* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download wounds and abscess
Gastroenteritis wikipedia , lookup
Sexually transmitted infection wikipedia , lookup
Trichinosis wikipedia , lookup
Leptospirosis wikipedia , lookup
Clostridium difficile infection wikipedia , lookup
Onchocerciasis wikipedia , lookup
African trypanosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Staphylococcus aureus wikipedia , lookup
Dirofilaria immitis wikipedia , lookup
Sarcocystis wikipedia , lookup
Neonatal infection wikipedia , lookup
Schistosoma mansoni wikipedia , lookup
Oesophagostomum wikipedia , lookup
Schistosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Hospital-acquired infection wikipedia , lookup
Visceral leishmaniasis wikipedia , lookup
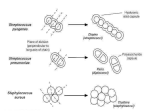
Microorganisms infecting the skin WOUNDS AND ABSCESS • Infections of soft tissues are associated with production of pus and said pyogenic. • A wide variety aerobic and anaerobic species participate singly or in combination in infectious of wounds. WOUNDS AND ABSCESS • The commonest pyogenic bacteria are S.aureus, S .pyogenes ,P. aeruginosa, coliforms bacilli., anaerobic organisem :particularly Clostridium perfringens , bacteroides spp ,anaerobic cocci.. • In many cases there is a mixed infection with more than one bacterial spp. • Wound infection and abscesses occur as complication of surgery, trauma or disease that may interrupt a mucosal or skin surface. wounds Wound infections may be endogenous or exogenous. –Endogenous infections are caused by organisms that are in commensal in the patient . –Exogenous infections the source is out of the body cross-infection is a particular example. the causal organism is spread from person to person. infection may occur after accidental or intentional trauma of the skin or tissue. (Surgical postoperative sepsis. ) Lab procedure • Firstly. In order to identify the different microorganism that cause wound infection, we should collect a proper specimen from the area of the wound. 1- Aspiration Technique This method considered to be the perfect and the most used method for specimen collection from an abscess or deep wound area. a. Disinfect the area by using 70% alcohol. b. Local anesthetic by using pethedin. c. Insert sterile needle deeply inside the abscess of the wound and aspirate the largest amount of specimen. 2- Swab procedure • Swabs are inefficient sampling and are strongly discouraged. It is not common as the aspiration because it holds less volume and more subjected to contamination. A. Disinfect using 70 % alcohol. B. Local anesthetic by using pethedin. C. Open the abscess with a sterile knife and drain the puss and purulent material that gets out. • D. put the sterile cotton swab in the area of the draining and rotate it to get the largest volume possible and then place the swab in its special container. • E. clean the area of the wound and remove the pus. Transportation • Transport the specimen to the lab as soon as possible. In case …… • Aspirated specimen: put it in to anaerobic containers, in which oxygen is excluded or filled with Co2. (Keep at Moist conditions & Room temperature). • Swab specimens: the cotton should be put in transport media called stiurts media. to preserve the specimen from drying and prevent the over growth of rapidly growing microorganism. Laboratory examination • Special methods of examination should be applied to particular specimens. • the basic procedures usually include – Naked eye examination, (for macroscopy criteria ,such as color , odor consistency,..) – The microscopical examination, – Culture Microscopy • Much useful information may be obtained from smear by Gram-staining. We should notice – presence and relative numbers of PMNs and bacteria. – morphology of Gram – positive or Gram – negative bacteria. – Examination of a wet film for fungi or motile bacteria. – A smear stained by the Ziehl- Neelsen method should be examined when the clinical circumstances suggest the tubercle bacillus., another mycobacterium or a nocardia may be present Specimen processing inoculation • Aspirated specimen: if it is thick we should emulsify in normal saline or thioglycolate media in order to make suspension. And we do the culture by streaking method. • Colonies of Streptococcus pyogenes on sheep blood agar. • Notice: * Presence of b hemolysis around colonies • * Enhanced hemolysis around stabbing sites • * Sensitivity to bacitracin (Disk A) Streptococcus pyogenes • Pin point colony: (white or gray) • Gram stain: G+ve, cocci, single chain. • Catalase enzyme: differentiate between Streptococcus –ve Staphylococcus +ve Staphylococcus aureus Identification Process Microscopic morphology • Gram Positive Cocci in clusters IDENTIFICATION PROCESS Biochemical Tests • Catalase • Coagulase • Mannitol salt Agar growth 1. Catalase Test • Place a drop of 3% H2O2 on glass slide. • Select colonies to be tested • Mix colonies in drop of H2O2 (Hydrogen Peroxide) • H2O2 catalase H2O + O2 Catalase Test Bubbles = positive catalase present No bubbles = negative no catalase present •All Staphylococcus species are catalase positive Catalase +ve Catalase -ve 2. COAGULASE TEST: 3. Coagulase converts fibrinogen to fibrin • Pathogenic strains coat themselves in fibrin to evade immune system 3. Growth on Salt Mannitol agar • streak plate with organism • if mannitol is fermented - acid is produced • Phenol red (indicator) turns yellow in presence of acid • incubate 18-24 hrs at 37o C Coagulase-negative Staphylococi Growth seen, but no color change • Staphylococcus aureus Growth AND color change Pseudomonas aeruginosa • Greenish discoloration of media due to production of pyocyanin by Pseudomonas aeruginosa Pseudomonas aeruginosa • Results of oxidase test CLOSTRIDIUM SPECIES • Genus Clostridium consists of Gram positive, anaerobic, spore forming bacilli. Common Species • Clostridium perfringens – Gas gangrene • Clostridium botulinum – Botulism • Clostridium tetani – Tetanus Microscopic morphology • Clostridium perfringens • Gram Positive bacilli Clostridium tetani Gram positive bacilli with drum stick appearance Anaerobic Jar & Gas Pack Leishmaniasis • Obligatory intracellular belong to genus Leishmania • It is transmitted by sandflies. Morphological stages of the Leshmania spp. affecting humans Leishmania species Amastigote Promastigote Intracellular in macrophages in humans In midgut, then proboscis of sandfly ( infective stage to human) and in culture Amastigotes of Leishmania Promastigotes of Leishmania Mode of infection • Bite of female sand flies • Phlebotomine (in Old World) • promastigotes (infective stage) Life cycle Depending on the species of parasite amastigotes may cutaneous leishmaniasis Diagnosis: • Smear: Giemsa stain – microscopy for LD bodies (amastigotes) • Biopsy: microscopy for LD bodies or culture in NNN medium for promastigotes NNN medium • agar slant overlaid with defibrinated rabbit blood used to detect the presence of Leishmania. Schistosomiasis • Females are slender and delicate, whereas males are much bigger and have a spiny trough or groove into which the female fits and locks in. • The male consumes blood and feeds the female most of it, which she turns into eggs, which pass out of the host and can begin the life cycle again. Blood fluke is a special kind of flukes because of following characters: (1) The adult worms look like nematodes, elongated cylindrical in shape. (2) Two sexes are separate. (3) egg without operculum, but with a terminal spine. (4) only one intermediate host required. (5) The infective stage is cercaria. (6) The infective route is by skin. (7) The eggs are main pathogenic stage. Paired male and female adult worms. The female is the darker, curled worm within the male's gynacophoric canal. Mature egg is oval in shape, slight yellow in color, shell is thin without an operculum but with a terminal spine. The content is a miracidium. Cercaria is infective stage. It is composed of the body and forked tail (including tail stem and fork) and has 5 pairs of penetrating glands in the body. oval in shape, slight yellow in color, shell is thin without an operculum but with a terminal spine. A Comparison of Schistosome Eggs S. mansoni Lateral spine S. haematobium Terminal spine S. japonicum No spine Cutaneous Fungal Infections oDermatophytosis - "ringworm" disease of the nails, hair, and the skin caused by fungi called dermatophytes. oDermatomycosis - more general name for any skin disease caused by a fungus. Diagnosis • Note the symptoms. • Microscopic examination of slides of skin scrapings, nail scrapings, and hair. Often tissue suspended in 10 % KOH solution to help clear tissue.