* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Vocabulary for Unit Four: Landforms and Topography
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
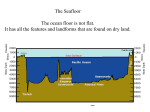
Vocabulary for Unit Four: Landforms and Topography 1. Plain large, flat landform that often has thick, fertile soil and is usually found in the interior region of a continent 2. Plateau flat, raised landform made up of nearly horizontal rocks that have been uplifted 3. Folded Mountain mountains formed when horizontal rock layers are squeezed from opposite sides, causing them to buckle and fold 4. Upwarped Mountain mountains formed when blocks of the Earth’s crust are pushed up by forces inside the Earth 5. Fault-blocked Mountain mountains formed from huge, tilted blocks of rock that are separated from surrounding rocks by faults 6. Volcanic Mountain mountains formed when molten material reaches the Earth’s surface through a weak crustal area and piles up into a cone-shape structure 7. Latitude distance in degrees north or south of the equator 8. Longitude/Meridian distance in degrees east or west of the prime meridian 9. Equator imaginary line that wraps around Earth at 0° latitude, halfway between the north and south poles 10.Prime Meridian imaginary line that represents 0° longitude and runs from the north pole through Greenwich, England to the south pole 11.International Date Line the transition line for calendar days 12.Contour line a line on a map that connects points of equal elevation 13.Index Contour line contour lines that are marked with the elevation 14.Topographic Map map that shows the changes in elevation of the Earth’s surface and indicates such features such as roads or cities 15.Continental Shelf gradually sloping end of a continent that extends beneath the ocean and provides a home for most marine organisms 16.Continental Slope ocean basin feature that dips steeply down from the continental shelf 17.Abyssal Plains flat seafloor area from 4,000m to 6,000m below the surface, formed by the deposition of sediments 18.mid-ocean ridge area in an ocean basin in which new ocean floor is formed 19.Trenches long, narrow, steep-sided depression in the seafloor formed when one crustal plate sinks beneath another