* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Best Practice in Spelling
Australian English wikipedia , lookup
Philippine English wikipedia , lookup
Phonological history of English high front vowels wikipedia , lookup
American English wikipedia , lookup
Middle English wikipedia , lookup
History of English wikipedia , lookup
Classical compound wikipedia , lookup
Ugandan English wikipedia , lookup
Phonological history of English consonant clusters wikipedia , lookup
Scripps National Spelling Bee wikipedia , lookup
American and British English spelling differences wikipedia , lookup
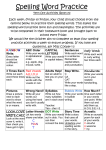
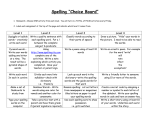
Strategies for spelling? • What strategies do you use to spell words? • Do these strategies work - sometimes - all the time - never? • What do you think you can do to be be a better speller? Best Practice in Spelling Methodologies which effectively help us to be accurate spellers : Phonemic spelling ‘Whole Word’ approach (Visual) Morphemic spelling Spelling should be explicitly taught because: • The English language DOES conform to predictable patterns • These patterns can be learnt Collins, 1983 Dixon, 1991 Graham, 1999 Dixon and Engelmann, 2002 1. Phonemic Spelling • Understanding the relationship between letters and their corresponding sounds is an important skill for successful reading and spelling performance. • We have less difficulty spelling words that are based on predictable letter-sound relationships. • About 87% of our language has predictable letter-sound patterns example • the word hat has three sounds: /h/, /a/, and /t/ • It can be correctly spelled using the three letters (h, a, and t) that correspond with each of those sounds. The Dyslexic Speller Disadvantage • The area of the brain that is used to connect the sounds to letters is normally a weak area in people with dyslexia. The Dyslexic Speller Advantage The brain can be rewired to work with these sounds (even in adults). Rewiring is achieved with • Systematic phonics instruction boosts the spelling skills (National Reading Panel, UK, 2000) • practice (research shows to form a neural pathway a word, sound, pattern must be reviewed over 20 times) 2. Whole Word Approach Not all words in the English language can be spelled correctly using lettersound correspondence. About 13% of words do not follow the letter- sound patterns Irregularly spelled words • Examples of irregular words include the words yacht, straight, and friend • These words cannot be spelled correctly by applying a regular phonics approach. • To learn irregularly spelled words, different strategies are required. Advantages: • Whole Word approach works well with words which do not conform to a regular spelling pattern. Disadvantages: • Memorisation is not the most efficient strategy for spelling instruction. • In a typical ‘Whole Word’ program, groupings of words are based on some similarity –Similar sound patterns sounds like th- or –and words –Word lists for a particular topic eg work related words, course words. Strategy for learning whole word spelling - the Look-say-cover-write method. • First, a student looks at a word. • Then, while touching each letter of the word, the student spells the word. • Next, the student covers the word so it is no longer visible. • The word is then written on a separate piece of paper. • Finally, the student uncovers the correctly spelled word and checks to see if he or she has copied it down correctly. • The English language contains words with both regular and irregular spellings. • Both the phonemic and whole-word approaches are required to teach regularly or irregularly spelled words. 3. Morphemic Approach • A morphograph is the smallest unit of identifiable meaning in written English. • Morphographs include prefixes, suffixes, and bases or roots. • Recognising different morphographs can help to create many words in the written English language. • For example, the word recovered is made up of the prefix re, the base cover, and the suffix ed. • Learn the basic rules applied when adding a suffix to the end of a word. • Eg try – tried • stop – stopped • wave - waved Advantages. First • Morphographs are generally spelled the same across different words. • For example, the morphograph port is spelled the same in the words porter, deport, and important. Second • When the spelling of a morphograph changes across words, it does so in predictable ways. • The morphograph trace is spelled differently in the words trace and tracing, but the change is governed by the rule for dropping the final e. Third • The number of morphographs is far fewer than the number of words in the written English language and • the number of principles for combining morphographs is relatively small. Therefore: Learning to spell morphographs and the rules for combining morphographs will allow students to spell a far larger set of words accurately than by learning individual words through rote memorisation of spelling lists. • In summary, phonemic, whole-word, and morphemic approaches are useful for teaching the wide variety of word types in the English language. • Together these approaches represent a comprehensive set of strategies for learning how to be an accurate speller. Whole words Auditory -phonics Common words, syllables Difficult words, sounds homonyms Morphemes Prefixes, suffixes Root words Spelling rules