* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download FM Transmitter
Sound reinforcement system wikipedia , lookup
Pulse-width modulation wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Spark-gap transmitter wikipedia , lookup
Public address system wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Resonant inductive coupling wikipedia , lookup
Semiconductor device wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Wien bridge oscillator wikipedia , lookup
Current mirror wikipedia , lookup
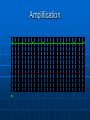
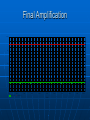
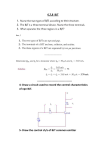
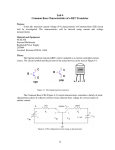
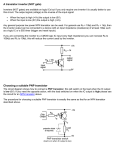
FM Transmitter Matt Baker Kevin Van Dyke Design Three stage, 9V FM transmitter • Audio amplification • Oscillation • RF amplification Electret microphone for input Dipole antenna – 160 cm Circuit Diagram Circuit Description Radio frequency oscillator (100MHz) Microphone picks up and amplifies audio and then feeds it to first transistor for amplification Output from collector is fed into base of the second transistor where it modulates the resonant frequency of the tank circuit • This is done by varying the junction capacitance of the transistor. • Junction capacitance is a function of the potential difference applied to the base of the second transistor. Oscillation occurs Final stage: Third transistor amplifies the output RF signal. Electret Microphone What is an electret? • It is a permanently charged dialectric. • The diaphragm of the microphone acts as one of the plates in the capacitor. • The movement of the plate changes the capacitance. • Amplified by a FET amplifier. First amplification stage Standard self-biasing common emitter amplifier The 22n capacitor isolates the microphone from the base voltage of the transmitter by blocking DC. First Transistor Amplification 800mV 400mV 0V -400mV 0s V(Q5:c) 1ms 2ms V(V5:+) 3ms 4ms 5ms Time 6ms 7ms 8ms 9ms 10ms Oscillator Stage Oscillator necessary to generate RF carrier waves Feedback signal makes the base-emitter current vary at the resonant frequency. This causes the emittercollector current to vary at the same frequency. This signal then radiated as radio waves. Final Amplification Stage This stage amplifies the RF signal. A Zetex ZTX320 RF transistor was used to do this efficiently. L2 and the 10p capacitor in parallel with it are designed to reduce harmonics from the circuit. Output power from this stage will be maximum when it is tuned to oscillate at the same frequency as the previous stage. • How? Peaking Circuit Peaking Circuit Uses diodes to charge a capacitor. Measure voltage across cap w/ voltmeter. To tune circuit, move turns of coil L3 further apart or closer together until the reading on the voltmeter is maximum. Third Transistor Final Amplification 10V 8V 6V 4V 2V 0s V(C7:2) 1ms V(L6:2) 2ms 3ms 4ms 5ms Time 6ms 7ms 8ms 9ms 10ms Signal Power VE 2.537 VC 9 P IC VCE IC .0252 VCE VC VE P 0.163 Watts