* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Circulatory System 63. Circulatory System
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Artificial heart valve wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Jatene procedure wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
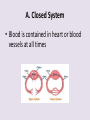
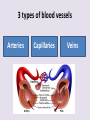
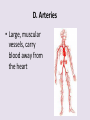
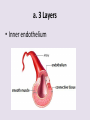
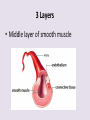
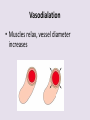
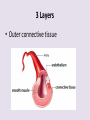
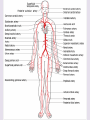
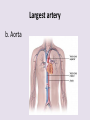
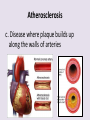
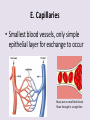
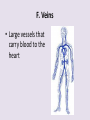
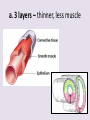
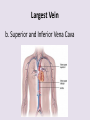
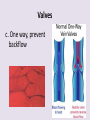
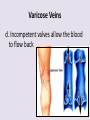
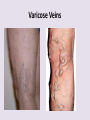
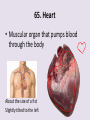
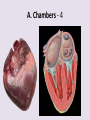
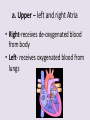
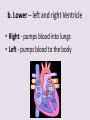
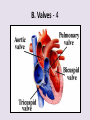
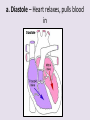
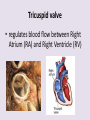
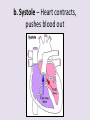
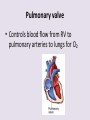
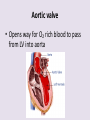
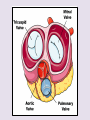
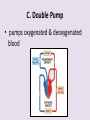
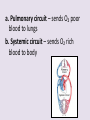
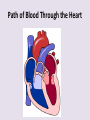
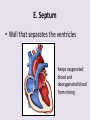
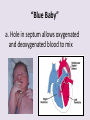
Circulatory System 63. Circulatory System • Transports substances throughout the body A. Substances transported a. Oxygen from lungs b. Nutrients absorbed by small intestines c. Antibodies that fight disease d. Hormones e. Wastes – CO₂, nitrogenous wastes Circulatory System • Made up of three main parts: Blood Vessels Heart Blood 64. Blood Vessels • Tubes that circulate blood through the body A. Closed System • Blood is contained in heart or blood vessels at all times B. Length • If stacked end to end, could stretch 60,000 miles 3 types of blood vessels Arteries Capillaries Veins D. Arteries • Large, muscular vessels, carry blood away from the heart a. 3 Layers • Inner endothelium 3 Layers • Middle layer of smooth muscle Vasoconstriction • Muscles contract, vessel diameter decreases Vasodialation • Muscles relax, vessel diameter increases 3 Layers • Outer connective tissue Main Arteries Largest artery b. Aorta Atherosclerosis c. Disease where plaque builds up along the walls of arteries Arterioles d. Smallest branches of the arteries, connect to capillaries E. Capillaries • Smallest blood vessels, only simple epithelial layer for exchange to occur Many are so small that blood flows through in a single line Capillaries Capillary Bed a. Interweaving networks of capillaries Venules b. Small tubes where capillaries unite to connect to the veins F. Veins • Large vessels that carry blood to the heart a. 3 layers – thinner, less muscle Largest Vein b. Superior and Inferior Vena Cava Valves c. One way, prevent backflow Varicose Veins d. Incompetent valves allow the blood to flow back Varicose Veins Pathway HAacvVH The Heart 65. Heart • Muscular organ that pumps blood through the body About the size of a fist Slightly tilted to the left A. Chambers - 4 a. Upper – left and right Atria • Right-receives de-oxygenated blood from body • Left- receives oxygenated blood from lungs b. Lower – left and right Ventricle • Right - pumps blood into lungs • Left - pumps blood to the body B. Valves - 4 a. Diastole – Heart relaxes, pulls blood in Tricuspid valve • regulates blood flow between Right Atrium (RA) and Right Ventricle (RV) Mitral Valve • lets O₂ rich blood from your lungs pass from LA to LV b. Systole – Heart contracts, pushes blood out Pulmonary valve • Controls blood flow from RV to pulmonary arteries to lungs for O₂ Aortic valve • Opens way for O₂ rich blood to pass from LV into aorta C. Double Pump • pumps oxygenated & deoxygenated blood a. Pulmonary circuit – sends O₂ poor blood to lungs b. Systemic circuit – sends O₂ rich blood to body Path of Blood Through the Heart Path of Blood Through the Heart a. Superior and inferior vena cava Path of Blood Through the Heart b. Right atrium Path of Blood Through the Heart c. Tricuspid Valve Path of Blood Through the Heart d. Right ventricle Path of Blood Through the Heart e. Pulmonary Valve Path of Blood Through the Heart f. Pulmonary arteries Path of Blood Through the Heart g. Lungs Path of Blood Through the Heart h. Pulmonary veins Path of Blood Through the Heart i. Left atrium Path of Blood Through the Heart j. Mitral Valve Path of Blood Through the Heart k. Left ventricle Path of Blood Through the Heart l. Aortic Valve Path of Blood Through the Heart m. Aorta E. Septum • Wall that separates the ventricles Keeps oxygenated blood and deoxygenated blood from mixing “Blue Baby” a. Hole in septum allows oxygenated and deoxygenated blood to mix F. Heart Rate • Number of times the heart beats per minute Males – 70 bpm Females – 75 bpm newborn-130 3 months-150 1 year- 125 3 years- 100 12 years- 85 adult- 60-101 “Lub-dup” • Lub – valves between atria and ventricles closing • Dup – valves between ventricles and blood vessels closing Heart Murmur • Abnormal heart sounds Can be from: Thin walls that vibrate Increased blood flow Valve problems