* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Thyroid, Parathyroid and Suprarenal Glands
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
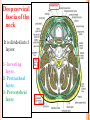
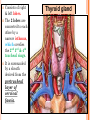
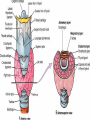
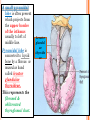
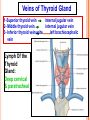
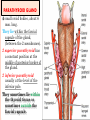
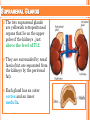
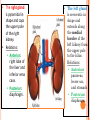
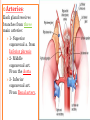
THYROID, PARATHYROID AND SUPRARENAL GLANDS Dr Rania Gabr OBJECTIVES By the end of the lecture, the student should be able to: Describe the shape, position, relations and structure of the thyroid gland. List the blood supply & lymphatic drainage of the thyroid gland. Describe the shape, position, blood supply & lymphatic drainage of the parathyroid glands. Describe the shape, position, blood supply & lymphatic drainage of the adenal glands. Deep cervical fascia of the neck It is divided into 3 layers: 1- Investing layer. 2- Pretracheal layer. 3- Prevertebral layer. 3 Consists of right & left lobes. The 2 lobes are connected to each other by a narrow isthmus, which overlies the 2nd 3rd & 4th tracheal rings. It is surrounded by a sheath derived from the pretracheal layer of cervical fascia. Thyroid gland 5 Each lobe is pear shaped, with its apex directed upward as for as the oblique line of the thyroid cartilage its base lies at the 4th or 5th tracheal ring. Posterior Anterior The isthmus extends across the midline in front of the 2nd 3rd & 4th 7 tracheal rings. Inside the pretracheal facial capsule, there is another capsule. So, it s surrounded by 2 membranes. A small pyramidal lobe is often present which projects from the upper border of the isthmus usually to left of middle line. Pyramidal lobe is connected to hyoid bone by a fibrous or muscular band called levator glandulae thyroideae. This represents the fibrosed & obliterated thyroglossal duct. Levator glandul ae thyroide ae 9 RELATIONs OF THE THYROID Anterolaterally: (4 S). 1. Sternothyroid. 2. Sternohyoid. 3. Superior belly of omohyoid 4. Sternomastoid. 10 ARTERIAL SUPPLY : 1-Superior thyroid artery: From the external carotid artery It descends to the upper pole of the lobe, with the external laryngeal nerve. It runs along the upper border of the isthmus to anastomosis with its fellow. 2- Thyroidea ima artery: If present, it arises from aortic arch or from brachiocephalic artery. It ascends in front of the trachea to reach the isthmus. 11 3-Inferior thyroid artery From the thyrocervical trunk of 1st part of subclavian artery, ascends behind the gland to the level of cricoid cartilage. It curves medially behind the carotid sheath. Then it reaches the posterior aspect of the gland & descends downwards. The recurrent laryngeal nerve crosses either in front or behind it. 12 Veins of Thyroid Gland 1-Superior thyroid vein internal jugular vein 2- Middle thyroid vein internal jugular vein 3- Inferior thyroid veinunite left brachiocephalic vein Lymph Of the Thyroid Gland: Deep cervical & paratracheal 14 Nerves: Sympathetic fibers from superior, middle, and inferior cervical ganglia reach the gland through the 1- laryngeal and 2- cardiac branches of the vagus nerve PARATHYROID GLAND 4 small ovoid bodies, about 6 mm. long. They lie within the fascial capsule of the gland, (between the 2 membranes). 2 superior parathyroid has a constant position at the middle of posterior border of the gland. 2 inferior parathyroid usually at the level of the inferior pole. They sometimes lie within the thyroid tissue or sometimes outside the fascial capsule. 16 • • • • • • • • Arterial supply They are supplied mainly by the inferior thyroid artery Venous Drainage Blood is drained mainly by inferior thyroid vein Lympahatic drainage Lymph is drained to deep cervical and paratracheal lymph nodes Nerve Supply They are supplied by sympathetic fibers SUPRARENAL GLANDS The two suprarenal glands are yellowish retroperitoneal organs that lie on the upper poles of the kidneys , just above the level of T12 They are surrounded by renal fascia (but are separated from the kidneys by the perirenal fat). Each gland has an outer cortex and an inner medulla. • The right gland is pyramidal in shape and caps the upper pole of the right kidney. • Relations: • Anterior: right lobe of the liver and inferior vena cava. • Posterior: diaphragm. • The left gland is crescentic in shape and extends along the medial border of the left kidney from the upper pole to the hilus. • Relations: • Anterior: pancreas, lesser sac, and stomach • Posterior: diaphragm. Arteries: Each gland receives branches from three main arteries: 1- Superior suprarenal a. from Inferior phrenic 2- Middle suprarenal art. From the Aorta 3- Inferior suprarenal art. From Renal artery. • Veins: • A single vein emerges from the hilum of each gland • The right adrenal vein drains into the Inferior vena cava • The left adrenal vein drains into the Lt Renal vein on the left. • Lymph Drainage: The lymph drains into the lateral aortic nodes. • Nerve Supply: Preganglionic sympathetic fibers derived from the splanchnic nerves. Most of the nerves end in the medulla of the gland.