* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download IBM® DB2® Database and MicroStrategy 10: A functional overview
Oracle Database wikipedia , lookup
Microsoft Access wikipedia , lookup
Concurrency control wikipedia , lookup
Entity–attribute–value model wikipedia , lookup
Microsoft Jet Database Engine wikipedia , lookup
Extensible Storage Engine wikipedia , lookup
Functional Database Model wikipedia , lookup
Microsoft SQL Server wikipedia , lookup
Open Database Connectivity wikipedia , lookup
Clusterpoint wikipedia , lookup
IBM® DB2® Database and MicroStrategy 10: A
functional overview including recommendations for
performance optimization
MicroStrategy World 2016
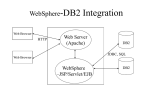
DB2 Is A Large Family of Relational Database Engines
IBM® DB2® for Linux, UNIX and Windows is a next generation data platform for
transactional and analytical operations
•
•
This session talks specifically
about IBM DB2 for Linux, UNIX
and Windows
Also applies to the latest cloud
based offerings, such as
dashDB
•
IBM DB2 is a commonly used by
MicroStrategy customers
•
MicroStrategy and DB2 team have
been working collaboratively on the
technical integration for 20 years
MicroStrategy Data Access Workflows
There are numerous ways for MicroStrategy to interact with IBM DB2
•
Adhoc Schema
•
• For Analysts familiar with data in database
• Schema is created automatically on the fly
• Optimal time-to-value
Live Connect
• User actions trigger analytical queries
against DB2
• Good for frequently changing data
•
•
Modeled Schema
• BI Architect creates logical model of data in
MicroStrategy
• Analyst or Consumers use model objects
(attributes and metrics) to express their
analytical needs
• MicroStrategy generates translated to multipass SQL to database
In-Memory Dataset
• Data is imported from database into Multidimensional In-Memory cache
• Can improve performance and user scale
MicroStrategy Pushes Analytical Workloads to IBM DB2
Analytical queries have specific technical characteristics
A typical analytical query
• Accesses a large amount of data (up to terabytes)
• Processes large amount of data
MicroStrategy customers like to have interactive experience
• Challenge is to achieve fast response times
MicroStrategy and IBM DB2 work together to tackle this challenge
• MicroStrategy formulates “good queries”
• DB2 executes queries well
MicroStrategy Provides Unique Optimizations for IBM DB2
•
DB2-optimized SQL syntax
•
– DB2 Analytical functions (OLAP functions)
– CASE expressions
– Full outer joins
– Set operators
– Subqueries
– Setting Isolation levels
Seamless support for key DB2 features
– DB2 BLU Acceleration
– DB2 Intrapartition Parallelism
– DB2 Compression
– DB2 Workload Manager
– DB2 function library
•
Multi-pass SQL for analytical sophistication •
– Use of common table expressions
– Use of declared global temporary tables
– Control over distribution keys for
intermediate results
– MicroStrategy Parallel SQL Execution
Extensions to DB2 functionality
– Aggregate awareness with physical
summary tables
– Middle-tier computation of calculations not
available in IBM DB2
– Middle-tier caching via Intelligent Cubes
– Report caching
– Application-level partitioning
DB2-Optimized SQL Syntax
MicroStrategy integrates with IBM DB2’s broad list of database functions and SQL
functionality to improve analytical performance
•
DB2-specific SQL
• DB2 version-specific MicroStrategy database connector
• Common table expressions, case expressions, full outer joins, set operators, subqueries, etc.
• Data type support
•
Function push-down
• MicroStrategy provides a library of mathematical, statistical, and financial functions
• Function push down to the database leverages the power of IBM DB2’s database server
• MicroStrategy’s SQL Engine pushes over 100 analytical functions to DB2
MicroStrategy Provides Analytical Sophistication
Multi-pass SQL optimized for IBM DB2 database
•
MicroStrategy provides analytical richness using multi-pass SQL
• Result of a SELECT statement used as input for the following
• Intermediate result is truly temporary in nature
•
MicroStrategy can handle intermediate data results in multiple ways
• Common Table Expression or CTE (Default)
• True Temporary Tables
•
Some MicroStrategy functionality cannot use CTE syntax
• Middle-tier processing of data (Analytical Engine)
• MicroStrategy Partitioning feature
SELECT
FROM
WHERE
SELECT
FROM
WHERE
MicroStrategy Switches Intermediate Table Syntax Dynamically
Depending on report design a different approach provides optimal query performance
•
•
•
In general, CTE syntax provides the best execution plan
In case of too many passes or when joining too many tables declared global
temp tables (DGTTs) are the better option
Two settings control whether to generate CTE or DGTT syntax
VLDB Category
VLDB Property Setting
Default Value
Tables
Maximum SQL Passes Before Fallback
0
Tables
Maximum Tables in From Clause Before Fallback
0
MicroStrategy Switches Intermediate Table Syntax Dynamically
Common Table Expression (CTE)
Declared Global Temp Tables (DGTTs)
Leveraging the power of DB2 BLU with MicroStrategy
IBM BLU Acceleration is designed for analytical workloads
BLU speeds up access to data
• Columnar storage
• Compression
• Data skipping
BLU speeds up data processing
• CPU optimized processing
• Next generation in-memory
computing
VLDB Category
Tables
Indexing
Pre/Post Statements
For optimal support in MicroStrategy
• Use the MicroStrategy database
object “IBM DB2 Version 10.5 for
Linux, UNIX and Windows”
• Update the settings below for
optimal intermediate table syntax
VLDB Property Setting
Intermediate Table Type
Intermediate Table Index
Insert Post Statement 1
Value
Permanent Table
Don’t create an index
CALL SYSPROC.ADMIN_CMD ('RUNSTATS ON TABLE ???
TABLESAMPLE SYSTEM(20)’)
Example: SQL Generation Configured for IBM BLU
No BLU? Other Key DB2 Features to Optimize Performance
Other DB2 features to improve MicroStrategy analytic workload performance
IBM DB2 Intrapartition Parallelism
•
Allows MSTR to throttle the degree of parallelism
depending on the type of query being submitted
•
MicroStrategy recommends the use of parallelism
for analytical workloads such as MicroStrategy
analytical queries
IBM Table Partitioning Feature
IBM DB2’s Adaptive Compression
•
Adaptive compression is automatic with column tables
•
For row-organized tables, Adaptive Row Compression
offers the best storage savings
•
MicroStrategy fully supports the use of Adaptive
Compression on warehouse base tables
Materialized Query Tables (MQT)
•
Table row data is distributed according to the
partitioning key
•
Store precomputed results which can improve
performance
•
Improves query performance when performing join
operations in analytical workloads
•
Not referenced in SQL but chosen by the IBM
optimizer at runtime if the MQT can improve
performance
•
Can be row-organized or column-organized
What is Workload Management? Why is it Important?
Workload Management (WLM) is necessary to optimize access to resources for
concurrently executing jobs or queries.
• The goals of a functional workload management are
• Optimally leverage available (hardware) resources for performance and
throughput
• Prioritize access for high priority jobs
• Assure resource availability by avoiding system lock-up by any small set of
jobs
Workload Management In MicroStrategy
Threads Have Priority Levels to Ensure High Priority Jobs Execute Quickly
Jobs are routed by
Priority to their
corresponding
database Connection
14
High Priority
Threads
Medium Priority
Threads
Low Priority
Threads
MicroStrategy
Report requests
are submitted
Workload Management in MicroStrategy
Job Priorities Can be Set on Different Application Parameters
15
MicroStrategy Can Integrate with IBM DB2 WLM
IBM DB2 Workload Manager (WLM) enables administrators to easily monitor and control
active work in the system
•
•
•
In a mixed workload environment (transactional and analytics) you need a way to
prioritize queries. DB2 WLM provides this functionality
With DB2 with BLU acceleration or dashDB, there is built-in WLM
Use WLM service classes to set different priorities for each of your MicroStrategy
workloads:
•
•
•
•
MicroStrategy Metadata Requests
MicroStrategy Element Requests
MicroStrategy Report Requests
A report pre statement tags the MicroStrategy job
VLDB Category VLDB Property Setting Value
Pre/Post
Statements
Report Pre Statement
CALL SYSPROC.WLM_SET_CLIENT_INFO(
'MSTRUser=!u', NULL, 'Project=!p', 'Report=!o',
NULL)
Managing MicroStrategy Workloads in IBM DB2
Create different WLM service classes for your various MicroStrategy workloads
Please refer to the “Workload Management with MicroStrategy Software and IBM DB2” paper for more implementation details
Summary
•
•
•
•
MicroStrategy and IBM DB2 work together to tackle challenges of analytics
Product defaults are optimized for “typical analytical scenarios”
MicroStrategy offers flexibility to quickly adjust to your environment
Details in the integration paper on MicroStrategy Community: TN45823
• Please email your feedback to [email protected]
Steps to leverage BLU with MicroStrategy
IBM BLU Acceleration is the single most important feature for improving analytical
workloads
MicroStrategy Recommendations
• Set the DB2 database default table orientation to column-organized
(DB2_WORKLOAD=ANALYTICS )
• Convert existing row-organized tables into column-organized tables
(db2convert)
• Use the MicroStrategy database object “IBM DB2 Version 10.5 for Linux,
UNIX and Windows”
• Update the MicroStrategy VLDB properties for proper intermediate table
syntax