* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Name: Ammie Hamilton S
Technical drawing wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Lie sphere geometry wikipedia , lookup
Apollonian network wikipedia , lookup
History of geometry wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
Euclidean geometry wikipedia , lookup
Integer triangle wikipedia , lookup
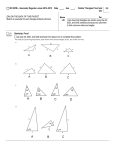
Name: Ammie Hamilton Date: Feb 1-‐12 Subject: Geometry Day 1 Tues Feb 2 Day 2 Thurs Feb 4 Day 3 Mon Feb 8 Day 4 Wed Feb 10 Day 5 Friday Feb 12 Learning Target Pythagorean Triples Level 1: I can identify, define, and perform dilations. G-‐SRT 1 Level 2: I can determine the similarity of two figures using similarity transformations. G-‐SRT 2, G-‐SRT 3 Level 3: I can prove theorems about triangles. G-‐SRT 4, G-‐C 1 Level 4: I can solve for and prove relationships in geometric figures using similarity criteria. G-‐SRT 5 Pythagorean Relationships and their 45-‐45-‐90 Triangles 45-‐45-‐90 Triangles Unit 7 – Right Triangles Unit 7 – Right Triangles Trigonometric Relationships Level 1: I can use the Pythagorean Level 1: I can use the Pythagorean Level 1: I can use the Theorem to solve right triangles in Theorem to solve right triangles in Pythagorean Theorem to solve applied problems. G-‐SRT 8 applied problems. G-‐SRT 8 right triangles in applied Level 2: I can solve special right Level 2: I can solve special right problems. G-‐SRT 8 triangles. G-‐SRT 6 triangles. G-‐SRT 6 Level 2: I can solve special right Level 3: I can use trigonometric Level 3: I can use trigonometric triangles. G-‐SRT 6 ratios to solve right triangles. G-‐ ratios to solve right triangles. G-‐SRT Level 3: I can use trigonometric SRT 6, G-‐SRT 7 6, G-‐SRT 7 ratios to solve right triangles. G-‐ Level 4: I can use trigonometric Level 4: I can use trigonometric SRT 6, G-‐SRT 7 ratios and special right triangle ratios and special right triangle Level 4: I can use trigonometric ratios to solve right triangles in ratios to solve right triangles in ratios and special right triangle applied problems. G-‐SRT 8 applied problems. G-‐SRT 8 ratios to solve right triangles in converse Level 1: I can identify, define, and perform dilations. G-‐SRT 1 Level 2: I can determine the similarity of two figures using similarity transformations. G-‐SRT 2, G-‐SRT 3 Level 3: I can prove theorems about triangles. G-‐SRT 4, G-‐C 1 Level 4: I can solve for and prove relationships in geometric figures using similarity criteria. G-‐SRT 5 applied problems. G-‐SRT 8 Common Core Standards Similarity: G-‐SRT Understand similarity in terms of similarity transformations G-‐SRT 1. Verify experimentally the properties of dilations given by a center and a scale factor: a. A dilation takes a line not passing through the center of the dilation to a parallel line, and leaves a line passing through the center unchanged. b. The dilation of a line segment is longer or shorter in the ratio given by the scale factor. G-‐SRT 2. Given two figures, use the definition of similarity in terms of similarity transformations to decide if they are similar; explain using similarity transformations the meaning of similarity for triangles as the equality of all corresponding pairs of angles and the proportionality of all corresponding pairs of sides. G-‐SRT 3. Use the properties of similarity transformations to establish the AA criterion for two triangles to be similar. Prove theorems involving similarity G-‐SRT 4. Prove theorems about triangles. Theorems include: a line parallel to one side of a triangle divides the other two Similarity: G-‐SRT Understand similarity in terms of similarity transformations G-‐SRT 1. Verify experimentally the properties of dilations given by a center and a scale factor: a. A dilation takes a line not passing through the center of the dilation to a parallel line, and leaves a line passing through the center unchanged. b. The dilation of a line segment is longer or shorter in the ratio given by the scale factor. G-‐SRT 2. Given two figures, use the definition of similarity in terms of similarity transformations to decide if they are similar; explain using similarity transformations the meaning of similarity for triangles as the equality of all corresponding pairs of angles and the proportionality of all corresponding pairs of sides. G-‐SRT 3. Use the properties of similarity transformations to establish the AA criterion for two triangles to be similar. Prove theorems involving similarity G-‐SRT 4. Prove theorems about triangles. Theorems include: a line parallel to one side of a triangle divides the other two proportionally, and conversely; the Pythagorean Theorem proved using triangle similarity. G-‐SRT 5. Use congruence and similarity Similarity: G-‐SRT Understand similarity in terms of similarity transformations G-‐SRT 1. Verify experimentally the properties of dilations given by a center and a scale factor: a. A dilation takes a line not passing through the center of the dilation to a parallel line, and leaves a line passing through the center unchanged. b. The dilation of a line segment is longer or shorter in the ratio given by the scale factor. G-‐SRT 2. Given two figures, use the definition of similarity in terms of similarity transformations to decide if they are similar; explain using similarity transformations the meaning of similarity for triangles as the equality of all corresponding pairs of angles and the proportionality of all corresponding pairs of sides. G-‐SRT 3. Use the properties of similarity transformations to establish the AA criterion for two triangles to be similar. Prove theorems involving similarity G-‐SRT 4. Prove theorems about triangles. Theorems include: a line parallel to one side of a triangle divides the other two Similarity: G-‐SRT Understand similarity in terms of similarity transformations G-‐SRT 1. Verify experimentally the properties of dilations given by a center and a scale factor: a. A dilation takes a line not passing through the center of the dilation to a parallel line, and leaves a line passing through the center unchanged. b. The dilation of a line segment is longer or shorter in the ratio given by the scale factor. G-‐SRT 2. Given two figures, use the definition of similarity in terms of similarity transformations to decide if they are similar; explain using similarity transformations the meaning of similarity for triangles as the equality of all corresponding pairs of angles and the proportionality of all corresponding pairs of sides. G-‐SRT 3. Use the properties of similarity transformations to establish the AA criterion for two triangles to be similar. Prove theorems involving similarity G-‐SRT 4. Prove theorems about triangles. Theorems include: a line parallel to one side of a triangle divides the other two proportionally, and conversely; the Pythagorean Similarity: G-‐SRT Define trigonometric ratios and solve problems involving right triangles G-‐SRT 6. Understand that by similarity, side ratios in right triangles are properties of the angles in the triangle, leading to definitions of trigonometric ratios for acute angles. G-‐SRT 7. Explain and use the relationship between the sine and cosine of complementary angles. G-‐SRT 8. Use trigonometric ratios and the Pythagorean Theorem to solve right triangles in applied problems Name: Ammie Hamilton Date: Feb 1-‐12 proportionally, and conversely; the Pythagorean Theorem proved using triangle similarity. G-‐SRT 5. Use congruence and similarity criteria for triangles to solve problems and to prove relationships in geometric figures. Circles: G-‐C Understand and apply theorems about circles G-‐C 1. Prove that all circles are similar. criteria for triangles to solve problems and to prove relationships in geometric figures. Circles: G-‐C Understand and apply theorems about circles G-‐C 1. Prove that all circles are similar. proportionally, and conversely; the Pythagorean Theorem proved using triangle similarity. G-‐SRT 5. Use congruence and similarity criteria for triangles to solve problems and to prove relationships in geometric figures. Circles: G-‐C Understand and apply theorems about circles G-‐C 1. Prove that all circles are similar. Bell Ringer ESTIMATAION 180: Building Number Sense Everyday of the ESTIMATAION 180: Building Number Sense Everyday of the Year! Year! Pythagorean Triples What are the triples? What relationship do they have to one another? ~Quiz: Pythagorean Triples ~ Determine if a triangle is acute, right, or obtuse ~Solve proportions within right triangles Exit Slip Have the four most common triples memorized for quiz next class meeting. Speed on ACT Assessment Formative during class Learning Plan ESTIMATAION 180: Building Number Sense Everyday of the Year! Subject: Geometry Theorem proved using triangle similarity. G-‐SRT 5. Use congruence and similarity criteria for triangles to solve problems and to prove relationships in geometric figures. Circles: G-‐C Understand and apply theorems about circles G-‐C 1. Prove that all circles are similar. ESTIMATAION 180: Building Number ESTIMATAION 180: Building Sense Everyday of the Year! Number Sense Everyday of the Year! ~Hypotenuse/Leg ~ 45/45/90 Triangles ISN page ~ACT practice problems Continue Right Triangle Solving. QR reader scavenger hunt What side ratios determine if a triangle is acute? How can you determine if a triangle is 45/45/90 or 30/60/90 When can the 45/45/90 rule be applied? ~QUIZ: Right Triangles ~ISN page Trig Relationships ~SOH CAH TOA ~ ACT practice Problems Why do you need to memorize SOH CAH TOA? Formative during class QUIZ Formative during class Formative during class Formative During Class QUIZ