* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Hearing, the Ear and Cochlear Implant
Telecommunications relay service wikipedia , lookup
Auditory processing disorder wikipedia , lookup
Sound from ultrasound wikipedia , lookup
Lip reading wikipedia , lookup
Olivocochlear system wikipedia , lookup
Hearing loss wikipedia , lookup
Sound localization wikipedia , lookup
Noise-induced hearing loss wikipedia , lookup
Audiology and hearing health professionals in developed and developing countries wikipedia , lookup
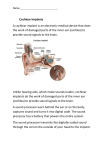
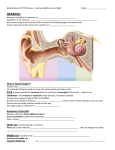
Hearing, the Ear and Cochlear Implant THE PATHWAY OF SOUND: 1. The _Pinna______ or _auricle_______ collects the sound. 2. Sound waves enter the outer ear through the auditory canal____ 3. These hit the __tympanic membrane or ear drum________ causing it to vibrate. 4. Then the 3 small bones of the __Ossicular____ Chain are put in motion. a. The _____Malleus________/__hammer______ b. Next the ____incus____/___anvil ________ c. Last, the _ stapes _______/_____stirup _____ 5. The ___stapes______ pushes on the fluid in the ____cochlea____. 6. _____Hair cells____ inside the Cochlea are stimulated by pressure changes of the __fluid___in the inner ear. 7. This begins an ____electrical current_____________ flowing to the _auditory ______ _____nerve______. 8. The auditory nerve transmits these __electrical_________ impulses to the ____brain_________ 9. Finally, the ____brain__________ interprets/decodes the message. TWO MAIN TYPES OF HEARING LOSS: conductive loss___ and ___ Sensory-Neural Loss _____ 1. Conductive Loss – hearing loss that occurs in the ____outer______ or _middle____ ear, ____prevents__________ sound transmission or conduction – to the inner ear: Can be caused by a. ____wax________ b. _perforated (hole) eardrum c. __infection in middle ear_ d. _problem with the bones of the middle ear__________________________________ Can be medically/surgically treated and often hearing can be ____restored____________. If normal can’t be restored ______Hearing aids_________maybe recommended. 2. Sensory-Neural Loss- hearing loss that occurs in the _____inner ____ear – ____damage___________ is permanent and irreversible. Sensory- neural loss can be caused by: a. ___damaged hair cells in cochlea__________________________ b. ___cochlea_________ c. _____auditory nerve________________________________________________________________ May be a candidate for ____cochlear implant_______________________. In __90%_ of the cases of those who are _profoundly (very)__ deaf, the problem is _NOT___ the auditory nerve, but rather the hair cells in the inner ear are destroyed by: a.____infection___________________ c.________trauma_______________ b. ____virus___________________ d.____environmental noise_________ e._____or the absence of hair cells at birth______________ CAUSES OF HEARING LOSS: 1. Hereditary (genetic) a. Passed by _one _______ or ___both_______ parents b. A _____recessive gene_______ carried by both parents can result in genetic trait being passed to the child. 2. Congenital – a. Present in the __womb__________ OR b. Occurs at ____time of birth______________________ . Can be due to a. ______premature__birth b. ___RH___ Blood Incompatibility between mother & baby c. Lack of ___oxygen_________ at birth d. Use of _____forceps_______ during birth process 3. Acquired – a. Occurs some time _____after birth________ for various reasons: 1.____disease_____________ 5. ________trauma_________________ 2.____illness_____ ________ 6. ________drugs__________________ 3._____accident________________ 7. _____environmental noise_________ 4. ____medication________ HEREDITARY SYNDROMES: a syndrome is a group of conditions rather than a single cause 1. Usher’s Syndrome a. Born ___deaf______ and later develop vision problems resulting in ____blindness__________ or near blindness. 2. Waardenburg’s Syndrome – Group of physical characteristics such as a. ______pigment disorder________ c. ___eyes of 2 different colors___ b. ______streak of white hair ______ d. ___may or may not be deaf__ AGE OF ONSET OF DEAFNESS: 1. Prelingual –Onset __prior to age 3_ – the child has not yet fully acquired its language 2. Postlingual – Onset occurs ___after age 3___ – child can talk and has learned language DEFINTIONS PERTAINING TO SOUND: 1. ____sound- begins with a vibrating source that causes __waves______ 2. Hertz or __frequency___ : a. The number of __waves___ that pass a given point in one __second____. 3. Pitch: are compared as "higher" and "lower" b. More waves = __higher __ pitch sound c. Fewer waves = ____lower______pitch sound 4. Decibel – abbreviated ____dB______________ : a. The ___loudness___ of sound b. dB scales begin at 0 dB, the _threshold (beginning)_ of hearing c. Each increase of 10 dB on the scale is actually a __ten_-fold increase in sound pressure. (Ex: 55 dB is Ten times as loud as 45 dB) HEARING TESTS: 1. Hearing test are measured on an ___audiogram_____, a chart showing the dB loss in both right & left ear. Cochlear Implants: 1. Cost is _$50,000-$100,000__(insurance my not pay or may only pay part) 2. Requires a commitment of ___speech therapy___________ for months/years 3. Do not replace ___normal__ hearing 4. Can be unsuccessful and result in surgical complications, infection, and even ___Death_________________ Deaf community has feared cochlear implant will cause the decline or disappearance of _____ASL language______ and ____Deaf Culture____ Hearing, the Ear and Cochlear Implant THE PATHWAY OF SOUND: 1. The _______________ or ______________ collects the sound. 2. Sound waves enter the outer ear through the _________________________ 3. These hit the _____________________________or ____________________________ causing it to vibrate. 4. Then the 3 small bones of the _____________________________ Chain are put in motion. a. The ____________________________________/_________________________ b. Next the ___________________/___________________________ c. Last, the ______________________/________________________ 5. The _____________ pushes on the fluid in the ____________________. 6. ______________________ inside the Cochlea are stimulated by pressure changes of the ________________in the inner ear. 7. This begins an _______________________________________ flowing to the __________________________ _______________________. 8. The auditory nerve transmits these _______________________ impulses to the ____________________ 9. Finally, the ______________ interprets/decodes the message. TWO MAIN TYPES OF HEARING LOSS:__________________________________ or______________________________ 1. Conductive Loss – hearing loss that occurs in the ______________ or _________________ear, __________________ sound transmission or conduction – to the inner ear: Can be caused by: a. _____________________________ b. __________________________________ c. _____________________________________________________________________ d. _____________________________________________________________________ Can be medically/surgically treated and often hearing can be _________________________. If normal can’t be restored ____________________________________maybe recommended. 2. Sensory-Neural Loss- hearing loss that occurs in the ________________ear – ________________ is permanent and irreversible. Sensory- neural loss can be caused by: a. _____________________________________________________________________ b. _____________________________________________________________________ c. _____________________________________________________________________ May be a candidate for _____________________________________________________. In _______ of the cases of those who are _______________ deaf, the problem is ________ the auditory nerve, but rather the hair cells in the inner ear are destroyed by: a._______________________ c._______________________ b. _______________________ d._______________________ e.___________________________________________________________ CAUSES OF HEARING LOSS: 1. Hereditary (genetic) a. Passed by ____________ or _____________ parents b. A ________________________________ carried by both parents can result in genetic trait being passed to the child. 2. Congenital – a. Present in the ____________ OR b. Occurs at _______________________________ . Can be due to 1. ____________________birth 2. ___________ Blood Incompatibility between mother & baby 3. Lack of _______________________ at birth 4. Use of _______________ during birth process 3. Acquired – a. Occurs some time _______________________________ for various reasons: 1._______________________________ 5. _______________________________ 2._______________________________ 6. _______________________________ 3._______________________________ 7. _______________________________ 4. _______________________________ HEREDITARY SYNDROMES: a syndrome is a group of conditions rather than a single cause 1. Usher’s Syndrome a. Born _______________ and later develop vision problems resulting in _______________________ or near blindness. 2. Waardenburg’s Syndrome – Group of physical characteristics such as a. _____________________________ c. _____________________________ b. _____________________________ d. _____________________________ AGE OF ONSET OF DEAFNESS: 1. Prelingual –Onset ________________________________ – the child has not yet fully acquired its language 2. Postlingual – Onset occurs __________________________ – child can talk and has learned language DEFINTIONS PERTAINING TO SOUND: 1. _________________begins with a vibrating source that causes __________________ 2. Hertz or _____________________ : a. The number of _______________ that pass a given point in one _______________. 3. Pitch: are compared as "higher" and "lower" a. More waves = _______________________ pitch sound b. Fewer waves = _______________________pitch sound 4. Decibel – abbreviated __________________ : a. The _________________________ of sound b. dB scales begin at 0 dB, the ________________________ of hearing c. Each increase of 10 dB on the scale is actually a __________-fold increase in sound pressure. (Ex: 55 dB is Ten times as loud as 45 dB) HEARING TESTS: 1. Hearing test are measured on an _______________________________, a chart showing the dB loss in both right & left ear. Cochlear Implants: 1. Cost is ____________________(insurance may not pay or may only pay part) 2. Requires a commitment of _______________________________________ for months/years 3. Do not replace ___________________ hearing 4. Can be unsuccessful and result in surgical complications, infections and even ____________________ Deaf community has feared cochlear implant will cause the decline or disappearance of ____________________________________ and _________________________________