* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Current Electricity Review Problems
Electric battery wikipedia , lookup
Negative resistance wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
RLC circuit wikipedia , lookup
Rechargeable battery wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Current mirror wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
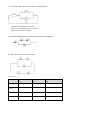
Current Electricity Review Problems Name:___________________ Definitions / Conceptual 1. Quantity Charge Definition Variable Units Relevant equations Force Electric Field Current Potential Resistance Power Energy 2. When work is done on a positive test charge by an external force to move it from one location to another, potential energy _________ (increases, decreases) and electric potential _________ (increases, decreases). 3 5. Why is it dangerous to handle electrical equipment with wet hands? 6. What does a transformer do? 7. Why do powerplants supply AC current? 8. You have two resistors. If you want to have high total resistance in a circuit, should you arrange the resistors in parallel or in series? Why? 9. If one light in a chain of lights connected in series burns out, none of the lights will work; however, if one light in a chain of lights connected in parallel burns out, the other lights will stay lit. Explain why this occurs. 10. Write 5 synonyms for potential. Problems SHOW WORK FOR CREDIT. 1. Two wires, A and B, with circular cross-sections have identical lengths and are made of the same material. Yet, wire A has four times the resistance of wire B. How many times greater is the diameter of wire B than wire A? 2. A certain wire has a resistance R. How does the resistance change if the length is doubled and the crosssectional area is halved? 3. A certain electrical circuit contains a battery with three cells, wires, and a light bulb. Which of the following would cause the bulb to shine less brightly? (choose all that apply) a. Increase the voltage of the battery (add another cell) b. Decrease the voltage of the battery (remove a cell) c. Decrease the resistance of the circuit d. Increase the resistance of the circuit 4. A circuit consists of a light bulb and a battery. What happens to the current in the light bulb if the resistance of the light bulb is halved? 5. A circuit consists of a light bulb and a battery. What happens to the current in the light bulb if both the resistance of the bulb and the potential difference supplied by the battery are doubled? 6. A circuit consists of a light bulb and a battery. How does the power change if the current is halved and the voltage drop across the light bulb is tripled? 7. A circuit consists of a light bulb and a battery. How does the power change if the current is doubled and the resistance of the lightbulb is halved? 8. A TV with a power rating of 200 W uses 0.8 kWh in one day. For how many hours was the TV on during this day? 9. A VCR that is not playing still uses 10.0 W of power. What is the current if the VCR is plugged into a 120 V electric outlet? 10. Calculate the current of a lightning bolt that delivers a charge of 35 coulombs to the ground in a time of 1/1000 second. 11. An electrical appliance is rated as 2.5 kW, 240 V. (a) Determine the current needed for it to operate. (b) Calculate the energy it would consume in 2.0 hours. 12. 13. From the diagram given in the figure (below), calculate (a) the total resistance of the circuit (b) the current flowing in the main circuit (c) the current in each resistor 14. What is the equivalent resistance for the resistors in the figure? 15. Fill in the chart for the circuit below. Total current:_______ Resistor 8 ohm 2 ohm 10 ohm 5 ohm Current through (A) Voltage across (V) Power dissipated by (W)