* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 7: Congruence of Triangles
Dessin d'enfant wikipedia , lookup
Line (geometry) wikipedia , lookup
Tessellation wikipedia , lookup
Multilateration wikipedia , lookup
History of geometry wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Penrose tiling wikipedia , lookup
Reuleaux triangle wikipedia , lookup
Apollonian network wikipedia , lookup
Euler angles wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
Technical drawing wikipedia , lookup
Pythagorean theorem wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
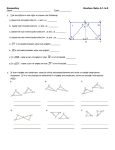
7 Congruence of Triangles Objectives: Understand the meaning of congruence and how it applies to geometrical shapes Identify congruence in line segments, angles and plane figures Understand the criteria for congruence in triangles and use them to identify congruent triangles Understand the concept of similarity as against congruency Differentiate between similar and congruent triangles Before We Begin: Terms Line segment Angle Triangle Vertices of a triangle Sides of a triangle Right-angled triangle Hypotenuse Symbols/ Notations Point A ∠Y ΔPQR Methods Measure the length of a line using a ruler Draw a line of given length using a ruler Measure an angle using a protractor Draw an angle using a protractor and ruler Lesson Plan: (Chapter 7 from last year's textbook - Mathematics for Class VII, CBSE) Content 7.1, 7.2 Introduction Teacher's Activity Student's Activity Introduce the term "congruency" Provide examples of congruent shapes and explain how it is a around them geometrical term for "sameness" in shape and size Explain how superimposing objects is a simple technique for testing congruency of plane figures Assignments 7.3, 7.4 Congruent Lines and Angles Ask children to point out examples of congruent shapes around them Draw out examples of lines and angles on the board Invite students to explain how they would test for congruency (other than superimposing) Deduce the rules for testing congruency in lines and angles Explain the various criteria for congruency of triangles (SSS, SAS, ASA, RHS) Solve examples to prove congruency of triangles Using the various criteria for Ex 7.1, 7.2 congruency, determine if two given triangles are congruent Find missing angles or sides for congruent triangles Solve real-world problems to understand the application of congruency 7.5, 7.6 Congruence of Triangles Similar Shapes Similar Triangles Real-world examples Self-assessment and Test Introduce the definition of "similarity" in geometrical shapes as sameness in shape but not in size Provide examples of similar shapes that are not congruent Identify similar shapes around them Explain why a given shape is similar but not congruent Understand that all congruent shapes are also similar Problems from NIOS/IG textbooks Explain the concept of proportionality for sides of triangles Explain the various criteria to determine similarity in triangles (AAA, SSS, SAS) Identify triangles that are similar Solve for missing sides or angles of similar triangles Problems from NIOS/IG textbooks Explain, through examples, how congruency and similarity of triangles can be used in realworld situations Understand how congruency and similarity of triangles can be used in realworld situations Why do we need to learn about Congruency? e.g. Bridges (congruent triangles form a good support structure); Creating multiple items that are identical (e.g. notebooks, paintings, etc) Sample real-world problem: The map below shows five different towns. The town of Meridian was given its name because it lies exactly halfway between two pairs of cities: Camden and Grenata, and Lowell and Morsetown. Using the information in the map, what is the distance between Camden and Lowell? Why do we need to learn about Similarity? e.g. Calculating the height of objects that are difficult to measure. Using shadows is a quick way to estimate the heights of trees, flagpoles, buildings, and other tall objects. To begin, pick an object whose height may be impractical to measure, and then measure the length of the shadow your object casts. Also measure the shadow cast at the same time of day by a yardstick (or some other object of known height) standing straight up on the ground. Since you know the lengths of the two shadows and the length of the yardstick, you can use the fact that the sun's rays are approximately parallel to set up a proportion with similar triangles. Because the sun's rays are parallel, the triangles are similar. Thus: Self-Assessment: Topic Understanding of the topic Working with simple cases High comfort-level and confidence with the topic Congruency I know the geometrical meaning of the word "congruent" and I can give examples of congruent shapes around me I can determine if two lines or two angles are congruent I can determine if two triangles are congruent by superimposing one on the other I can determine if two triangles are congruent by using one of the criteria for congruency (SSS, SAS, ASA, RHS) I can use the congruence property of triangles to find missing angles or sides Similarity I know the geometrical meaning of the word "similar" and I can give examples of similar shapes around me I can determine if sides of a triangle are proportional (in a ratio) I can determine if two triangles are similar by measuring their angles and sides I can determine if two triangles are similar by using one of the criteria for similarity (AAA, SSS, SAS) I can use the similarity property of triangles to find missing angles or sides Real-world application I can give examples of congruent and similar shapes in the real world I know the difference between congruent and similar shapes and can explain why a shape is similar but not congruent I can provide examples of how congruent and similar triangles can be used to solve real-world problems I can solve real-world problems involving congruent and similar triangles and solve for missing lengths and angles