* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download PSY2005 Week 8 - Complex Experimental Designs
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
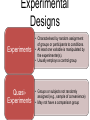
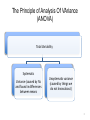
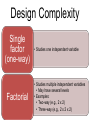
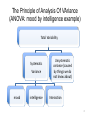
Lecture 8 Complex Experimental Designs PSY2004 Research Methods & Ethics in Psychology PSY2005 Applied Psychology Research Methods & Ethics Experimental Designs Experiments • Characterised by random assignment of groups or participants to conditions. • At least one variable is manipulated by the experimenter(s). • Usually employs a control group QuasiExperiments • Groups or subjects not randomly assigned (e.g., sample of convenience) • May not have a comparison group The Principle of Analysis Of VAriance (ANOVA) Total Variability Systematic Variance (caused by IVs and found in differences between means Unsystematic variance (caused by things we do not know about) 3 Types of Variable Independent Variables Dependent Variables • what is manipulated in the experiment • what is measured Control Variables • what is held constant Random Variables • what is allowed to vary randomly Confounding variable • correlated with an independent variable Design Terminology Between Groups Repeated Measures Mixed • An “independent groups” design • Different groups • Dependent measures taken one time • A “within groups” design • One group, different conditions • Dependent measures taken multiple times • Between and repeated Design Complexity Single factor (one-way) Factorial • Studies one independent variable • Studies multiple independent variables • May have several levels • Examples: • Two-way (e.g., 2 x 2) • Three-way (e.g., 2 x 2 x 2) Factorial Design The Principle of Analysis Of VAriance (ANOVA: mood by intelligence example) Total Variability Systematic Variance mood intelligence Unsystematic variance (caused by things we do not know about) Interaction 8 Main Effect Example Main Effect of Intelligence on Creativity Conclusion: people that are high in IQ score higher on creativity Tests regardless of mood. No effect for mood Interaction Effect Main Effects & Interactions High High High Low High Low Lightness Seasonal Affective Disorder No Seasonal Affective Disorder Lightness A Detailed Example Godden and Baddeley (1975) Memory Context Study • Participants (who were divers) learned lists of words either on the beach, or beneath 15 feet of water and then recall in the same or opposite environment. • 2 IVs: • Place of learning (2 levels: Beach or Underwater) • Place of recall (2 levels: Beach or Underwater) • DV: Number of words recalled A Detailed Example Four Conditions: Learn on Beach Recall on Beach Learn Underwater Recall Underwater Learn on Beach Recall Underwater Learn Underwater Recall on Beach A Detailed Example Advantages of Factorial Designs More than one hypothesis can be tested. Potentially confounding Enables variables can interaction be built into effects to be the design tested. as factors. Randomised Controlled Trials An experimental design used to evaluate the effectiveness of psychological interventions. Participants assigned randomly, to one of at least two conditions Pre & post tests Control group • Outcomes measured before & after intervention • Includes no treatment; treatment as usual; and ‘wait list’ sample. 17 Example Does Psychological Therapy improve outcomes for People with Mild/Moderate Depression? Psychological Therapy (CBT + TAU) Sample Ramdomise Treatment as Usual TAU 2 IVs: 1) Time of measurement (pre- or post) 2) Treatment Group (CBT or TAU) DV: Self-reported mood/symptoms Results of Study • • • Main effect of Time? Yes Main effect of type of treatment? Possibly but not important Interaction between time and type of treatment? Yes – Simple main effects? Conclusion: These results show a significant interaction between time and intervention. Whilst the participants reported lower depression following Treatment this effect was stronger in the CBT Treatment Complex Designs 1 • Complex designs represent research which has more than one independent variable. • Complex designs have more than one outcome: main effects and interaction effects • Example complex designs – Two independent groups IVs and one DV • • • • Place of learning (beach/underwater): Main effect 1 Place of recall (beach/underwater): Main effect 2 Learning by recall: interaction effect DV: memory recall Complex Designs 2: Independent Groups • A independent groups designs is one in which the participant is in a single level of one IV. • The role of attraction and type of crime in determining prison sentence – IV1: Attraction: Attractive/Ordinary – IV2: Type of Crime: Robbery/Swindle – DV: Time spent in jail The role of type of crime and attraction on determining prison sentence ME Attraction: NS ME Type of Crime: Swindle > Robbery A x TofC: Significant cross-over effect Conclusion: Although attractive people are likely to be given lenient sentences, when they use their attractiveness to commit a crime they are given longer sentences. Complex Designs 2: Repeated Measures Design • A repeated measures designs in which the participant takes part in all of the conditions in the experiment • Can mood effect performance on visual and verbal forms of creativity – Mood (positive/negative) – Type of creativity (visual/verbal) – DV: creativity task performance Results Type of Creative: main effect fully explained by interaction Mood: main effect fully explained by interation T x M: Significant effect that explains the systematic variance found Conclusion: that people perform better on visual creativity tasks When they are in a positive mood. Complex Designs: The mixed model • A mixed model is one in which there is at least one independent groups IV and at least one repeated measures IV. • Example: The effects of sex differences on types of intelligence – Sex (male/female): IG variable – Intelligence (spatial/verbal): RM variable – Sex by type of intelligence: Interaction effect – Intelligence score: DV Outcome for the mixed model ME Intelligence: No effect ME sex: No effect I x S: Significant crossover effect Conclusion: both within and between women are better at verbal tasks and men are better at Spatial tasks