* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download AP Statistics Lesson Plans 2016-2017
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
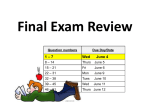
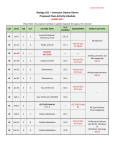
AP Statistics Lesson Plans 2016-2017 AP Stat Test 5/11/17 (Noon-4pm) All assignments and assessments are subject to change, so please see the classroom board daily for changes. 8/15 – 8/19 Date Objective/Standard Mon 8/15 Tues 8/16 Wed 8/17 Thurs 8/18 Fri 8/19 Identify individuals & variables in set of data; Classify variables as categorical/quantitative; Identify units of measurements for quantitative data. Make bar graph; Recognize when a pie chart can & can’t be used; Identify what makes some graphs deceptive From a two-way table of counts, answer questions involving marginal & conditional distributions; Describe the relationship between two categorical variables by computing appropriate conditional distribution; Construct bar graphs to display the relationship btw two categorical variables Make a dotplot or stemplot to display small sets of data; Describe the overall pattern (SOCS) & identify the shape of a distribution Make a histogram with a reasonable choice of classes and interpret histograms 8/22 – 8/26 Date Objective/Standard Mon 8/22 Review 1:1-1:2 Tues 8/23 Wed 8/24 Thurs 8/25 Fri 8/26 Calculate & interpret measures of center & spread; Identify outliers using 1.5 X IQR Rule Make a boxplot; Calculate & interpret measures of spread; Select appropriate measures of center & spread; Use appropriate graphs & numerical summaries to compare distributions of quantitative variables Review Chapter 1 Activity Assessment Assignment Hiring Discrimination Act Student produced data; Simulation; Creating & analyzing a distribution; Making a decision using inferential reasoning Discussion Examples Teacher Ob Examples Discussion Examples Examples Read Overview and p. 1-11 and 1:1-1:2 Quiz 8/23 Do p.7 (1,3,5,7-8) Teacher Ob Do p. 22 (11,13,15,17) and 1:1-1:2 Quiz 8/23 Teacher Ob Read p.12-21 1:1-1:2 Quiz 8/23 And Read p. 27-34 Teacher Ob Do p.42 (37,39,41,43,45,47) 1:1-1:2 Quiz 8/23 Teacher Ob 1:1-1:2 Quiz 8/23 And Read p.35-42 Do p. 24 (19,21,23,25,27-32) Do p. 45 (53,55,57,60,69-74) Activity Assessment Assignment Q&A Teacher Ob 1:1-1:2 Quiz 8/26 Quiz 1:1-1:2 Discovery:Mean as a “balance point” Discussion Examples Examples Discussion Q&A Teacher Ob Ch 1 Test 8/29 Teacher Ob Ch 1 Test 8/29 Teacher Ob Test 8/29 1:1-1:2 review worksheets Read p. 50-58 Do Activity Mean as a “balance point” on p.52 Do p. 70 (79,81,83,87,89) and Read p.59-69 Do p.71 (91,93,95,97,103,105,107-110) Do p. 78 (1-15) &Practice Test & Free Response 8/29-9/2 Date Mon 8/29 Tues 8/30 Wed 8/31 Objective/Standard Activity Assessment Ch 1 Test Use percentiles to locate individual values within distributions of data; Interpret a cumulative relative frequency graph; Find the standardized value (z-score) of an observation. Interpret z-scores in context. Describe the effect of adding, subtracting, multiplying by, or dividing by a constant on the shape, center, and spread of a distribution of data. Approximately locate the median (equal-areas point) and the mean (balance point) on a density curve. Where do I stand? Activity p.84 Teacher Ob Quiz 2:1 9/2 Discussion Examples Teacher Ob Quiz 2:1 9/2 Thurs 9/1 Review 2:1 Mon 9/5 Tues 9/6 Wed 9/7 Early Release! Thurs 9/8 Fri 9/9 Objective/Standard HOLIDAY! Use the 68–95–99.7 rule to estimate the percent of observations from a Normal distribution that fall in an interval involving points one, two, or three standard deviations on either side of the mean; Use the standard Normal distribution to calculate the proportion of values in a specified interval; Use the standard Normal distribution to determine a z-score from a percentile. Use Table A to find the percentile of a value from any Normal distribution and the value that corresponds to a given percentile. Make an appropriate graph to determine if a distribution is bell-shaped; Use the 68-95-99.7 rule to assess Normality of a data set. Interpret a Normal probability plot Review 2:2 p. 105 1,5, 7, 9, 11, 13, 15 p. 107 19, 21, 23, 31, 3338 Q&A Teacher Ob Quiz 2:1 9/2 Quiz 2:1 Study for quiz Activity Assessment Assignment Examples Teacher Ob Ch 2 Test 9/13 Fri 9/2 9/5 – 9/9 Date Assignment Read 2:1 p. 131 41, 43, 45, 47, 49, 51 Examples Teacher Ob Test 9/13 p. 132 53, 55, 57, 59 Examples Teacher Ob Test 9/13 p. 133 63, 65, 66, 68, 6974 Q&A Teacher Ob Test 9/13 2:2 worksheets; Ch 2 Review Ex p.136 (1-12) Objective/Standard Review Chapter 2 Activity Q&A Assessment Teacher Ob Test 9/13 Assignment FRQ Ch 2 & p.138 (1-13) Practice Test Describe why it is important to investigate relationships between variables; Identify explanatory and response variables in situations where one variable helps to explain or influences the other; Make a scatterplot to display the relationship between two quantitative variables.; Describe the direction, form, and strength of the overall pattern of a scatterplot; Recognize outliers in a scatterplot. Know the basic properties of correlation; Calculate and interpret correlation; Explain how the correlation r is influenced by extreme observations. CSI Stats: The case of the missing cookies Activity p.142 9/12– 9/16 Date Mon 9/12 Tues 9/13 Wed 9/14 Thurs 9/15 Interims! Fri 9/16 Examples Ch 2 Test Teacher Ob 3:1 Quiz 9/16 Teacher Ob Quiz 9/16 Quiz 3:1 p.158 1, 5, 7, 11, 13 p. 160 14–18, 21, 26 and p.161 (27-32) 9/19 – 9/23 Date Mon 9/19 Tues 9/20 Wed 9/21 Thurs 9/22 Fri Activity Assessment Assignment Interpret the slope and y intercept of a least-squares regression line; Use the least-squares regression line to predict y for a given x; Explain the dangers of extrapolation. Calculate and interpret residuals. Explain the concept of least squares. Use technology to find a least-squares regression line. Find the slope and intercept of the least-squares regression line from the means and standard deviations of x and y and their correlation. Construct and interpret residual plots to assess if a linear model is appropriate. Use the standard deviation of the residuals to assess how well the line fits the data. Use r2 to assess how well the line fits the data. Identify the equation of a least-squares regression line from computer output. Explain why association doesn’t imply causation. Recognize how the slope, y intercept, standard deviation of the residuals, and r2 are influenced by extreme observations. Discussion Teacher Ob 3:2 Quiz 9/23 Teacher Ob 3:2 Quiz 9/23 p.191 35, 37, 39, 41 Tues 9/27 Wed 9/28 Thurs 9/29 9/30 Tues 10/4 Wed 10/5 Early Release Thurs 10/6 10/7 p.191 43, 45, 47, 53 Examples Teacher Ob 3:2 Quiz 9/23 p. 192 49, 54, 56, 58–61 Discussion Teacher Ob 3:2 Quiz 9/23 p.194 63, 65, 68, 69, 71– 78 Quiz 3:2 Chapter Review Ex p.198 (1-7) Objective/Standard Activity Assessment Assignment Review Chapter 3 Q&A Practice Test p.200 (1-13) & FRQ Identify the population and sample in a sample survey. Identify voluntary response samples and convenience samples. Explain how these bad sampling methods can lead to bias.Describe how to use Table D to select a simple random sample (SRS). Distinguish a simple random sample from a stratified random sample or cluster sample. Give advantages and disadvantages of each sampling method. Explain how undercoverage, nonresponse, and question wording can lead to bias in a sample survey. See no evil, hear no evil? Activity p.206 Discussion Teacher Ob Ch 3 Test 9/27 Ch 3 Test Teacher Ob 4:1-4:2 Quiz 10/7 Teacher Ob Quiz 10/7 p.227 17, 19, 21, 23, 25 Teacher Ob Quiz 10/7 p.229 27, 28, 29, 31, 33, 35 10/6 – 10/10 Date Objective/Standard Mon 10/3 Distinguish between an observational study and an Fri Examples 9/23 9/26 – 9/30 Date Mon 9/26 Fri Objective/Standard experiment. Explain how a lurking variable in an observational study can lead to confounding. Identify the experimental units or subjects, explanatory variables (factors), treatments, and response variables in an experiment Describe a completely randomized design for an experiment. Explain why random assignment is an important experimental design principle. Describe how to avoid the placebo effect in an experiment. Explain the meaning and the purpose of blinding in an experiment. Explain in context what “statistically significant” means. Distinguish between a completely randomized design and a randomized block design. Know when a matched pairs experimental design is appropriate and how to implement such a design. Discussion p.226 1, 3, 5, 7, 9, 11 Activity Assessment Assignment Examples Teacher Ob Quiz 10/7 p.230 (37-42), p.253 45, 47, 49, 51, 53 Discussion Examples Teacher Ob Quiz 10/7 p.254 57, 63, 65, 67 Discussion Teacher Ob Quiz 10/7 p.256 69, 71, 73, 75 Discussion Examples Teacher Ob Quiz 10/7 p. 257 77, 79, 81, 85, p.260 (91-98) 4:1-4:2 Quiz 10/10 – 10/14 Date Objective/Standard Mon 10/10 Determine the scope of inference for a Tues 10/11 Activity Assessment Assignment Discussion Q&A “1 in 6 wins” Act p.282 Teacher Ob Test 10/12 Teacher Ob Test 10/12 Ch 4 Test Teacher Ob Teacher Ob 5:1-5:2 Quiz 10/21 p.269 102-108 FRQ & p.271 (1-12) & p.274 (1-14) p.276 (1-14) p.278 (15-17) p. 293 1, 3, 7, 9, 11 Objective/Standard Parent/Teacher Conference Activity Assessment Assignment Use simulation to model chance behavior. Examples Describe a probability model for a chance process. Use basic probability rules, including the complement rule and the addition rule for mutually exclusive events. Use a Venn diagram to model a chance process involving two events. Use the general addition rule to calculate P(A B) Discussion Examples Teacher Ob Quiz 10/21 Teacher Ob Quiz 10/21 p.295 15, 17, 19, 23, 25 p.297 (27, 31, 32), p.309 (43, 45, 47) Examples Q&A Teacher Ob Quiz 10/21 p.297 (29, 33-36), p.310 (49, 51, 53, 55, 57-60) statistical study. Review Ch 4 Test Wed 10/12 Thurs 10/13 Review Chapters 1-4 Fri 10/14 Interpret probability as a long-run relative frequency. 10/17 – 10/21 Date Mon 10/17 Tues 10/18 Wed 10/19 Thurs 10/20 Fri 10/21 10/24 – 10/28 Date Mon 10/24 Tues 10/25 Wed 10/26 Thurs 10/27 Fri 10/28 10/31 – 11/4 Date Mon 10/31 Tues 11/1 Wed 11/2 Thurs 11/3 Fri 11/4 Q&A Quiz 5:1-5:2 Objective/Standard Activity Assessment Assignment When appropriate, use a tree diagram to describe chance behavior. Use the general multiplication rule to solve probability questions. Determine whether two events are independent. Find the probability that an event occurs using a two-way table. When appropriate, use the multiplication rule for independent events to compute probabilities. Compute conditional probabilities Review Chapter 5 Examples Teacher Ob Ch 5 Test 10/27 p. 329 63, 65, 67, 69, 73, 77, 79 Examples Teacher Ob Ch 5 Test 10/27 Teacher Ob Ch 5 Test 10/27 p.330 83, 85, 87, 91, 93, 95, 97, 99 FRQ & p.334 (1-11) & p.336 (1-14) Use a probability distribution to answer questions about possible values of a random variable. Calculate the mean of a discrete random variable. Interpret the mean of a random variable. Bottle Water versus Tap Water Act p.340 Ch 5 Test Teacher Ob 6:1-6:2 Quiz 11/10 p.353 1, 5, 7, 9, 13,14, 18, 19 Objective/Standard Activity Assessment Assignment Calculate the standard deviation of a discrete random variable. Interpret the standard deviation of a random variable. Describe the effects of transforming a random variable by adding or subtracting a constant and multiplying or dividing by a constant. Find the mean and standard deviation of the sum or difference of independent random variables. Determine whether two random variables are independent. Find probabilities involving the sum or difference of independent Normal random variables. Examples Teacher Ob 6:1-6:2 Quiz 11/3 Teacher Ob 6:1-6:2 Quiz 11/3 Teacher Ob 6:1-6:2 Quiz 11/3 p.354 23, 25, 27-30 Determine whether the conditions for a binomial random variable are met. Compute and interpret probabilities involving binomial distributions Q&A Discussion Examples Examples Discussion Quiz 6:1-6:2 Teacher Ob Ch 6 Test 11/11 p.378 37, 39-41, 43, 45 p.379 49, 51, 57-59, 61, 63, 65, 66 p.403 69, 71, 73, 75, 77, 79 11/7 – 11/11 Date Mon 11/7 Tues 11/8 Wed 11/9 Thurs 11/10 Fri Objective/Standard Activity Assessment Assignment Calculate the mean and standard deviation of a binomial random variable. Interpret these values in context. Examples Teacher Ob Ch 6 Test 11/11 p.404 81, 83, 85, 87, 89 Examples Teacher Ob Test 11/11 Teacher Ob Test 11/11 p.405 93, 95, 97, 99, 101-103 FRQ & p.408 (1-8) and p.409 (1-14) Holiday! Election Day! Find probabilities involving geometric random variables. Review Chapter 6 Q&A 11/11 11/14 – 11/18 Date Mon 11/14 Tues 11/15 Wed 11/16 Thurs 11/17 Fri 11/18 11/21 – 11/25 Date Mon 11/21 Interims! Tues 11/22 Wed 11/23 Thurs 11/24 Fri 11/25 Ch 6 Test Objective/Standard Activity Assessment Assignment Distinguish between a parameter and a statistic. German Tank Problem Act p.414 Discussion Teacher Ob 7:1-7:2 Quiz 11/18 p.428 1, 3, 5, 7 Teacher Ob 7:1-7:2 Quiz 11/18 p.429 9, 11, 13, 17-20, 21-24 Examples Discussion Teacher Ob 7:1-7:2 Quiz 11/18 p.439 27, 29, 33, 35, 37, 41, 43-46 distribution of p̂ to evaluate a claim about a population proportion. Review 7:1-7:2 Q&A Teacher Ob Quiz 7:1-7:2 Study for quiz Objective/Standard Activity Assessment Assignment Find the mean and standard deviation of the sampling distribution of a sample mean x from an SRS of size n. Calculate probabilities involving a sample mean x when the population distribution is Normal. Explain how the shape of the sampling distribution of x is related to the shape of the population distribution. Use the central limit theorem to help find probabilities involving a sample mean x Examples Teacher Ob Ch 7 Test 12/2 p.454 49, 51, 53, 55 Discussion Teacher Ob Ch 7 Test 11/29 p.455 57, 59, 61, 63, 65-68 Understand the definition of a sampling distribution. Distinguish between population distribution, sampling distribution, and the distribution of sample data. Determine whether a statistic is an unbiased estimator of a population parameter. Understand the relationship between sample size and the variability of an estimator. Find the mean and standard deviation of the sampling distribution of a sample proportion p̂ for an SRS of size n from a population having proportion p of successes. Check whether the 10% and Normal conditions are met in a given setting. Use Normal approximation to calculate probabilities involving p̂ . Use the sampling HOLIDAY! HOLIDAY! HOLIDAY! Happy Thanksgiving!!!! 11/28 – 12/2 Date Objective/Standard Activity Assessment Assignment Mon 11/28 Chapter 7 Review Q&A FRQ & p.458 (1-7) and p.459 (1-13) Tues 11/29 Wed 11/30 Review Chapters 1-7 Q&A Teacher Ob Test 11/29 Ch 7 Test Teacher Ob Thurs 12/1 Review Chapters 1-7 Q&A Teacher Ob Fri Review Chapters 1-7 Q&A Teacher Ob 12/2 12/5 – 12/9 Date Objective/Standard Mon 12/5 Interpret a confidence level. Interpret a confidence interval in Tues 12/6 Wed 12/7 context. Understand that a confidence interval gives a range of plausible values for the parameter. Understand why each of the three inference conditions—Random, Normal, and Independent—is important. Explain how practical issues like nonresponse, undercoverage, and response bias can affect the interpretation of a confidence interval. Construct and interpret a confidence interval for a population proportion. Determine critical values for calculating a confidence interval using a table or your calculator. Carry out the steps in constructing a confidence interval for a population proportion: define the parameter; check conditions; perform calculations; interpret results in context. Determine the sample size required to obtain a level C confidence interval for a population proportion with a specified margin of error. Understand how the margin of error of a confidence interval changes with the sample size and the level of confidence C. Understand why each of the three inference conditions—Random, Normal, and Independent—is important. Thurs12/8 Fri 12/9 Review for Exam Ch 1-8 12/12 – 12/16 Date Objective/Standard Mon 12/12 Tues 12/13 Wed 12/14 Thurs 12/15 Fri 12/16 Construct and interpret a confidence interval for a population mean. Determine the sample size required to obtain a level C confidence interval for a population mean with a specified margin of error. Carry out the steps in constructing a confidence interval for a population mean: define the parameter; check conditions; perform calculations; interpret results in context. Construct and interpret a confidence interval for a population mean. Determine the sample size required to obtain a level C confidence interval for a population mean with a specified margin of error. Carry out the steps in constructing a confidence interval for a population mean: define the parameter; check conditions; perform calculations; interpret results in context. Cumulative AP Practice Test 2 p.461 (1-21) MC Cumulative AP Practice Test 2 p.464 (22-25) FR Review for Exam Activity Assessment The Mystery Mean Act p.468 Discussion Teacher Ob 8:1-8:2 Quiz 12/8 Teacher Ob Quiz 12/8 5, 7, 9, 11, 13 p.483 (17, 19–24) Teacher Ob Quiz 12/8 p.496 35, 37, 41, 43, 47, 49-52 Quiz 8:1-8:2 Teacher Ob Study for Exam Study for exam Ch 1-8:2 Activity Assessment Assignment Examples Teacher Ob p.518 55, 57, 59, 63 Examples Teacher Ob p.518 55, 57, 59, 63 Discussion Examples Q&A Assignment p.481 p. 496 (27, 31, 33) 1st Sem EXAM Understand why each of the three inference conditions— Random, Normal, and Independent—is important. Determine sample statistics from a confidence interval. Understand why each of the three inference conditions— Random, Normal, and Independent—is important. Determine sample statistics from a confidence interval. CHRISTMAS BREAK!!!!!!! Discussion Teacher Ob Discussion Teacher Ob p.519 65, 67, 71, 73, 75–78 p.519 65, 67, 71, 73, 75–78 1/2 – 1/6 Date Mon 1/2 Tues 1/3 Wed 1/4 Thurs 1/5 Fri 1/6 1/9 – 1/13 Date Mon 1/9 Tues 1/10 Wed 1/11 Thurs 1/12 Fri 1/13 Objective/Standard HOLIDAY! TEACHER WORKDAY! Chapter 8 Review Activity Assessment Assignment Q&A p.522 (1-10) FRQ & p.524 (1-13) State correct hypotheses for significance test about a population proportion or mean. Interpret Pvalues in context. I’m a Great Freethrow Shooter Act p.528 Teacher Ob Test 1/5 Ch 8 Test Teacher Ob 9:1-9:2 Quiz 1/12 p. 546 1, 3, 5, 7, 9, 11, 13 Objective/Standard Activity Assessment Assignment Interpret a Type I error and a Type II error in context, and give the consequences of each. Understand the relationship between the significance level of a test, P(Type II error), and power. Check conditions for carrying out a test about a population proportion. If conditions are met, conduct a significance test about a population proportion. Use a confidence interval to draw a conclusion for a twosided test about a population proportion. Discussion Teacher Ob 9:1-9:2 Quiz 1/12 p.547 15, 19, 21, 23, 25 Discussion Examples Teacher Ob 9:1-9:2 Quiz 1/12 Examples Q&A Teacher Ob 9:1-9:2 Quiz 1/12 Quiz 9:1-9:2 p.548 (27–30), p.562 (41,43, 45 p.563 47, 49, 51, 53, 55, 5760 Teacher In-Service! 1/16 – 1/20 Date Mon 1/16 Tues 1/17 Wed 1/18 Thurs 1/19 Fri Objective/Standard HOLIDAY! Check conditions for carrying out a test about a population mean. If conditions are met, conduct a one-sample t test about a population mean . Use a confidence interval to draw a conclusion for a two-sided test about a population mean. Recognize paired data and use one-sample t procedures to perform significance tests for such data. Chapter 9 Review Activity Assessment Assignment Examples Discussion Teacher Ob Ch 9 Test 1/20 p.588 71, 73, 75, 77 Examples Q&A Teacher Ob Test 1/20 Teacher Ob Test 1/20 Ch 9 Test p.590 89, 94–97, 99–104 FRQ & p.594 (1-9) and p.597 (1-13) 1/20 1/23 – 1/27 Date Objective/Standard Activity Assessment Assignment Mon 1/23 Describe the characteristics of the sampling distribution ˆ1 pˆ 2 . Calculate probabilities using the sampling of p Is Yawning Contagious? Act p.602 Teacher Ob 10:1 Quiz 1/26 1, 3, 5 Determine whether the conditions for performing inference are met. Construct and interpret a confidence interval to compare two proportions. Perform a significance test to compare two proportions. Interpret the results of inference procedures in a randomized experiment. Examples Teacher Ob 10:1 Quiz 1/26 Teacher Ob 10:1 Quiz 1/26 Quiz 10:1 p.622 7, 9, 11, 13 Describe the characteristics of the sampling distribution of x1 x2 .Calculate probabilities using the sampling Discussion Examples Teacher Ob Ch 10 Test 2/6 p.652 (35, 37), p.657 (57) distribution of Tues 1/24 Wed 1/25 pˆ1 pˆ 2 Examples Discussion Thurs 1/26 Fri 1/27 distribution of x1 x2 p.621 p.623 5, 17, 21, 23, 29-32 1/30 – 2/3 Date Mon 1/30 Tues 1/31 Wed 2/1 Thurs 2/2 Fri Objective/Standard Activity Assessment Assignment Determine whether the conditions for performing inference are met. Use two-sample t procedures to compare two means based on summary statistics. Use two-sample t procedures to compare two means from raw data. Interpret standard computer output for two-sample t procedures. Perform a significance test to compare two means. Check conditions for using two-sample t procedures in a randomized experiment. Interpret the results of inference procedures in a randomized experiment. Determine the proper inference procedure to use in a given setting. Early Release! Review Chapter 10 Review Chapter 10 Examples Teacher Ob Ch 10 Test 2/3 p.652 39, 41, 43, 45 Examples Discussion Teacher Ob Ch 10 Test 2/3 p.655 51, 53, 59, 65, 67-70 Q&A Teacher Ob Test 2/3 Teacher Ob Test 2/3 Ch 10 Test p.661 (1-10) Q&A 2/3 2/6 – 2/10 Date FRQ & p.664 (1-13) Objective/Standard Activity Assessment Assignment Mon 2/6 Review Chapters 1-10 Q&A Teacher Ob Tues 2/7 Wed 2/8 Thurs 2/9 Review Chapters 1-10 Review Chapters 1-10 Know how to compute expected counts, conditional distributions, and contributions to the chi-square statistic. Check the Random, Large sample size, and Independent conditions before performing a chisquare test. Use a chi-square goodness-of-fit test to determine whether sample data are consistent with a specified distribution of a categorical variable. Examine individual components of the chi-square statistic as part of a follow-up analysis. Q&A Q&A Candy Man Can Act p.676 Examples Teacher Ob Teacher Ob Teacher Ob 11:1 Quiz 2/13 Teacher Ob 11:1 Quiz 2/13 AP Practice Test 3 p.667 (1-16) MC p.669 (17-30) MC p.671 (31-35) FR p.692 1, 3, 5 Fri 2/10 p.692 7, 9, 11, 17, 19-22 2/13 – 2/17 Date Mon 2/13 Tues 2/14 Wed 2/15 Thurs 2/16 Interims! Fri 2/17 Objective/Standard Check the Random, Large sample size, and Independent conditions before performing a chi-square test. Use a chi-square test for homogeneity to determine whether the distribution of a categorical variable differs for several populations or treatments. Interpret computer output for a chi-square test based on a two-way table. Examine individual components of the chi-square statistic as part of a follow-up analysis. Show that the two-sample z test for comparing two proportions and the chi-square test for a 2-by-2 two-way table give equivalent results. Check the Random, Large sample size, and Independent conditions before performing a chi-square test. Use a chi-square test of association/independence to determine whether there is convincing evidence of an association between two categorical variables. Interpret computer output for a chi-square test based on a two-way table. Examine individual components of the chi-square statistic as part of a follow-up analysis. Distinguish between the three types of chi-square tests. Review Chapter 11 Activity Examples Examples Q&A Assessment Assignment Quiz 11:1 Teacher Ob Ch 11 Test 2/17 p.724 27, 29, 31, 33, 35, 43 Teacher Ob Ch 11 Test 2/17 45, 49, 51, 53-58 Teacher Ob Test 2/17 FRQ and p.732 (1-6) & p.733 (1-13) Ch 11 Test p.727 2/20 – 2/24 Date Mon 2/20 Tues 2/21 Wed 2/22 Thurs 2/23 Fri 2/24 2/27 – 3/3 Date Mon 2/27 Tues 2/28 Wed 3/1 Early Release! Thurs 3/2 Fri Objective/Standard Holiday! Check conditions for performing inference about the slope of the population regression line. Interpret computer output from a least-squares regression analysis. Construct and interpret a confidence interval for the slope of the population regression line. Perform a significance test about the slope of a population regression line. Review 12:1 Activity Assessment Assignment Helicopter Experiment Act p.738 Examples Teacher Ob 12:1 Quiz 2/27 p.759 1, 3 Teacher Ob 12:1 Quiz 2/27 p.760 5, 7, 9, 11 Examples Teacher Ob 12:1 Quiz 2/27 Teacher Ob Quiz 2/27 p. 761 13, 15, 17, 19, 21-26 Review worksheets Q&A Objective/Standard Activity Assessment Assignment Use transformations involving powers and roots to achieve linearity for a relationship between two variables. Make predictions from a least-squares regression line involving transformed data. Use transformations involving logarithms to achieve linearity for a relationship between two variables. Make predictions from a least-squares regression line involving transformed data. Determine which of several transformations does a better job of producing a linear relationship. Review 12:2 Examples Discussion Quiz 12:1 Teacher Ob 12:2 Quiz 3/3 p.786 33, 35 Examples Discussion Teacher Ob 12:2 Quiz 3/3 p.788 37, 39, 41, 45-48 Q&A Teacher Ob 12:2 Quiz 3/3 Quiz 12:2 Review worksheets Assignment FRQ & p.796 (1-12) 3/3 p.793 (1-6) 3/6 – 3/10 Date Mon 3/6 Objective/Standard Review Chapter 12 Activity Q&A Tues 3/7 Wed 3/8 Review Chapters 1-12 Q&A Assessment Teacher Ob Test 3/7 Ch 12 Test Teacher Ob Thurs 3/9 Fri 3/10 Review Chapters 1-12 Review Chapters 1-12 Q&A Q&A Teacher Ob Teacher Ob AP Practice Test 4 p.799 (1-11) MC p.800 (12-20) MC p.802 (21-32) MC Activity Q&A Q&A Q&A Q&A Assessment Teacher Ob Teacher Ob Teacher Ob Teacher Ob Assignment p.804 (32-40) MC p.807 (41-43) FR p.807 (44-46) FR Go over FR p.807 3/13 – 3/17 Date Mon 3/13 Tues 3/14 Wed 3/15 Thurs 3/16 Fri 3/17 Objective/Standard Review Chapters 1-12 Review Chapters 1-12 Review Chapters 1-12 Review Chapters 1-12 Teacher Workday! 3/20 – 3/24 Date Mon 3/20 Tues 3/21 Wed 3/22 Thurs 3/23 Fri 3/24 Objective/Standard Review Chapters 1-12 Review for AP Test Review for AP Test Review for AP Test Review for AP Test Activity Q&A Q&A Q&A Q&A Q&A Assessment Teacher Ob Teacher Ob Teacher Ob Teacher Ob Teacher Ob Assignment Go over FR p.807 Take AP Exam 1 p.168 (1-40) MC Take AP Exam 1 p.168 (1-40) MC Take AP Exam 1 p.189 (1-6) FR Take AP Exam 1 p.189 (1-6) FR We have finished the textbook and will be reviewing for the AP exam for the rest of the school year using other supplementary materials. Using AP* Test Prep Series AP Statistics for Stats: Modeling the World booklet. 3/27 – 3/31 Date Mon 3/27 Tues 3/28 Wed 3/29 Thurs 3/30 Fri 3/31 Objective/Standard Activity Assessment Assignment Review for AP Test Review for AP Test Review for AP Test Review Topic 1: Exploring and Understanding Data: Using graphical displays; describing distributions numerically; Finding normal percentiles Review Topic 2: Exploring Relationships between Variables Analyzing Scatterplots, correlation, LSRL, Regression wisdom, and re-expressing data Q&A Q&A Q&A Q&A Teacher Ob Teacher Ob Teacher Ob Teacher Ob Go over AP Exam 1 Go over AP Exam 1 Go over AP Exam 1 Review for AP Test p.31 (1-10) MC & FR Q&A Teacher Ob Review for AP Test Objective/Standard Activity Assessment Assignment Review Topic 2: Exploring Relationships between Variables Topic 3: Gathering Data Understanding Randomness, perform a simulation; sampling surveys; design experiments Topic 4: Randomness and Probability; Applying probability rules Topic 4: Types of random variables and probability models using geometric and binomial distributions HOLIDAY! Q&A Teacher Ob p.50 (1-10) MC & FR Q&A Teacher Ob Review for AP Test Q&A Teacher Ob Review for AP Test Q&A Teacher Ob Review for AP Test SPRING BREAK! 4/10 – 4/14 Date Mon 4/10 Tues 4/11 Wed 4/12 Thurs 4/13 Fri 4/14 4/17– 4/21 Date Mon 4/17 Tues 4/18 Wed 4/19 Thurs 4/20 Fri 4/21 4/24 – 4/28 Date Mon 4/24 Tues 4/25 Wed 4/26 Thurs 4/27 Fri 4/28 Objective/Standard Activity Assessment Assignment Topic 4: Randomness and Probability Topic 5: From the data at hand to the world at large: Using sampling distributions to draw conclusions about the population using proportions and sample means; Create and interpreting a confidence interval Topic 5: From the data at hand to the world at large: Using sampling distributions to draw conclusions about the population using proportions and sample means; Create and interpreting a confidence interval Testing hypotheses about proportions Review Topic 5 Q&A Q&A Teacher Ob Teacher Ob p.89 (1-10) MC & FR Review for AP Test Q&A Teacher Ob Review for AP Test Q&A Q&A Teacher Ob Teacher Ob p.118 (1-10) MC & FR Review for AP Test Objective/Standard Activity Assessment Assignment Topic 6: Learning about the world using inference about means Topic 7: Inference when variables are related: Comparing counts using chi-square and inference for regression Take Practice AP Exam Take Practice AP Exam Take Practice AP Exam Q&A Teacher Ob p.139 (1-10) MC & FR Q&A Teacher Ob Review for AP Test AP Test AP Test AP Test MC (1-40) MC (1-40) FR (1-6) 5/1 – 5/5 Date Mon 5/1 Tues 5/2 Wed 5/3 Thurs 5/4 Fri 5/5 Objective/Standard Take Practice AP Exam Interims! Review AP Exam Review AP Exam Take Practice AP Exam Take Practice AP Exam Activity Assessment Assignment AP Test FR (1-6) Go over AP Exam Go over AP Exam AP Test MC (1-40) AP Test MC (1-40) and FR 5/8 – 5/12 Date Mon 5/8 Tues 5/9 Wed 5/10 Objective/Standard Review AP Exam Review AP Exam Review AP Exam Activity Assessment Assignment Study for AP Exam Study for AP Exam Study for AP Exam Thurs 5/11 Fri NO CLASS!! AP EXAM!!!!!! GOOD LUCK!!! 5/12 The AP Statistics Exam is on Thursday, May 11th (Noon – 4pm).