* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Seeds and Plants - Whitman College
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Ecology of Banksia wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Gartons Agricultural Plant Breeders wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Historia Plantarum (Theophrastus) wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant reproduction wikipedia , lookup
Verbascum thapsus wikipedia , lookup
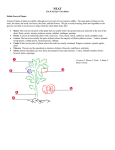
Seeds and Plants What is a seed and how does it grow? A seed is the part of the plant that produces the next plant. Think of it like a baby or a pre-baby—an embryo; it grows from a small creature into an adult than can then produce more seeds aka babies/embryos. Seeds need warmth and moisture to grow. They do not need light. They also need food. Depending on the species, the seed’s energy comes from either coytledon or endosperm, both things that provide essential nutrients for the seed to jumpstarts its young life. Seed becomes Plant! Once the seed sprouts and emerges from the soil it starts the process of photosynthesis-turning the sun’s energy into food it can use to grow. http://bbg-aura.gaia.com/photos/56/551205/large/seedsprout-424_1_.jpg Components of a Plant • Seeds • Roots • Stems • Flowers • Fruits • Leaves http://www.uic.edu/classes/bios/bios100/summer2005/pl antbod.gif Seeds Seeds produce plants! Plants put vital nutrients into seeds to ensure the next generation of plants. What foods are seeds? http://hopeseeds.org/images/seed.jpg Lots! Popcorn, peas, coffee beans, beans. Seeds are high in protein and are the best source of non-meat protein for humans. Roots Roots anchor plants, absorb water and nutrients, and store nutrients What foods are roots? Carrots, radishes, potatoes, onions (root vegetables) They offer a good source of complex carbohydrates which give us long term energy. http://www.biodiversityexplor er.org/plants/apiaceae/image s/enb07436x_carrots.jpg http://fotosa.ru/ru/stock/search.asp?ID=2570461 Stems Stems are like our skeleton; they help plants stand tall and strong. They carry water and nutrients to the rest of the plant from the roots. What foods are stems? Celery, sugar cane, asparagus They provide us with a good source of fiber Flowers Flowers form seeds What flowers are foods? Broccoli, cauliflower Provide humans with lots of nutrients http://tinyfarmblog.com/wpcontent/uploads/2007/11/fal2007_broccoli_vs_cauliflower.jpg Fruits Fruits hold and protect seeds What foods are fruits? Lots! Apples, tomatoes, cucumbers, strawberries, oranges Fruits contain tons of vitamins that help keep us healthy http://www.biteofthebest.com/wpcontent/uploads/FB_BabyVegetable-Basket_2.jpg Leaves Leaves absorb the sun’s energy and turn it into food the plant can use to grow What foods are leaves? Lettuce, basil, kale Offer us lots of nutrients to make us healthy http://verdavivocooks.files.wordpress.com/2008/04/kale.jpg Work Cited Health Foods from Healthy Soils by Elizabeth Patten and Kathy Lyons Pictures have source underneath photo PowerPoint created by Robin Lewis, Environmental Studies Intern, Whitman College Spring 2010