* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Astronomyunitbingo
Astrobiology wikipedia , lookup
Outer space wikipedia , lookup
Equation of time wikipedia , lookup
Rare Earth hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial life wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Astronomy on Mars wikipedia , lookup
Late Heavy Bombardment wikipedia , lookup
Geocentric model wikipedia , lookup
Comparative planetary science wikipedia , lookup
Lunar theory wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial skies wikipedia , lookup
Tropical year wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical unit wikipedia , lookup
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
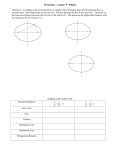
Test Review Terms • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • Elliptical orbit Rotation Axis Full moon Aphelion Major axis Foci Semimajor axis Perihelion Sun Maunder minimum Solar day Seasons Lunar phases photosphere • • • • • • • • • • • • • Fission Fusion Electromagnetic radiation Ecliptic Vernal equinox Solar eclipse Lunar eclipse Summer solstice Autumnal equinox Winter solstice Keplar’s laws Law of universal gravitation precession sun occupies one focus of the ellipse, not the center. The other focus is empty. An ellipse is “almost” a circle, so the universe is geometric although not perfect. The formula used to determine the shape of the ellipse is e=d/l where eccentricity is equal to the distance between the foci divided by the length of the major axis Keplers 1st Law – law of Ellipses Spring day characterized by day and night of equal lengths Vernal equinox Plane of the Earth’s orbit about the sun ecliptic equation that validates his second law. 2 3 P =a Keplers 3rd Law Earth’s position around December 21st, at which the northern hemisphere has its minimum daylight hours Winter solstice Periods of low sunspot activity Maunder minimum Imaginary line through which the Earth rotates on axis Phase of the moon in which it appears entirely illuminated Full moon point that determines the shape of ellipse foci Half the distance of the major axis Semi major axis Occurs when the moon passes directly between the sun and earth Solar eclipse The statement that describes the relationship among the masses of two bodies and the distance between them Law of universal gravitation Wobble of the Earth’s axis caused by the Moon’s gravitational force on Earth precession Star closest to our planet sun Caused by the tilt of the Earth and its orbit around the sun seasons Passes through the foci of an ellipse Major axis An imaginary line between the Sun and a planet that sweeps out equal amounts of area in equal amounts of time Kepler’s Second Law Point in Earth’s revolution around the sun at which it is furthest aphelion Electric and magnetic disturbances that travel through space Electromagnetic radiation 24 hours, our time keeping system is based on it. Solar day Occurs when the moon passes through the earths shadow Lunar eclipse Orbit that is less than one but greater than 0 in eccentricity Elliptical orbit Earth’s position around June 21, at which the northern hemisphere has its maximum daylight hours Summer solstice Point in the Earth’s orbit when closest to the sun perihelion Sequential changes in the appearance of the moon Lunar phases Earth spining on its axis in a 24 hour cycle rotation High energy required, fusing of 2 or more lighter atoms into a larger 1, produces radiant energy of stars, hydrogen bomb fusion Splitting of a large atom into two or more smaller ones, takes little energy, produces many highly radioactive particles, atomic bomb fission Emits most of the light from the sun photosphere Fall day characterized by day and night of equal lengths Autumnal equinox