* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Causes of the Civil War
East Tennessee bridge burnings wikipedia , lookup
Red River Campaign wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Antietam wikipedia , lookup
Lost Cause of the Confederacy wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Port Royal wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Harpers Ferry wikipedia , lookup
Hampton Roads Conference wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Island Number Ten wikipedia , lookup
Fort Fisher wikipedia , lookup
Economy of the Confederate States of America wikipedia , lookup
Tennessee in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Appomattox Station wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Seven Pines wikipedia , lookup
Capture of New Orleans wikipedia , lookup
List of American Civil War generals wikipedia , lookup
Battle of New Bern wikipedia , lookup
Opposition to the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Fort Pillow wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Shiloh wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Gaines's Mill wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Cedar Creek wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Lewis's Farm wikipedia , lookup
Western Theater of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Wilson's Creek wikipedia , lookup
United States presidential election, 1860 wikipedia , lookup
Commemoration of the American Civil War on postage stamps wikipedia , lookup
First Battle of Bull Run wikipedia , lookup
South Carolina in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Virginia in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Namozine Church wikipedia , lookup
Alabama in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Union (American Civil War) wikipedia , lookup
United Kingdom and the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Border states (American Civil War) wikipedia , lookup
Conclusion of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Military history of African Americans in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Issues of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
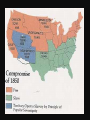
Unit 3: The American Civil War April Missouri Compromise • • • • Slave State- allowed slavery Free state- did not allow slavery Date- 1820 What did it do? Missouri joined the Union as a slave state. Maine joined as a free state. This kept the balance of slave states and free states. • How long did it last? 30 years Compromise of 1850 • California- joined the Union as a free state • New Mexico and Utah- the people here decided if they wanted slavery or not (popular sovereignty (vote) • Fugitive Slave Law- said that anyone caught helping slaves escape would be punished and all slaves had to be returned back to the south. Kansas Nebraska Act • Date- 1854 • Canceled out- the rules of the Missouri Compromise • What did this do? Said that the people in Kansas and Nebraska could vote on if they would be a slave state or free state (popular sovereignty). • Bleeding Kansas- people for and against slavery began fighting. The fighting was so bad it became known as this. • Better or worst for the North and South? Worse, because it increase tensions. John Brown’s raid on Harpers Ferry • John Brown- white abolitionist from the north – abolitionist- person who wanted to end slavery. • Harper’s Ferry- in Virginia, a federal armory where muskets and rifles were stored. • What happened: John Brown raided Harper’s Ferry. He planned on stealing the guns and weapons and give them to the slaves to fight with. The US Army showed up and captured Brown, who was later hanged. Uncle Tom’s Cabin • Author- Harriet Beecher Stowe • Date- 1852 • Story- Stowe wrote Uncle Tom’s Cabin. This book was very popular, but was not a true story. It gave many people the wrong idea about slavery. The Underground Railroad • Harriet Tubman was one of the best known conductors. She returned to the south 20 times and guided 300 people to freedom. • Really underground? No • Where did the routes go? From the south to the northern states and to Canada. Some went to Mexico and the Caribbean Islands. • Where were the hiding places? Barns, attics, secret rooms, called stations • Who were the conductors? Free Africans, white northerners who opposed slavery and some church leaders. Dred Scott Decision • What happened? Scott took his case to court. He said he should be free, because he lived on free land and his owner died. He lost because slaves didn’t have any privileges and • Slaves were labeled as- property. The judge said property is protected under the Constitution. • Missouri Compromise- was keeping people from owning property and this was unconstitutional. • North- was very upset; made the tension worse. • South- liked the ruling. States’ Rights • States’ Rights- constitutional issue saying that states should have the final authority over the federal government. The sates should make all the rules. • Who were for them? Southerners • What did these defend? Slavery – The northerners believed that the nation was a Union and shouldn’t be divided. Lincoln’s Election • Date- 1860 • Who supported who? Northern democrats supported Stephen Douglas. Republicans wanted to stop the spread of slavery and supported Abraham Lincoln • What happened- Douglas and Lincoln debated. Douglas said states should vote, Lincoln said there should not be slavery. Lincoln won the election. • Who left (seceded)- South Carolina, then Mississippi, Alabama, Georgia, Florida, Louisiana and Texas and formed the Confederate States of America. CIVIL WAR BATTLES Abraham Lincoln February 12, 1809 – April 15, 1865 1. He was the 16th President of the United States from 1860-1865. 2. He was also the Commander-inChief of the Union Army. 3. He appointed generals to command his troops. 4. He issued the Emancipation Proclamation, freeing the slaves. 5. He made his famous speech, the Gettysburg Address. Jefferson Davis June 3, 1808 – December 6, 1889 1. The President of the Confederate States of America. 2. He was also Commander -in Chief of the Confederate Army. 3. Appointed General Robert E. Lee as commander of the Army of Virginia 4. Encouraged industrial enterprise throughout the South. 5. Could not obtain help for the Confederacy from foreign governments. Ulysses S. Grant April 27, 1822 – July 23, 1885 1. Appointed General of the Union Army. 2. Considered the Union match to Robert E. Lee of the Confederacy. 3. Captured Forts Henry and Donelson. 4. Conducted the battle of Pittsburg Landing, or Shiloh. 5. Accepted Lee’s surrender at Appomattox Courthouse on April 9, 1865. Robert E. Lee January 19, 1807 – October 12, 1870 1. Was the South's greatest general during the Civil War. 2. Turned down position of Commander of Union army to stay loyal to Virginia. 3. Successful in defeating Union troops in the “Seven Days' Battle”, the Battle of Antietam, Fredericksburg, and Chancellorsville. 4. Fought in the Battle of Gettysburg. 5. Surrendered to Grant at Appomattox Courthouse, VA on April 9, 1865. Thomas “Stonewall” Jackson January 21, 1824 – May 10, 1863 1. Took command at Harper's Ferry, where he organized the troops. 2. Battle of 1st Manassas, where he acquired the legendary nickname Stonewall. 3. Promoted to Major General. Placed in command of the Valley of Virginia (Shenandoah Valley) 4. Second Bull Run, commanded the Confederate Army of Northern Virginia. 5. Was accidentally shot by his own troops and died 7 days later. William Tecumseh Sherman February 8, 1820 - February 14, 1891 1. Commanded a brigade at the Battle of Bull Run. 2. Commanded one of the three corps in the siege of Vicksburg. 3. At the head of 20,000 troops he made a most destructive raid from Jackson to the intersection of important railways at Meridian, MS. 4. Placed in command of a division of Grant's Army of the Tennessee, and served in the Battle of Shiloh. 5. Famous for his March to the Sea. CIVIL WAR BATTLES Fort Sumter Place: Fort Sumter, South Carolina Date: April 12-14, 1861 Generals: ◦ Union: Major Robert Anderson ◦ Confederate: Brigadier General P.G.T. Beauregard Results: Confederate Victory Significance: Civil War Begins Place: Gettysburg Pennsylvania Date: July 1-3, 1863 Generals: Union: George G. Meade Confederate: Robert E. Lee Results: Union Victory Significance: Civil War Turning point in Atlanta Campaign Place: Georgia Date: July 22, 1864 Generals: Union: William T. Sherman Confederate: John Bell Hood Results: Union Victory Significance: the South Bring the war to Sherman’s March to the Sea Place: Atlanta to Savannah, Georgia Date: November 15 – December 22, 1864 Generals: Union: William T. Sherman Confederate: John Bell Hood Results: Union Victory Significance: Destroyed everything that could help the South in the war. Appomattox Courthouse Place: Virginia Date: April 9, 1865 Generals: Union: Ulysses S. Grant Confederate: Robert E. Lee Results: Union Victory Significance: to Grant Lee surrendered