* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Series and Parallel Circuit Problems
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Ground (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Electric battery wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Earthing system wikipedia , lookup
Two-port network wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
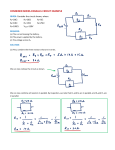
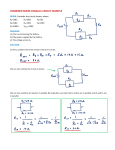
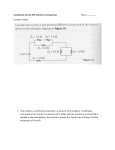
Physics 513 Series and Parallel Problems Name Date 1. Three resistors are connected in series to a 10 V battery. The first resistor is a 16 Ω resistor, the second is a 36 Ω resistor and the third is a 28 Ω resistor. a) Draw and label the circuit using the correct schematic symbols. b) Find the total (or equivalent) resistance of the circuit (RT). c) Find the current through the battery (IT). d) Find the potential drop across each of the resistors. e) Find the power dissipated at each resistor. If these resistors were light bulbs, which of them would be the brightest? f) Find the power supplied by the battery. 2. Two resistors are connected in parallel to a 30 V battery. The first resistor is 40 Ω and the second resistor is 40 Ω. a) Draw and label the circuit using the correct schematic symbols. b) Find the total (or equivalent) resistance of the circuit (RT). c) Find the current through the battery (IT). d) Find the current through each of the resistors. e) Find the power dissipated at each resistor. If these resistors were light bulbs, which of them would be the brightest? f) Find the power supplied by the battery. 3. The reading on the voltmeter in the circuit to the right is 4 V. a) What is the current through resistor 3? b) What is the total resistance of the circuit? c) What is the current through the battery? d) What is the potential drop across each of the other resistors? e) What is the voltage supplied by the battery? 4. Given the circuit to the right, the reading on the ammeter is 2 A. a) What is the potential drop across resistor 2? b) What is the total resistance of the circuit? c) What is the voltage supplied by the battery? d) What is the current through each of the resistors? e) What is the current through the battery? R1 R2 R3 V R4 R1 = 10 Ω, R2 = 15 Ω, R3 = 25 Ω, R4 = 5 Ω R1 = 10 Ω R2 = 15 Ω R2 R1 R3 R3 = 20 Ω A 5. Let’s say that I have a string of non-denominational holiday lights hooked up to a 100 V voltage source. They are all connected in series. Each bulb has a resistance of 10 Ω. a) If I have 4 bulbs in the series, what is the total resistance of the circuit, the current through the battery, and the voltage drop across each resistor? b) If I add a 5th bulb to the end of the string, recalculate the total resistance of the circuit, the current through the battery, and the voltage drop across each resistor. 6. Let’s say I take those same bulbs and the same 100 V source but, this time, connect the bulbs each in parallel to the source. a) If I have 4 bulbs in parallel, what is the total resistance of the circuit, the current through the battery, and the current through each resistor? b) If I add a 5th bulb to the end of the string, recalculate the total resistance of the circuit, the current through the battery, and the current through each resistor. 7. Three resistors are placed in series to a 120 V source. The first resistor dissipates power at a rate of 20 W, the second at 10 W and the third at 50W. a) What is the rate at which the battery is supplying energy to the circuit? b) What is the current through the battery? c) What is the resistance of each of the resistors? d) What is the voltage drop across each of the resistors? 8. Three resistors are placed in parallel to a 120 V source. The first resistor dissipates power at a rate of 60 W, the second at 80 W and the third at 100W. a) What is the rate at which the battery is supplying energy to the circuit? b) What is the current through the battery? c) What is the resistance of each of the resistors? d) What is the current through each of the resistors? 9. When two specific resistors are placed in series, they have an equivalent resistance of 50 Ω. When these same two resistors are placed in parallel, they have an equivalent resistance of 8 Ω. What are the two resistances? 10. For a certain series circuit, we are given the following information. Complete the table R I ΔV P T 100 Ω 1 25 Ω 2 0.4 A 3 10 V 4 6W 11. For a certain parallel circuit, we are given the following information. Complete the table. R I ΔV P T 4Ω 1 40 Ω 2 3 4 1.2 A 24 V 12 W