* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
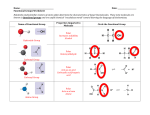
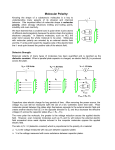
Molecular Polarity • Polar describes a bond where one atom has a partial positive charge and the other a partial negative charge • Molecules as a whole can be polar • In a polar molecule electron density accumulates toward one side of the molecule • Experimental measurement of polarity of a molecule Molecular Polarity • When polar molecules are placed in electric field they experience a force that aligns them with the field • Electric field is created by pair of oppositely charged plates, positive end of molecule is attracted to negative plate and vice versa • The extent to which the molecules line up with the field depends on their dipole moment µ Molecular Polarity defined as the product of the magnitude of the partial charges (ᵟ+ and ᵟ-) & the distance they are seperated SI unit is coloumb-meter Force of attraction b/w negative end of one polar molecule and positive end of another is dipole-dipole force Intermolecular forces influence the temperature Molecular Polarity • At which a liquid freezes or boils • The forces determine whether a liquid dissolves certain gases or solids or whether it mixes with other liquids • To predict whether a molecule is polar need to consider if it has polar bonds and how these bonds are positioned • Eg diatomic molecules composed of two atoms with different electronegativities are always polar • What happens to 𝐴𝐵2 , 𝐴𝐵3 or 𝐴𝐵4 • Will evaluate how the choice of substituent or terminal groups (B) and molecular geometry influence molecular polarity • 𝐴𝐵2 eg 𝐶𝑂2 the the C and O pond is polar. The terminal atoms are at the same distance from C and both have ᵟ- charge and is symmetrically arranged around C atom, therefore 𝐶𝑂2 has no molecular dipole even though each bond is polar. • 𝐻2 𝑂 bent triatomic molecule, O has larger electronegativity then H each O-H bond is polar • Electron density accumulates on O side making the molecule electrically lopsided and therefore polar