* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download electronic devices ii
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Pulse-width modulation wikipedia , lookup
Ground loop (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Thermal runaway wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Negative feedback wikipedia , lookup
Dynamic range compression wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Flip-flop (electronics) wikipedia , lookup
Signal-flow graph wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative circuit wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Wien bridge oscillator wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Two-port network wikipedia , lookup
Semiconductor device wikipedia , lookup
History of the transistor wikipedia , lookup
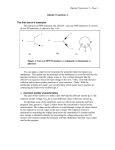
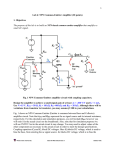
physicsbeckons.wordpress.com ELECTRONIC DEVICES- II In continuation to ED I, Part II of the Unit is being posted here. It is an easy unit in class XII CBSE Physics syllabus. You may complete this unit and follow up with problems from CBSE papers. Some sample problems have been included here. GET STARTED: HAPPY LEARNING! TRANSISTOR: physicswithikgogia Page 1 physicsbeckons.wordpress.com Consider the circuit diagram below with common emitter p-n-p transistor having emitter-base junction forward (Veb) biased and the collector reverse biased due to Vce. Due to Veb; the negative potential of the base attract the holes from hole-rich p-type emitter if the applied Veb is large enough to overcome the barrier potential. The base region being thin and low doped does not stop the holes. Only a small fraction of the holes (< 5%) combine with electrons in the thin base region. Most of the holes(>90%) cross over to the collector region which sweeps them due to large reverse bias applied to the collector. physicswithikgogia Page 2 physicsbeckons.wordpress.com If the base potential is increased slightly, it attracts a larger no. of charge carriers from the emitter. Being low doped, the base cannot stop a large fraction of the carriers. Most of carriers cross over to the collector resulting in a large increase in Ic. This is principle of operation of transistor as an amplifier. The behavior of npn transistor can be explained in the same way with the battery bias reversed and the majority carriers ie electrons contributing to conduction. NOTE: The input resistance is low due to forward bias and output resistance is high due to reverse bias. TRANSISTOR CHARACTERISTICS: The circuit arrangement for studying the characteristics of a common emitter npn is as shown below: Input Characteristics: For Input characteristics; set Vce = 0 volts. Gradually increase the voltage Vb applied to the base (in small steps) and record the corresponding values of base current Ib till the value of the base current shows a sudden, sharp increase. Adjust Vce = 2 V; 6 V; 10 V and record Ib for different values of Vb in each case. Plot Vb v/s Ib graph for different fixed values of Vce to get a family of input characteristic curves. Output Characteristics: For output characteristics, take Vc = 0 volts. Adjust base voltage Vb so that Ib = 10 µA. Record the corresponding value of collector current. physicswithikgogia Page 3 physicsbeckons.wordpress.com Increase collector voltage in small steps (say 1V of 2V) each and record the corresponding values of collector current. Plot a graph between Vc and Ic. Record values of Ic for different values of Vc. Repeat the experiment taking base current Ib = 20 µA, 30 µA, 40 µA, 50 µA, 60 µA and 70 µA. Plot a graph between Vc and Ic for different fixed values of Ib to get a family of output characteristic curves. The typical shape of the two curves is as under. Note: The curves may be used to determine the following parameters typical of a transistor. TRANSISTOR PARAMETETRS: Input resistance, Current Amplification factor ( current gain) Input resistance ri of the transistor in CE configuration is defined as ratio of small change in base-emitter voltage to the corresponding small change in the base current, when the collector-emitter voltage is kept fixed 𝑟𝑖 = ∆𝑉𝑖 ∆𝐼𝑒𝑏 Current amplification factor (β) is the ratio of the change in collector current (output current) to the small change in base current when the transistor is in the active stage. D C Current gain physicswithikgogia 𝐼 (β𝑑𝑐 = 𝐼𝑐 )𝑉𝑐 = 𝑐𝑜𝑛𝑠𝑡𝑎𝑛𝑡 𝑏 Page 4 physicsbeckons.wordpress.com A C Current gain ∆𝐼 (β𝑑𝑐 = ∆𝐼𝑐 )𝑉𝑐 = 𝑐𝑜𝑛𝑠𝑡𝑎𝑛𝑡 Transconductance: 𝑏 ∆𝐼 gm = ∆𝑉𝑐 𝑖 It is a very important parameter in a transistor as measures the ability of base potential to control collector current, AMPLIFIER An amplifier is a device used to reinforce a weak electrical signal. Circuit diagram & Working The circuit diagram using an npn transistor in common emitter mode is as shown below. The negative sign in the expression indicates that the output is out of phase with the input as shown in the shapes of the output and input voltages. physicswithikgogia Page 5 physicsbeckons.wordpress.com Difference: The output signal is out of phase with the input.This is also called Phase reversal in amplifier. Why Phase Reversal? As the input signal rises to positive side, the forward potential of the EB increases resulting in a large increase in collector current. But in the output circuit, we have Vce = Ic. RL + Output signal (voltage) From above equation. An increase in collector current decreases Vout because Vce remains constant. Similarly decrease in nput voltage increases Vout . Application of Amplifier: (i) Public Address system (ii) Radio receiver Hi- Fi Amplifier : A hi-fi amplifier is the one in which the output signal is a faithful reproduction of the shape of the input signal. Characteristics of the base for hi fi amplication: (i) The base region should be thin. (ii) The base region should have a low doping level. If the base has a higher doping level, the output is distorted due to large base current. P.S. Please refer to book for definition of resistance gain and power gain. physicswithikgogia Page 6 physicsbeckons.wordpress.com Transistor as an oscillator: In electronics, LC circuit also called Tank Circuit is used as basic oscillatory circuit. The energy given to the circuit alternately changes from pure electric to pure magnetic resulting in oscillations. The total energy is subject to losses due to resistance in the circuit. If this loss is compensated, the oscillations will never die out. A transistor amplifier helps in sustaining the oscillations as explained below. The oscillating signal is amplified by the common emitter amplifier. The amplified signal appears in the collector circuit. This signal is out of phase with the input. So it cannot be used to compensate the energy loss in the tank cicuit. By means of inductive coupling between L and L’, a suitable part of the output energy is brought back in phase and given to the tank for sustain the oscillations. The frequency of oscillations is physicswithikgogia Page 7 physicsbeckons.wordpress.com Transistor as a switch: The circuit diagram is as shown below. The transistor as a switch operates either in cut-off region or in saturation region. P. S.: Draw transfer characteristics with this explanation from NCERT book. physicswithikgogia Page 8 physicsbeckons.wordpress.com SAMPLE PROBLEMS FROM CBSE PAPERS (with solution). *** *** physicswithikgogia Page 9 physicsbeckons.wordpress.com Solution: (i) Dynamic output resistance physicswithikgogia Page 10