 4 28 36 M Bacterial The most WIDLY SPREAD STD. Transmitted by: Sexual contact (vaginal, anal, and oral sex) with an infected partner Mother to child 75% of women and 50% of men have no signs or symptoms Abnormal discharge from penis or vagina Abnormal discharge from penis or vagina Burning feeling when urinating Rectal pain, discharge or bleeding Can be found in throat Women: Pain during intercourse Painful periods Men: Burning and itching around the opening of the penis Women Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID) Infertility Ectopic pregnancies Chronic pelvic pain Increased risk of getting HIV Men Infection of the urethra Spread to the tube that carries sperm from the testis Increased risk of getting HIV In babies Linked to premature delivery Low birth weight Respiratory disease Eye infections, blindness in severe cases 8 M Bacterial STI Grows and multiplies in warm, moist, dark areas of the reproductive tract Cervix, uterus, fallopian tubes, urethra, rectum, anus, mouth, throat, and eyes Transmitted by: Sexual Contact (vaginal, anal and oral sex) Mother to child Creamy or green pus-like discharge Creamy or green pus-like discharge Painful urination Sore throat Rectal Infection Constipation, itching, painful bowel movements Men Testicular pain Women Bleeding between periods or excessive bleeding during period Irritation of vulva Painful intercourse Men Epididymitis Scarring in urine canal Women Major cause of PID Ectopic pregnancies Both Can spread to blood or joints Risk of HIV infection increases Newborns Pass to baby through birth canal Joint infection Life-threatening blood infection Eye infection or blindness 12 M Bacterial STI Four Stages Primary Secondary Latent Tertiary Transmitted by: Direct contact with a syphilis sore Vaginal, anal, or oral sex Mother to child Primary Stage Appearance of a painless sore called a chancre Sore forms where bacteria enters the body Secondary Stage Appears after chancre has gone away Rough, red or reddish-brown rash on the bottom of the feet and the palms of the hands Latent Stage “Hidden Stage” No signs or symptoms for years as bacteria multiplies and causes damage to the body Tertiary Stage Damage the heart and brain Attacks the eyes, blood vessels, liver, bones, and joints Paralysis, numbness, blindness, dementia, and death Easier to get and spread HIV Newborns Can become infected while still in womb Miscarriage, stillbirth Left untreated Deformities Delays in development Seizures Death 20 32 M Most common viral STI 30 different virus can infect the genital area Genital warts Cervical cancer Most people don’t know that they have it Body’s immune system fights the virus in about 2 years No cure, but it can be treated Transmitted by: Touching the genitals of an infected partner Genital Warts – raised, flat, single, multiple, small, large, looks like the top of cauliflower Cervical Cancer No early signs or symptoms Helps protect against 4 types of HPV 2 types that cause 70% of cervical cancer cases 2 types that cause 90% of genital wart cases For girls and young women ages 9-26 Three doses over 6 months Vaccine doesn’t protect everyone or every type of HPV Important to get routine cervical cancer screenings 16 M Very common viral STI 45 million people currently infected in the U.S. 1 in 4 women and 1 in 5 men Two types HSV-1 (infects the mouth and lips, “cold sores”) HSV-2 (infects the genital area) Transmitted by: Sexual activity (vaginal, anal, oral sex) Skin-to-Skin contact (hand-to-genital or genital-to-genital) Mother to child Can be given to another person even if no blisters are present Small red bumps appear, develop into blisters, then become painful and itchy sores Women and Men No serious health concerns Virus stay in body for life Outbreaks can be severe in people with weakened immune systems Makes people more at risk to HIV infection Makes HIV+ people more infectious Newborns and babies Can be born with a herpes infection Serious brain, skin or eye problems Death a possibility Mother will be given a C-section to avoid transmission to baby 24 M HIV (Human Immunodeficiency Virus AIDS (Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome) HIV can be transmitted through BLOOD, vaginal secretions and semen. The HIV/AIDS virus must pass from one person’s body fluids in to another BLOOD STREAM. A positive HIV antibody test means that the person has been infected by HIV and can PASS IT ON. AIDS is contracted through intravenous drug use and/or SEXUAL ACTIVITY. AIDS is characterized by a reduction in white blood cell count and it can cause DEATH. AIDS doesn’t kill the person, opportunistic infections do Kaposi's Sarcoma Identified opportunistic infections 1. Bacterial infections 2. Cancers 3. Viral infections 4. Fungal infections 5. Protozoal infections 6. Neurological Conditions 7. Canker sores 8. Wasting syndrome 30 Caused by a parasite Symptoms Men Rarely have symptoms Women Genital itching Green-white or yellow discharge Foul odor Painful urination or intercourse Transmission Sexual intercourse Insect Sucks on blood Lives on course hair Symptoms Very itchy See spots on skin and pubic hair Transmitted by: Sexual contact Sharing clothing, towels, sheets, etc. with an infected person Can be treated with medicated shampoos