* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Black Death - AP European History at University High School
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
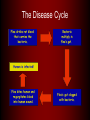
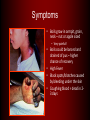
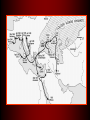
The Black Death Contributing Factors • Italian sea trade expanded around 1300 – Opened Strait of Gibraltar – Advances in shipbuilding • Year-round, far-reaching trade • Mongols controlled Eurasian landmass – facilitated long-distance trade (Silk Road) • “Great Famine” from 1315-1322 – Greater susceptibility to disease Pathology • Bubonic plague = bacillus Yersinia pestis • Fleas – Rats – Sometimes Humans • Pneumonic transmission (coughing, sneezing) The Disease Cycle Flea drinks rat blood that carries the bacteria. Bacteria multiply in flea’s gut. Human is infected! Flea bites human and regurgitates blood into human wound. Flea’s gut clogged with bacteria. Symptoms • Boils grow in armpit, groin, neck – nut or apple sized – Very painful! • Boils could be lanced and drained of pus – higher chance of recovery • High Fever • Black spots/blotches caused by bleeding under the skin • Coughing blood = dead in 23 days Spread of the Disease • First description – SW China 1331 • Mongol armies and merchants carried rats across Central Asia • Reached Black Sea by 1340s • Chemical warfare – Mongols catapulted plague bodies into Kaffa - 1346 • 1347 – Genoese ships brought plague from Kaffa to Sicily • 1348 – Plague hit Italian ports, spread through Europe • Poor urban conditions contributed to spread of disease • Low standards of personal hygiene – weakened immune system • Estimate of 1/3 of European population killed in 1348 • Recurrences of plague from 1360s to 1400 Various Forms of Care • 14thC Physicians could ease pain, but no cure • Crowded cities + warm/moist conditions = higher death rate • “Corrupted air” caused imbalance of fluid – bloodletting • Burning herbs, church bells, cryptograms Reactions • Wealthy fled to countryside • Towns isolated themselves • Scapegoats – Jews poisoned the wells! – Led to persecution • Some areas had hospital facilities – limited availability and comfort • Many saw plague as punishment from God Pograms against the Jews “Jew” hat “Golden Circle” obligatory badge Social and Economic Consequences • High mortality rate for clergy – stayed to care for sick • Helped agrarian economy – population decline led to increased productivity – Balance between labor, land, capital • New members brought into urban guilds • General inflation – High mortality = Fall in production, shortage of goods, rise in prices – Shortage of workers = demand for higher wages, higher standard of living – Pop. decline = increase in per capita wealth Intellectual and Cultural Consequences • Pervasive pessimism • Various reactions – Party time! – Severe asceticism & religious fervor – Flagellants – Blame the Jews • Pogroms, persecution – caused flight to E. Europe • • • • Fancy funerals to mass graves Holy pilgrimages – got them out of the city! Quarantine of travelers and ships More endowments to universities = new colleges • International character of medieval culture weakened Death Triumphant !: A Major Artistic Theme Boccaccio in The Decameron “The victims ate lunch with their friends and dinner with their ancestors.”