* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Biceps femoris muscle - Kettlebell Training Education
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
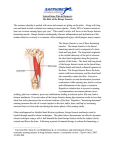
Biceps femoris muscle The biceps femoris (/ˈbaɪsɛps ˈfɛmərᵻs/) is a muscle of A slip may pass to the gastrocnemius.[1] the thigh located to the posterior, or back. As its name implies, it has two parts, one of which (the long head) 1.2 Innervation forms part of the hamstrings muscle group. 1 It is a composite muscle as the short head of the biceps femoris develops in the flexor compartment of the thigh and is thus innervated by common fibular branch of the sciatic nerve (L5, S2), while the long head is innervated by the tibial branch of the sciatic nerve (L5, S2).[3] Structure It has two heads of origin; • one, the long head, arises from the lower and inner impression on the back part of the tuberosity 1.3 Blood supply of the ischium, by a tendon common to it and the semitendinosus, and from the lower part of the The muscle’s vascular supply is derived from the sacrotuberous ligament;[1] anastomoses of several arteries: the perforating branches • the other, the short head, arises from the lateral lip of the profunda femoris artery, the inferior gluteal artery, [3] of the linea aspera, between the adductor magnus and the popliteal artery. and vastus lateralis, extending up almost as high as the insertion of the gluteus maximus; from the lateral prolongation of the linea aspera to within 5 cm. 2 Function of the lateral condyle; and from the lateral intermuscular septum.[1] Both heads of the biceps femoris perform knee flexion.[4] The fibers of the long head form a fusiform belly, which passes obliquely downward and lateralward across the sciatic nerve to end in an aponeurosis which covers the posterior surface of the muscle, and receives the fibers of the short head; this aponeurosis becomes gradually contracted into a tendon, which is inserted into the lateral side of the head of the fibula, and by a small slip into the lateral condyle of the tibia.[1] Since the long head originates in the pelvis it is also involved in hip extension.[4] The long head of the biceps femoris is a weaker knee flexor when the hip is extended (because of active insufficiency). For the same reason the long head is a weaker hip extender when the knee is flexed. From the posterior border of the tendon a thin expansion is given off to the fascia of the leg. The tendon of insertion of this muscle forms the lateral hamstring; the common fibular (peroneal) nerve descends along its medial border.[1] 3 Clinical significance When the knee is semi-flexed, the biceps femoris in consequence of its oblique direction rotates the leg slightly At its insertion the tendon divides into two portions, outward. which embrace the fibular collateral ligament of the kneejoint.[1] 1.1 4 See also This article uses anatomical terminology; overview, see Anatomical terminology. Variations The short head may be absent; additional heads may arise from the ischial tuberosity, the linea aspera, the medial 4.1 Additional images supracondylar ridge of the femur, or from various other parts.[1] The tendon of insertion may be attached to the • Right hip bone. External surface. Iliotibial band and to retinacular fibers of the lateral joint capsule.[2] • Bones of the right leg. Anterior surface. 1 for an 2 7 • Cross-section through the middle of the thigh. • Muscles of the gluteal and posterior femoral regions. • The popliteal, posterior tibial, and peroneal arteries. • Nerves of the right lower extremity Posterior view. • Back of left lower extremity. • Biceps femoris 5 References This article incorporates text in the public domain from the 20th edition of Gray’s Anatomy (1918) [1] “Gray’s Anatomy”. 1918. [2] The Adult Knee, vol. 1, ed. Callaghan, p. 70 [3] −865402803 at GPnotebook [4] Origin, insertion and nerve supply of the muscle at Loyola University Chicago Stritch School of Medicine 6 Further reading • Kumakura, Hiroo (July 1989). “Functional analysis of the biceps femoris muscle during locomotor behavior in some primates”. American Journal of Physical Anthropology 79 (3): 379–391. doi:10.1002/ajpa.1330790314. PMID 2504047. • Marshall, John L.; Girgis, Fakhry G.; Zelko, Russel R. (1972). “The Biceps Femoris Tendon and Its Functional Significance (PDF)". J Bone Joint Surg Am. 54 (54): 1444–1450. • Sneath, R. S. (October 1955). “The insertion of the biceps femoris”. J Anat. 89 (89(Pt 4)): 550–553. PMC 1244747. PMID 13278305. 7 External links • UWash - long head • UWash - short head • Anatomy photo:14:06-0100 at the SUNY Downstate Medical Center • Anatomy photo:14:st-0402 at the SUNY Downstate Medical Center EXTERNAL LINKS 3 8 Text and image sources, contributors, and licenses 8.1 Text • Biceps femoris muscle Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Biceps_femoris_muscle?oldid=686804648 Contributors: Diberri, Rich Farmbrough, Mecanismo, CDN99, Brim, Arcadian, Rjwilmsi, Huw Powell, NawlinWiki, Slodave, Mconst, Nick C, Mikepascoe, EncycloPetey, Eskimbot, Gilliam, Colonies Chris, Grover cleveland, Scientizzle, Iridescent, Mcstrother, Gogo Dodo, Kazubon~enwiki, Thijs!bot, Headbomb, Oreo Priest, Calaka, Kauczuk, Inbetweener, Olavrg, WhatamIdoing, Duendeverde, R'n'B, CFCF, Mikael Häggström, ELLusKa 86, VolkovBot, TXiKiBoT, SieBot, יוסי, Fimbriata, Mr. Stradivarius, ClueBot, Plastikspork, Tomas e, DumZiBoT, Addbot, CanadianLinuxUser, Diptanshu.D, Bubbafuzz16, Tide rolls, Luckas-bot, Vedran12, THEN WHO WAS PHONE?, AnomieBOT, ThaddeusB, Piano non troppo, Citation bot, Xqbot, Юрий Педаченко, Dinamik-bot, RjwilmsiBot, EmausBot, Rahopkinsiii, SporkBot, Gongoozler123, ClueBot NG, Frietjes, Dictabeard, Widr, BG19bot, Anatomist90, BattyBot, JakobSteenberg, LT910001, Tilifa Ocaufa, Swastikinu7 and Anonymous: 40 8.2 Images • File:Wiki_letter_w_cropped.svg Source: https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/1/1c/Wiki_letter_w_cropped.svg License: CC-BY-SA-3.0 Contributors: This file was derived from Wiki letter w.svg: <a href='//commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File: Wiki_letter_w.svg' class='image'><img alt='Wiki letter w.svg' src='https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/6c/Wiki_ letter_w.svg/50px-Wiki_letter_w.svg.png' width='50' height='50' srcset='https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/6c/ Wiki_letter_w.svg/75px-Wiki_letter_w.svg.png 1.5x, https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/6c/Wiki_letter_w.svg/ 100px-Wiki_letter_w.svg.png 2x' data-file-width='44' data-file-height='44' /></a> Original artist: Derivative work by Thumperward 8.3 Content license • Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 3.0