* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Rise of the Roman Republic
Education in ancient Rome wikipedia , lookup
Berber kings of Roman-era Tunisia wikipedia , lookup
Roman army of the late Republic wikipedia , lookup
Roman historiography wikipedia , lookup
Cursus honorum wikipedia , lookup
Factorum ac dictorum memorabilium libri IX wikipedia , lookup
Culture of ancient Rome wikipedia , lookup
Roman Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Roman agriculture wikipedia , lookup
History of the Roman Constitution wikipedia , lookup
Demography of the Roman Empire wikipedia , lookup
Elections in the Roman Republic wikipedia , lookup
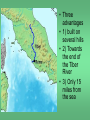
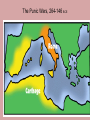
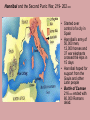
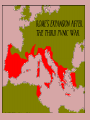
The Rise of the Roman Republic 509 BC – 27 BC Rome’s greatest achievements: • Established the first Republic and the principle of separation of powers; • Used law and government to unite many different regions, cultures and people. [a trend of cosmopolitanism started during the Hellenistic Age] • Practical engineering projects to promote civilization: roads, bridges, aqueducts, sewers, bath houses and amphitheatres. Caesar Augustus asked Rome’s greatest poet, Virgil to write a poem to glorify the creation of Rome [30-19 BCE] 12 books 1-6: Odyssey & 7-12: The Iliad Aeneas reaches Latium, Italy Romulus and Remustwin sons of the god Mars, and Princess Rhea who feared for their lives Romulus and Remus: nurtured by a she-wolf The Archaeological Record • 2500 BC- Paleolithic settlements • 1500 BC The Bronze Age • 1000 BC tombs of cremated dead with bronze tools and weapons • 800 BC Distinct groups occupied the Italian peninsula- Umbrians, the Sabines, the Samnites, the Etruscans and the Latins • Three advantages • 1) built on several hills • 2) Towards the end of the Tiber River • 3) Only 15 miles from the sea The Republic is established, 509 BC • The last Etruscan king, Tarquin the Proud, ignored the Senate and was overthrown, the Latin patricians (wealthy landowners) created a representative government. Two Consuls replaced the king The Roman Senate: • Senators came from the Patrician class • Acted as an advisory body to the king/consuls • Controlled the finances; money for public works • Served as a Jury for treason, conspiracy, murder, & foreign relations The Struggle of the Orders 494 – 287 BC • • • • • • 494 BC – Office of the Tribune created 460 BC – Voting: residence replaced wealth 450 BC – Twelve Tables 445 BC – Lex Canuleia-marriage 367 BC – Licinian-Sextian Rogation-consuls 287 BC – Lex Hortensia- Plebeian Council Roman Expansion • • • • 493 BCE – Battle of Lake Regillus/Latin League 396 BCE – Battle of Veii/Etruscans 390 BCE – first & only setback – Gauls seige on Rome 350 BCE - Romans bounced back- rebuilt the Servian Wall and remodeled the army • 340- 290 BCE The Latin Wars/Roman Federation • 282-270 BCE defeated Greeks/Tarentum & Epirus • 264-146 BCE The Punic Wars By 264 BC, 5 major world powers: Syria, Egypt, Macedonia, Carthage and Rome The Punic Wars • Three wars against Carthage started in 264 BCE and ended with Rome an international superpower in 146 BCE. The Punic Wars, 264-146 BCE Hannibal Barca 247–183 BCE Hannibal’s army of 50,000 men and 37 war elephants crossed the Alps Hannibal and the Second Punic War, 219- 202 BCE • Started over control of a city in Spain • Hannibal’s army of 50,000 men, 12,000 horses and 37 war elephants crossed the Alps in 15 days • Hannibal hoped for support from the Gauls and other Latin people • Battle of Cannae 216 BCE ended with 60,000 Romans dead. Publius Cornelius Scipio Rome sent an army under Scipio to Carthage, forcing Hannibal to return to Carthage to protect his homeland Scipio Africanus The 3rd Punic War, 149-146 BCE • A one-sided affair! Effects of expansion… • • • • The Hellenization of Rome Rise of a business/merchant class Immense wealth –a taste of luxury for the few Most benefits of expansion went to the wealthy, patrician class • Serious economic dislocations for the common people was under way The legacy of wars… • Farms had been ravaged and remained unproductive • Citizen-soldiers returned after prolonged absence to find their families on the brink of bankruptcy • Growth of Patrician latifundia (slave plantations) • Growing slave population drove down wages Problems for the small, independent, selfsufficient farmer… • The increase in the slave population displaced the common farmers… • In debt, without prospects for work, ruined farmers joined the ranks of unemployed in Rome… • By 150BCE -a revolution was brewing! Any Questions?