* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Resistors
Wireless power transfer wikipedia , lookup
Skin effect wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Electrification wikipedia , lookup
Ground (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Electric power system wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Thermal runaway wikipedia , lookup
Earthing system wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Two-port network wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Lumped element model wikipedia , lookup
Power engineering wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Surface-mount technology wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Network analysis (electrical circuits) wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
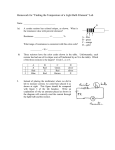
Resistors Electronics 1 CVHS Review • Resistance is the opposition to current flow provided by a material • The symbol for resistance is Ω • The schematic symbol for a resistor is • When measuring resistance YOU MUST ALWAYS REMOVE POWER from the circuit Resistance • One ohm = 1 amp @ 1 volt • A larger resistance value will allow less current to flow • A smaller resistance value will allow more current to flow http://www.colorado.edu/physics/phet/simulations/veqir/VeqIRColored.swf Resistor Uses • Used to limit current flow in a circuit • Many circuits and components require different voltage and current levels • Resistors reduce these levels down to the required level for each component or area of a circuit Resistor Types • Fixed (resistance is preset and cannot be changed) • Variable (The internal resistance of the device can be adjusted) Fixed Resistor Composition Fixed resistors • Carbon Film • Metal film • Wire wound • Wire wound ceramic coated • Symbol: High Voltage Resistors Tapped Resistors • These are wire wound fixed resistors • One or more “taps” are located between the ends of the resistor to provide different resistances • Symbol: Variable Resistors • Used as circuit controls • Most use a wire wound resistor and a pole • Carbon coatings, and specialty materials may also be used for certain applications Potentiometers • Has three terminals • Shaft rotation changes the resistance between the center terminal and two end terminals • Most “Pots” are linear • One degree rotation of the shaft = the same change in resistance regardless of the shaft location Potentiometers • Non-linear Pots (audio taper) • One degree of shaft rotation does not = the same change in resistance at different shaft rotations. • Used in volume and tone controls • Symbol: Rheostats • Like Pots but only have 2 terminals • Used to adjust current in high power circuits • In low current situations, a pot may be used as a rheostat • Symbol: Adjustable • Used in high power applications • Used when frequent changes are not necessary • Power is usually removed from the circuit for adjustment • Symbol: Thermistor • Changes internal resistance with temperature • Used as temperature control and safety device. • Symbol: Photocell • Changes internal resistance with amount of light • Used in “electronic eye” • Symbol: Resistor Power Ratings • Resistors convert electrical energy into thermal energy (heat) • As current is passed through a resistor it gets hot • The power rating of a resistor indicates how much power the resistor can dissipate without being destroyed • There is no relationship between the resistance value and the power rating of a resistor • The proper power rating for a resistor is determined by the circuit designer • Power rating is displayed by a resistor’s physical size (printed on ceramic wire resistors) Review • What are the two major classifications of resistors? • What does one ohm equal? • As resistance increases, current… • What is the relationship between r-value and power rating? … between power rating and size? … between r-value and size? • What is the difference between a rheostat and a pot?