* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download cscope Kingdoms of Life Characteristics ppt notes
Plant tolerance to herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Pollination wikipedia , lookup
Venus flytrap wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Cultivated plant taxonomy wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
History of herbalism wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Historia Plantarum (Theophrastus) wikipedia , lookup
Sustainable landscaping wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Glossary of plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
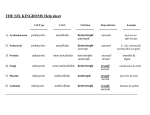
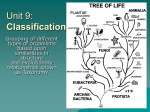
Kingdoms of Life Characteristics CSCOPE UNIT 10 LESSON 02 ARCHAE Major Characteristics Formerly called “Archaebacteria” Prokaryote Unicellular (one celled) Have cell wall (peptidoglycan) Autotroph or heterotroph Asexual reproduction BACTERIA Major Characteristics Prokaryote Unicellular (one celled) Have cell wall (peptidoglycan) Autotroph or heterotroph Asexual reproduction Helpful and harmful PROTISTA Major Characteristics Eukaryote Most unicellular Some colonial, some multicellular May have a cell wall (cellulose) Autotroph or heterotroph Asexual or sexual reproduction FUNGI Major Characteristics Eukaryote Most multicellular, some unicellular Cell wall (chitin) Heterotroph Asexual or sexual reproduction PLANTAE Major Characteristics Eukaryote Multicellular Cell wall (cellulose) Autotroph Asexual or sexual reproduction ANIMALIA Major Characteristics Eukaryote Multicellular No cell wall Heterotroph Sexual reproduction Prokaryotes: Eubacteria: “true bacteria” Very diverse Examples of Eubacteria: Escherichia coli (E. coli) Steptococcus (Strep) Staphlococcus (Staph) Methicillin Resistant Staph Aureus (MRSA) Archaebacteria Prokaryotes: Name means “ancient.” May be ancestors to eukaryotes Look almost identical to eubacteria, but genetically are as different as animals and plants. Inhabit extreme environments such as hot springs and salt ponds http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ZskEUGRlqrI&feature=related http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4LoiInUoRMQ Hydrothermal vent (black smoker) Extremeophiles: meaning they love extreme (hot, cold, salty, acidic) environments. Thermoacidophiles (Yellowstone) Multicellular Plantae: Make their food by photosynthesis 4 Types: Non-vascular Vascular without seeds Seeded vascular- Gymnosperms Flowering Plants- Angiosperms Nonvascular Plants Mosses and liverworts Lack vascular tissue (tubes for water flow) That’s why they only grow close to the ground in wet areas!! Nonvascular Plants Liverwort s Liverworts Hornwor t Bryophyte Moss Vascular Plants Seedless vascular plants: Have tubes for water flow in stems. Ferns Horsetail Vascular Plants Seedless Ferns and Horsetails have spores instead Vascular Plants Carboniferous period was dominated by seedless vascular plants. They are now the source of all our fossil fuels, such as oil and coal. Vascular Seed plants Gymnosperms = “Naked-Seed”: Conifers, such as pines, fir and ginkgo trees and other plants with cones. Vascular Seed Plants Likely evolved as Earth’s climate changed from warm and moist to hot and dry between 410 and 360 million years ago Evolutionally, have a number advantages over non-seed plants Can reproduce without free-standing water Pollination occurs when pollen is carried between plants of the same species by wind or insects; fertilization follows Seeds feed and protect developing plant embryos Seeds allow plants to colonize new places Often carried by wind, water, or animals Flowering plants Angiosperm-“Clothed Seed” Seed is found within a protective chamber called a fruit- which is the ripened ovary of the flower. (in contrast with bearing naked seeds in conifers) Flowering plants Flowering plants Most nuts are fruits too! Instead of becoming ripe and juicy, the ovary becomes hard and the seed becomes attached to it. Evolutionary History of Plants