* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 5.8 Acid Deposition
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
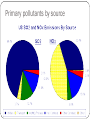
5.8 Acid Deposition (Rain) The pH Scale…What is acidic? Acid Deposition (Process) Chemistry of acidified precipitations Acid deposition can be either wet or dry: Wet deposition - acidic rain, snow, or other precipitation Dry deposition - acidic gas or dry particles, not mixed with water Pollutants can be classified as either primary or secondary: Primary pollutants - those directly emitted by a factory or automobile SO2 - sulfur dioxide NO and NO2, usually identified as NOx Primary pollutants by source Chemistry Cont. Secondary pollutants - primary pollutants react with other substances in the atmosphere and create different pollutants H2SO3 - sulfurous acid H2SO4 - sulfuric acid HNO3 - nitric acid Effects of acid deposition on environment Direct effects (Know 1): Inhibits embryonic development of fish Chlorophyll loss & yellowing of tree leaves and buds → diminished growth Thinning of cuticle (the waxy coating on needles) Symbiotic root microbes killed (i.e. Rhizobium spp. and other beneficial fungi) Toxic effects (Know 1): Aluminum (Al) leaches out of soil into streams Al disrupts salt, water, and oxygen regulating mechanisms in fish Al can also adhere to fish gills, causing suffocation Lichens sensitive to SO2 gases and used as indicator species Effects of acid deposition on environment Nutrient effects (Know 1): Soil particles can’t retain Ca, Mg, K, and other nutrients in acidic environment, so those nutrients are leached out of soil and not available to trees Dissolved Al ions damage root hairs (the smallest roots, which are the most effective at absorbing nutrients), so the trees are unable to absorb as many nutrients N-fixing bacteria don’t function as well, so less N is added to soil matrix Acid deposition is regional Acid precipitation falls back to Earth rather than entering stratospheric jet stream Most areas are downwind of pollution sources Canadian forests damaged by coal-fired power plants in USA Scandinavian and German forests damaged by British coal plants Pollution management strategies for acid deposition See Table 15.7 on p.298 of the IB ESS 2010 Course Companion Replace Switch to renewable energy sources (reduce fossil fuel use) Increase energy efficiency (better light bulbs and appliances) More public transportation (fewer automobiles on the road) Use low-sulfur fuels Regulate Install ‘scrubbers’ on smokestacks of coal-fired power plants to remove SO2 Catalytic converters installed on automobiles (required by law in the US, Canada, and Europe) Management cont. Restore Add limestone to acidified lakes and streams Using limestone or calcium carbonate (CaCO3) can neutralize (buffer) the impact of acids. Freshwater ecosystems much more vulnerable Expensive and hard to determine how much to add