* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download How did War change life in Nazi Germany?
Reichskommissariat Ostland wikipedia , lookup
Nazi Germany wikipedia , lookup
Allied Control Council wikipedia , lookup
Swedish iron-ore mining during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Technology during World War II wikipedia , lookup
British propaganda during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Foreign relations of the Axis powers wikipedia , lookup
Diplomatic history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
New Order (Nazism) wikipedia , lookup
Écouché in the Second World War wikipedia , lookup
End of World War II in Europe wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of Nazism wikipedia , lookup
Causes of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Allied plans for German industry after World War II wikipedia , lookup
Economy of Nazi Germany wikipedia , lookup
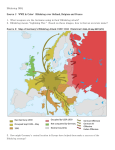
HOW DID WAR CHANGE LIFE IN NAZI GERMANY? www.educationforum.co.uk The War Went Through 4 Stages for Germany 1939-41 Blitzkrieg - a successful phase 2. June 1941 – 1943 Operation Barbarossa – the invasion of Russia (Soviet Union) 3. Feb 1943 – Total War – Germany lost the battle of Stalingrad and start to retreat – a turning point 4. Defeat – July 1944 -45 – Germany encircled Britain and Amerca advancing in the West, Russia in the East 1. Stage 1:Blitzkrieg 1939-41 1939-41 Blitzkrieg – The Nazis fought a successful ‘lighting war’ conquering many territories including Poland, Austria, Czechoslovakia and France – the Hitler myth appeared to be true! Impact Rationing introduced but seen as fair – Germans also benefited from food from conquered countries Germany well defended – some bombing of German cities but not extensive Stage 2: Operation Barbarossa June 1941 -Operation Barbarossa – Hitler invades Russia – now a war of two fronts putting enormous stress on German economy and army Impact Shortages of clothes and food in Germany – rations of basics reduced Hours in factories increased and overtime payment and holidays banned Conscription to the army for men Labour conscription to the factories for women Increased bombing of German cities by RAF Stage 3: Total War Feb 1943 – Total War – Germany defeated at Battle of Stalingrad Feb 1943 and start having to retreat. Gobbel's ‘total war’ speech – attempt to unite the whole country in a final push to avoid defeat Impact Massive, heavy bombing of cities – tens of thousands of deaths, essential supplies cut off, homelessness Women working in factories longer and longer hours Shortages and rationing Massive surge in propaganda after total war speech Growth in opposition. Stage 4: Defeat Defeat – by July 1944 it was clear that Germany was losing the war. Allied troops (Britain and America) had landed in France (D Day) and were advancing towards Germany and the Russians in the East moving towards Berlin Impact Brutal bombings of German cities e.g. in Dresden 1945 Feb – nearly 150,000 Germans killed in 2 nights Very serious shortages of everything, hunger, hopelessness, millions of refugees Child soldiers ‘protecting’ Berlin