* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Earth`s Internal Properties
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
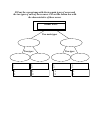
The Earth’s Internal Properties Homework: read Ch 12: pages 294-308 Seismic Waves • Earthquake waves have revealed that the Earth is ______________ Waves travel through different mediums at different speeds • Air is slower than water • Water is slower than solids Waves are measured on a ___________________ • Seismograph is the______________________ • ____________________ is the paper readout • Modern ones electronic-seismometer • Basic variety-heavy mass that resists movement Two types of seismic waves • I. Body waves— travel through the Earth’s interior—two types – – A. P-waves B. S-waves • II. Surface waves— travel on the Earth’s surface—two types – – A. Love waves B. Rayleigh waves Body waves: two types • Primary waves—p-waves – _______________ – ___________________—expand and contract – Travel through _______+ liquid Secondary waves—swaves – _____________________ – _________—vibrate up and down and side to side – Travel through _________ Surface Waves • Rayleigh waves • Love Waves • Both are slower than body waves Rayleigh Waves • Move in an up and down fashion Love Waves • Move in a side-to-side, ______like fashion Earthquake terms • __________________—the point on the surface directly above the focus • ________________—the exact location of the break Earthquakes are measured on the _________________ ________________ • Each magnitude is ______times more powerful than the preceding How to Read a Seismogram • The p-waves are the _______________to arrive • The secondary are larger and arrive _________________ Locating Earthquakes • Scientists draw lines perpendicular to the time from the first big deviation of the p and s waves ________________ between arrival of p and s waves gives a __________________ from the earthquake Time Travel Curve • Next they use a time-travel ____________ • The time ___________ between arrival times indicates _____________ Locating an Earthquake • The _____________ is where the _________ overlap ? How many stations do you need to locate an earthquake? ______ Earthquake Lab • Read the directions carefully • USE PENCIL Locating Earthquakes 1. Scientists draw lines perpendicular to the time from the first big deviation of the p and s waves 2. Difference between arrival of p and s waves gives a distance from the earthquake 3. Next use the Time Travel Curve Fill out the concept map with the two main types of waves and the two types of each of those waves. Fill out the bottom box with the characteristics of those waves. Seismic Waves Two main types Two types 1. 2. 1. 2. 1. 2. 1. 2. Two types 1. 2. 1. 2. 1. 2. 1. 2. Part II What Seismic Waves Tell Us So . . . How do we know what the inside of the Earth is like? Seismic Waves • Earthquake waves have revealed that the Earth is _____________ • Remember the different characteristics of different _________ waves – _____-waves—solids and liquids – _____-waves—solids only Waves travel through different mediums at different s____________________ • • Air is slower than water • Andrija Mohorovièiæ studied seismographs and discovered waves pick up ______________________at a certain depth • • He said, “Earth is _____________________” Water is slower than solids Earth's Internal Layers Drew a map of the upper _____________________ of Earth's mantle, Mohorovicic discontinuity Cool geologists call it the ____________________________ Shadow Zone: Remember p and s waves • 104 to 140 degrees does not receive any direct P waves • The shadow zone results from S waves being ____________ entirely by the _______________ core • and P waves being bent (__________________) by the liquid core. Shadow Zones—caused by refraction and s-waves cannot go through liquid Layers of the Earth • In Elementary and middle school you learned about crust, mantle, and core The crust is the uppermost part of the _________________________ Lithosphere • The lithosphere varies – from _______________ on the ocean floor – to _________________at the mountain ranges • The crust is 10km thick under the oceans – Made of ______________ • Continental crust is between 20-60 km thick – Made of _______________rocks that are less dense than basalt The lithosphere is very narrow and is rigid and brittle. It floats on the ________________________. The Mantle • 3000 kilometers thick • Hot iron-rich silicate rocks • Behaves _______________________—a solid that flows – Taffy example • ______________ part asthenosphere • Upper lithosphere includes _____________________ • ____________________________ _______________________ occur here – Hot less dense material __________________ – Cooler more dense material __________________ Asthenosphere • The lower part of the mantle is called the _______________________ • Hot, iron-rich silicate rocks • • The asthenosphere is hot and behaves with ___________________ It is a solid that ____________________like a liquid Thermal convection currents occur here Convection currents: hot material rises, cools, and begins to falls again. The core is still the core. The core has two parts: • the inner and outer cores 1. Inner core: _______________iron and nickel 2. Outer core: ___________________iron, nickel & sulfur The Earth's interior is _______________ 1. Part of the heat and pressure is from _________________ 2. Part is __________ ____________ from _________________ of the Earth (sometimes called residual heat) 3. and part is from the decay of ___________________ elements The Earth's inner core spins within the liquid outer core producing a _____________________ _____________________ Function (Fxn) of magnetic field • The magnetic field protects us from the ______________ _________________ - a high speed stream of radiation from the sun