* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 25 August: Getting Oriented, Astronomical Coordinate Systems
Equation of time wikipedia , lookup
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
Definition of planet wikipedia , lookup
Cassiopeia (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Geocentric model wikipedia , lookup
Armillary sphere wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Astronomy in the medieval Islamic world wikipedia , lookup
Perseus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical clock wikipedia , lookup
Planetarium wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Observational astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Astrophotography wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial skies wikipedia , lookup
Tropical year wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical unit wikipedia , lookup
Corvus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
History of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Epoch (astronomy) wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Archaeoastronomy wikipedia , lookup
Chinese astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Hebrew astronomy wikipedia , lookup
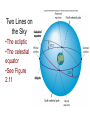
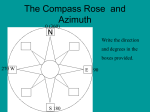
Getting Oriented: Astronomical Coordinate Systems • Why are we doing this? • Lecture material for next week’s lab • Basis for many important technological accomplishments (Pyramid of Cheops) The basic idea • Express the position in the sky of an astronomical object in terms of numbers • One part of the Greek concept that there is a mathematical basis to nature First reference system: the Horizon System Two coordinates: altitude and azimuth Coordinates in the horizon system • Altitude angle goes from 0d to 90d • Azimuth angle goes from 0d to 360d In Horizon System, we see motions in the sky • The Sun rises in the east, reaches highest altitude angle due south, sets in the west • When the Sun sets, it gets dark and we see the stars and planets • The Moon “ “ “ “ “ • The Moon rises at a different time each night and is seen against a different constellation • The constellations in the evening sky are different in different seasons Fundamental astronomical observation: The rising and setting of the Sun. Most people don’t realize other astronomical objects do this as well Question for the audience: What is going on to cause this east-towest motion of all objects, rising in east and setting in west? Demo There are other aspects of the night sky (and daytime sky) that are not obvious to modern people Seasonal Variations in the Position of the Sun (back in horizon system) This year, September 22, 10:09 PM The changes in the rising (and setting) locations of the Sun are big Seasonal differences in the night sky: go out tonight at 9 PM • Constellations Bootes in west • Bright star Vega straight overhead • Constellation of Scorpius (with bright star Antares) low in southwest. • Constellations of Pegasus and Andromeda just rising • Check it out with the help of star charts! By the end of the semester, the situation will be entirely Different. There is a phenomenon that could be called the “Parade of the Constellations”? Measuring the position of the Sun against the background stars The path of the Sun through the stars The “parade of the constellations” Demo Obliquity of the Ecliptic and the Altitude Angle of the Sun Explanation of Seasonal Variations: tilt of the Earth’s axis: obliquity of the ecliptic Two Lines on the Sky •The ecliptic •The celestial equator •See Figure 2.11 For new purposes, we need a different coordinate system Analogy: I am riding my bike on a dirt road near Lone Tree, and want to describe to someone in London the location of a radio tower I see in the distance. Question: what system of coordinates do I use? A New Coordinate System: Celestial Coordinates • The stars “stick together” and define their own reference system. The planets move with respect to them • Celestial coordinates are Right Ascension and Declination • Right Ascension ….. Longitude • Declination ….latitude • http://sohowww.nascom.nasa.gov/