* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Optimization of Phase Contrast Imaging
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
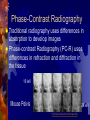
Optimization of Phase Contrast Imaging Luke Powers Chris Weaver Jonathan Fermo Alfred Luk Phase-Contrast Radiography Traditional radiography uses differences in absorption to develop images Phase-contrast Radiography (PC-R) uses differences in refraction and diffraction in the tissue 16 keV Mouse Pelvis 29 keV http://www.mxisystems.com/images.html Phase-Contrast Radiography Edge enhancements unique to PC-R Result of combination between constructive and destructive interference Potential Has potential to detect objects that are invisible on conventional radiography Edge enhancements and early detection of breast cancer Monochromatic beam reduces excess radiation dosage to patient Advisors Advisors: Frank E. Carroll, M.D. Gary Shearer Robert Traeger Principal Investigator: Edwin Donnelly, M.D., Ph.D. Facilities W.M. Keck Free Electron Laser Center at Vanderbilt Vanderbilt BME Department Resources Monochromatic Xray source at FEL LabVIEW and Virtual Instruments Stages, controllers, etc… for design construction provided by FEL & outside contractors Objectives To build a device that aids in testing PCR parameters Requires controlled movement in the x-, y-, & z-axes Rotation in the x-y plane Computer interface for real-time control Parameters Distances: Movements: Source-to-object ≤ 5 meters Object-to-detector ≤ 1 meter x-,y-axes ≤ 15 cm (total) z-axis ≤ 1 meter (per side) 360° rotation Independent object & detector movement along z-axis Components Software (LabView) Microcontroller Stepper Drivers Stepper Motors (200 steps/revolution) Can Linear micro-step for up to 64,000 steps/rev Translation Stages (x,y,z) Rotational Stage Selected Components Microcontroller Linear Translation Stage (z) Selected Components Detector and Rotational Stage