* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 1 - Sitecom
Distributed firewall wikipedia , lookup
Internet protocol suite wikipedia , lookup
Recursive InterNetwork Architecture (RINA) wikipedia , lookup
Piggybacking (Internet access) wikipedia , lookup
Computer network wikipedia , lookup
Network tap wikipedia , lookup
Remote Desktop Services wikipedia , lookup
Airborne Networking wikipedia , lookup
Wake-on-LAN wikipedia , lookup
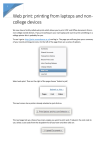
Network configuration Quick Installation Guide 1 Hardware installation 1.1 PCI Fast Ethernet Card 1.1.1 Hardware Installation To insert the network interface card into the computer, follow these steps: 1. Turn the computer power off and unplug power cord and any other cables that are connected to the computer. Remove the computer cover. 2. Select an available PCI slot and remove the back plate from the selected slot using a small screwdriver. 3. Insert the card in the PCI slot, and make sure it is completely seated and secure the screw you removed from the back plate. 4. Replace computer cover and reconnect power cord and other cables. 5. Align the RJ-45 connector on one end of the cable with the notch on the network interface card’s RJ-45 port and insert it into the card. 6. Connect the RJ-45 connector on the other end of the cable to the network interface card on the other computer. 3.2.2. Windows 98 Installation 1. Turn the power on and boot from Windows 98. 2. Windows 98 will prompt “PCI Ethernet Controller” in “New Hardware Found” dialog box. 3. Select "Search for the best driver" from “New Hardware Found” dialog box, then click Next. 4. Insert the Sitecom Driver Diskette in your floppy drive. 5. Select “specify a location”, type ‘A:\WIN98’, then click Next. 6. Follow the on screen instructions to complete the process. 7. Restart your computer. 8. When the computer restarts, you are prompted for the user name and password. Please enter a name (you do not have to use a password). If you enter a password, you must use this password each time you use the computer, or Windows 98 does not let you login the network. Before you proceed with the installation steps, you need to have the Windows 98 CDROM, if the “Insert Disk” window opens and the “Please insert the disk labeled Windows 98...” message appears at any time during the installation process, insert the Windows 98 CD-ROM in appropriate drive (the CD-ROM drive) and click on “OK”. Then follow the next step in the instructions. 3.2.3. Windows ME/2000/XP Installation For these Operating Systems it is not necessary to install the Network adapter with the driver disk. The adapter will be found and installed automatically by Windows Check to see if the adapter is correctly installed: Windows ME Click the “My Computer” icon on the desktop with the right mouse button, choose “properties”. Select the “Device manager” tab. In the next screen click on the plus (+) besides “Network adapters” and check if the ND010 Fast Ethernet adapter or RTL 8139 PCI Fast Ethernet-adapter is installed Windows 2000 Click the “My Computer” icon on the desktop with the right mouse button, choose “properties”. Select the ‘hardware’ tab; Click the “Device manager” button. In the next screen click on the plus (+) besides “Network adapters” and check if the RTL 8139 PCI Fast Ethernet-adapter is installed Windows XP Click start, Click the “My Computer” with the right mouse button, choose “properties”. Select the ‘hardware’ tab; Click the “Device manager” button. In the next screen click on the plus (+) besides “Network adapters” and check if the RTL 8139 PCI Fast Ethernet-adapter is installed 1..3 DOS ODI driver installation In the driver diskette, the "NWCLIENT" directory contains DOS ODI drivers to support Novell's NetWare 3.x and 4.x network operating system. 4. Setting Up a Local Area Network 4.1 Network Protocols Windows installs 3 network protocols automatically during the installation of the hardware. Network applications only use 1 protocol at a time. However, just leave all 3 protocols because different applications can use different protocols. Internet sharing in example uses TCP/IP while some network games use IPX/SPX. NetBEUI: The acronym stands for NetBIOS Extended User Interface. This is Windows native network protocol. NetBEUI does not contain a network address, so it’s not a routable protocol. This means data cannot be routed from one network to another. IPX/SPX: This acronym stands for Internet work Packet Exchange/Sequenced Packet Exchange. This is a Novell NetWare-based protocol that is used to route messages from one network node to another. IPX/SPX is a routable protocol, and because IPX packets include network addresses, data can be exchanged between different networks. SPX ensures that an entire message (a data IPX packet) arrives intact. TCP/IP: An acronym for Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol, TCP/IP was developed by the U.S. Department of Defence to connect and network to dissimilar systems. TCP provides the data-transport functions, while IP provides the routing mechanism. TCP/IP is a routable protocol. Every client and server in a TCP/IP network requires an IP address, which can be assigned either permanently or dynamically (DH CP – Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol), meaning that it draws from a pool of addresses each time the machine starts up. 4.2 Configuration for TCP/IP The TCP/IP protocol is used to setup a network between the two pc’s, which has to be configured. Windows 98/ME Right click the icon “My Network places” on the desktop, choose “properties”. If you have multiple network cards, be sure to select the correct one: each network card, including the dial-up adapter, requires a unique IP address. In the “general” tab choose “Use this IP-address”, use 192.168.1.1 for the IP address, incrementing the last digit of the IP address for each machine (the second machine's address would be 192.168.1.2, the third 192.168.1.3, and so on). The Subnet Mask should be the same (255.255.255.0) for all of the machines. You don't need to worry about Gateway or DNS numbers in this situation. Windows 2000 Right click the icon “My Network places” on the desktop, choose “properties”. Right click the LAN connection of the Sitecom Network adapter, choose “properties”. Click the TCP/IP protocol. In the “general” tab choose “Use this IP-address”. Fill in the address as mentioned in the Windows ME/98 section. Windows XP Click start, Right click the icon “My Network places”, and choose “properties”. Right click the LAN connection of the Sitecom Network adapter, choose “properties”. Click the TCP/IP protocol. In the “general” tab choose “Use this IP-address”. Fill in the address as mentioned in the Windows ME/98 section. Now you are ready to configure file and printer sharing. Do so before rebooting the PCs 4.3 File and Printer sharing Windows 98/ME To enable File and Printersharing on your network, Right click the icon “My Network places” on the desktop, choose “properties”. Click the ‘file and printersharing” button. Simply click the two boxes you see in the resulting dialog box, then click OK. But before you reboot your computer, you'll need to check a few other settings. 1. Click the Identification tab in the Network Control Panel. Enter a unique COMPUTERNAME, and a brief description of your computer in the Computer Description slot. The WORKGROUP name you assign to each computer must be exactly the same for every computer on your network. If you're running an NT server, and it's a Domain Controller, you'll want to put the name of your server's domain in the Workgroup section on all of your computers. This enables each user to log in and share resources with the server directly; just make sure to create user accounts on the server first 2. Sharing Drives and Folders. When you want to share a hard drive (or any other storage device) on one machine with all of the other machines on the network, simply right-click the drive letter or folder you wish to share, then select Sharing from the pop-up menu. After you select Sharing, you'll be presented with a dialog box containing several options. Type in the Share Name, add a comment, and set the access type. If you choose Read Only, other computers on the network will be prevented from copying files into the shared drive or folder. If you select Full, any machine on the network will be able to write to them as well. 3. Sharing Printers. Click ‘start’, ‘settings’, and ‘printers’. Right click the printer you want to share on the network and choose “sharing”. In the following screen enable sharing and fill in a sharename, the printer is now shared. To use the network printer on other PCs in the network, it has to be installed on the other PCs first. Click ‘start’, ‘settings’, and ‘printers’. Click the ‘Add New Printer’ icon. The ‘New Printer Wizard’ starts. Choose ‘network printer’. In the following screen browse to the correct printer via network environment. The printer will now be installed. Repeat this steps for all PC’s in the network. The printer can now be used from every PC in the network. Windows 2000/XP File and Printer sharing will be installed automatically under Windows 2000/XP. Sharing files, folders and printers is the same as under Windows 98/ME, however assigning the computer and workgroup name as in step one is different. Windows 2000 Right click the ‘My Computer’ icon on the desktop, choose ‘properties’. Click the ‘computer name’ tab. Fill in the COMPUTERNAME and the WORKGROUPNAME by the same specifications as Windows 98/ME Windows XP Click ‘start’. Right click the ‘My Computer’ icon, choose ‘properties’. Click the ‘computer name’ tab. Fill in the COMPUTERNAME and the WORKGROUPNAME by the same specifications as Windows 98/ME Congratulations! After a reboot your network is complete!