* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Slide Show Mastering Databases
Open Database Connectivity wikipedia , lookup
Microsoft SQL Server wikipedia , lookup
Concurrency control wikipedia , lookup
Entity–attribute–value model wikipedia , lookup
Ingres (database) wikipedia , lookup
Microsoft Jet Database Engine wikipedia , lookup
Functional Database Model wikipedia , lookup
Extensible Storage Engine wikipedia , lookup
Versant Object Database wikipedia , lookup
Relational model wikipedia , lookup
ContactPoint wikipedia , lookup
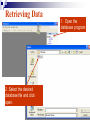
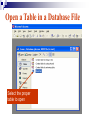
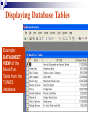
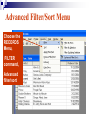
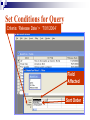
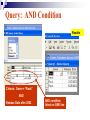
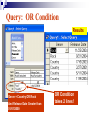
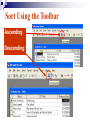
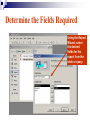
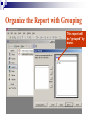
Databases Competency 7.00 Objective 7.02 Explain advanced database concepts and functions. Retrieving Data 2. Select the desired database file and click open. 1. Open the database program Open a Table in a Database File Select the proper table to open Displaying Database Tables Example: DATASHEET VIEW of the MusicFun Table from the TUNES database Use Filters to Select Data Filter: Displays records in a database that match specified criteria. Advantages of using filters Easier to use than query Fast Disadvantages of filters All fields are displayed when using a filter Cannot save filters like queries Types of filters By Form (key criteria into a form; more flexible because criteria can be set for more than one field) By Selection (quick/easy option by highlighting a cell as criteria) Excluding Selection (excludes data highlighted in cell) Advanced Filter/Sort (works like a query) Advanced Filter/Sort Menu Choose the RECORDS Menu, FILTER command, Advanced filter/sort Build a Query Query: A database object that allows the user to select records/data from a database using multiple criteria (comparison operators) and arrangement (sorting) standards. Advantages Queries can be saved Each table can be associated with multiple queries Set Conditions for Query Criteria: ‘Release Date’ > ‘7/01/2004’ Field Affected Sort Order Comparison Operators for Queries and Filters Equals Does not equal Between and Less than Greater than Equal to or less than Equal to or greater than = <> between and < > <= >= Query: Advanced Criteria AND Condition: Uses the same row in the Query Design window The AND condition reduces the number of records because both conditions must be met. OR Condition: Uses different rows in the Query Design window The OR condition increases the number of records because records are selected if either condition is met. Query: AND Condition Results Criteria: Genre = “Rock” AND Release Date after 2002 AND condition listed on ONE line Query: OR Condition Results Genre = Country OR Rock And Release Date Greater than 01/01/2000 OR Condition takes 2 lines! Search Records To search for specific records, select Find command from the Edit menu. Key the search string (data) in the dialog box. Key “where” to find the records (which table). Similar to Find/Replace commands in other programs Not case sensitive Sorting To sort is to arrange data in a specific order. Ascending sort: Alphabetical order (A to Z) or numerical order (1 to 9) Descending sort: Reverse alphabetical order (Z to A) and largest to lowest number (9 to 1) Simple sort: Arranges by only one field Complex sort: Arranges data by multiple fields (first field, primary; second field, secondary) Sort Using the Toolbar Ascending Descending Complex Sort Multiple field sort: Primary sort – first field chosen Secondary sort – second field chosen Datasheet View Sort In Datasheet View, sorted fields must be highlighted and adjacent (sides touching). Sort priority: sort left to right Leftmost column (field) = primary sort Next field = secondary sort The Database Report A database object used to organize, summarize, and print all or some of the data in a database. Advantages of a Report Data is viewed in an attractive format Allows variations in fonts, colors, shading, and borders Allows page layout design Allows images to be inserted Shows specific fields or selected records rather than an entire table Allows records to be grouped/sorted with summaries and totals Displays fields from multiple tables Plan and Create a Report Determine the table/queries to be used in the report Determine what fields/data will be desired in the report Plan the groupings and summary totals if desired Enhance the appearance and design before printing Determine the Fields Required Using the Report Wizard, select the desired fields for the report from the table or query. Organize the Report with Grouping This report will be “grouped” by name. Sort Data in the Report Sorting a field within the selected group will further organize the report. Design the Appearance Follow the Wizard’s Next Steps to format the design, style, and appearance of the report. Name and preview the completed report. Insert Pictures/Customize Database Reports Insert pictures, labels, text boxes, and other graphic elements while in Design View. Database Relationships Relationship - A linked connection between two tables that share a common field. Join Line - graphically represents the relationship between two tables The related field between the two tables must be of the same data type and size Establishing Relationships Relationship established between two tables One record in the Student Table is related to one record in the Participation Table