* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Practical training № 6
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
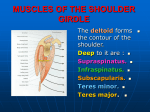
Practical training № 6 Topic. Topographical anatomy of the scapular and deltoid regions. Surgical anatomy of the shoulder joint. Punction, arthrotomy and resection of the shoulder joint. Topographical anatomy of the axillar region and shoulder region. Relevance of the topic: diagnosing and treatment of the inflammations of the anterior and posterior prescapular gaps, osteofibrous compartments, subdeltoid fibrous tissue, omarthritis and dislocations of the joint attract attention to the studying of this topic. Deep knowledge of the topographical anatomy of the neurovascular bunches of the axillar region and shoulder are necessary for their exposure at the traumas and diseases. Purpose of the lesson: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. Study topographical anatomy of the scapular and deltoid regions. Study surgical anatomy of the shoulder joint. Give topographical and anatomical justification of the ways of spreading of inflammatory purulent processes of the scapular and deltoid regions. Master the technique of dissection and drainage of the fibro-osseal compartments, prescapular gaps and subdeltoid fibrous tissue. Justify the ways of spreading of the periarticular phlegmons at the purulent omarthritis. Master the technique of punction, arthrotomy and resection of the shoulder joint. Study the topographical anatomy of the axillar region and shoulder. Study the topography of the neurovascular formations of the axillar region for their exposure. Justify the ways of spreading of the purulent processes of the axillar fossa and perform cuts for their drainage. Control questions: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. Topographical anatomy of the scapular region. Surgical anatomy of the osteofibrous compartments and prescapular gaps. Cuts for their drainage. Topographical anatomy of the deltoid region. Surgical anatomy of the subdeltoid fibrous tissue. Ways of spreading of the inflammatory processes. Cuts for their drainage. Surgical anatomy of the shoulder joint. Ways of spreading of the periarticular phlegmons. Punction, arthrotomy and resection of the shoulder joint. Indications. Technique. Topographical anatomy of the axillar region. Axillar fossa, its walls, triangles, holes and content. Surgical anatomy of a. axillaris. Surgical anatomy of the axillar plexus. Blockade of the axillar plexus. Indications. Technique. Topography of the lymphatic nodes of the axillar region. Ways of spreading of the phlegmons of the axillar fossa and cuts for their drainage. Topographical anatomy of the anterior region of the shoulder. Fascial compartments and their content. Surgical anatomy of the neurovascular bunches in the upper, middle and lower third of the shoulder. 13. Topographical anatomy of the posterior region of the shoulder. Canal of the radial nerve and its content. 14. Exposure of the radial and median nerves in the middle third of the shoulder. Indications. Technique. Practical skills: 1. 2. Show on the body: supra- and subspinatus, subscapular osteofibrous compartments, their content and connections muscles connected to the scapula arteries that form scapular arterial circle anterior and posterior prescapular gaps, their walls and connections subdeltoid fibrous tissue, its content and connections vagina synovialis intertubercularis ligaments of the shoulder joint lig. coracoacromiale walls and content of the axillar fossa triangles of the axillar fossa and their content foramen trilaterum and its content foramen quadrilaterum and its content a. axillaris and its branches v. cephalica v. basilica anterior fascial compartment of the shoulder and its content posterior fascial compartment of the shoulder and its content neurovascular bunch of the anterior region in the upper, middle and lower third of the shoulder canalis humeroulnaris, its walls and content Perform on the body: dissection for the drainage of the phlegmons of the osteofibrous compartments, prescapular gaps and subdeltoid fibrous tissue punction, arthrotomy and resection of the shoulder joint blockade of the shoulder bunch by Kulenkampff cuts for the dissection of the phlegmons of shoulder expose n. radialis in the middle third of the shoulder expose n. medianus in the middle third of the shoulder Computer questions for the practical training № 6 Topographical anatomy of the scapular and deltoid regions. Surgical anatomy of the shoulder joint. Punction, arthrotomy and resection of the shoulder joint. Topographical anatomy of the axillar region and shoulder region. 1. What is supraspinous osseous- fibrous sheath formed by? 2. What is situated in supraspinous osseous- fibrous sheath of scapula area? 3. What is infraspinous osseous- fibrous sheath formed by? 4. What is situated in infraspinous osseous- fibrous sheath of scapula area? 5. Name the possible ways of pus spreading from supraspinous osseous- fibrous sheath of scapula? 6. Name the possible ways of pus spreading from infraspinous osseous- fibrous sheath of scapula? 7. What is situated in infrascapula osseous- fibrous sheath? 8. What is front prescapula gap limited by? 9. What is back prescapula gap limited by? 10.What incisions are made for draining front and bach prescapula gap? 11.Which arteries form arterial ring of scapula? 12.What goes through subcutaneous tissue of deltoid area? 13.What is subdeltoid tissue space limited by? 14.What is situated in tissue of subdeltoid space? 15.Which synovial bursas are situated in subteltoid space? 16.Name the projection of nervovascular fascicle of subdeltoid space? 17.What is observed with patients with damage of n. axillaris? 18.Name the possible ways of pus spreading from subdeltoid space 19.Which incisions are used to open phlegmons of subdeltoid space? 20.Name the weak places of capsole of shoulder joint 21.Name ligaments that strengthen shoulder joint 22.Which muscles strengthen shoulder joint from the front? 23.Which muscles strengthen shoulder joint from the back? 24.Which muscle strengthen shoulder joint externally? 25.Which arteries furnish circulation of shoulder joint? 26.What is shoulder joint innervated by? 27.Name the external marks of the place of needle puncture when puncture of shoulder joint is done from the back 28.Name the external marks of the place of needle puncture when puncture of shoulder joint is done from the front 29.Name the external marks of the place of needle puncture when puncture of shoulder joint is done from the side 30.Name the direction of soft tissues cut for arterothomy of shoulder joint according to Langenbeck 31.Which muscles are splited up by hooks for arterothomy of shoulder joint according to Langenbeck? 32.Which compartment of shoulder joint capsule is cut for arterothomy according to Langenbeck? 33.What is front wall of cavum axillare formed by? 34.What is back wall of cavum axillare formed by? 35.What is medial wall of cavum axillare formed by? 36.What is lateral wall of cavum axillare formed by? 37.Which triangles are projected to the front wall of axilla? 38.What is foramen quadrilaterum limited by from above? 39.What is foramen quadrilaterum limited by from beneath? 40.What is foramen quadrilaterum limited by laterally? 41.What is foramen quadrilaterum limited by medially? 42.What is foramen trilaterum limited by from above? 43.What is foramen trilaterum limited by from laterally? 44.What is foramen trilaterum limited by from beneath? 45.Where is nervovascular fescical of axilla situated? 46.What does go through the foramen trilaterum? 47.What does go through the foramen quadrilaterum? 48.What is situated in trigonum subpectorale below, more medial and more superficial from a. axillaris? 49.What is situated in trigonum subpectorale more lateral from a. axillaris? 50.What is situated in trigonum subpectorale at the front of a. axillaris? 51.What is situated in trigonum subpectorale medially from a. axillaris? 52.What is situated in trigonum subpectorale behind a. axillaris? 53.What arteries branch out of a. axillaris to trigonum subpectorale? 54.Name the projecting line of a. axillaris 55.Where is the incision made to expose a. axilaris? 56.Where is the incision done for phlegmona of axilla? 57.Which incisions are made to open pyogenic abscess in axilla according to Voyno-Yasentsky? 58.Which nerves branch out of back fascicle of brachial plexus? 59.Which nerves branch out of lateral fascicle of brachial plexus? 60.Which nerves branch out of medial fascicle of brachial plexus? 61.Name branches of a. axillaris 62.What artery is important for development of collateral circulation when occlusion of a. axillaris happens? 63. Where is better to legate a. axillaris? !What is supraspinous osseous- fibrous sheath formed by? By deep layer of proper fascia, margos of scapula, spina scapulae, fossa supraspinata #By superficial layer of proper fascia, margos of scapula, spina scapulae, fossa infraspinata By deep layer of proper fascia, chest, m. serratus anterior By superficial layer of proper fascia, m. subscapularis, m. serratus anterior !What is situated in supraspinous osseous- fibrous sheath of scapula area? M.supraspinatus, a.suprascapularis, v.suprascapularis, n.suprascapularis #M.infraspinatus, a.suprascapularis, v.suprascapularis, n.suprascapularis, а.circumflexa scapulae, r.profundus a.transversae colli M.subscapularis, гiлки a.subscapularis, n.subscapularis M.teres minor, m.teres major, a.suprascapularis, a.circumflexa scapulae, r.profundus a.transversae colli !What is infraspinous osseous- fibrous sheath formed by? By deep layer of proper fascia, margos of scapula, spina scapulae, fossa infraspinata #By superficial layer of proper fascia, margos of scapula, spina scapulae, fossa infraspinata By superficial layer of proper fascia, chest, m. serratus anterior By deep layer of proper fascia, m. subscapularis, m. serratus anterior !What is situated in infraspinous osseous- fibrous sheath of scapula area? M.infraspinatus, a.suprascapularis, v.suprascapularis, n.suprascapularis, а.circumflexa scapulae, r.profundus a.transversae colli #M.supraspinatus, a.suprascapularis, v.suprascapularis, n.suprascapularis M.subscapularis, гiлки a.subscapularis, n.subscapularis M.teres minor, m.teres major, a.suprascapularis, a.circumflexa scapulae, r.profundus a.transversae colli !Name the possible ways of pus spreading from supraspinous osseous- fibrous sheath of scapula? Into tissue space of lateral triangle of neck, into infraspinous osseous- fibrous sheath, into subdeltoid tissue space #Into tissue of inguinal fossa, front prescapula gap, back prescapula gap Into supraspinous osseous- fibrous sheath formed, tissue of inguinal fossa, subdeltoid tissue space Into inguinal fossa, infrascapula osseous- fibrous sheath, infraspinous and supraspinous fossas, back and front sheath of shoulder, subpectoral space !Name the possible ways of pus spreading from infraspinous osseous- fibrous sheath of scapula? Into supraspinous osseous- fibrous sheath formed, tissue of inguinal fossa, subdeltoid tissue space #Into subpectoral space, front fascial sheath of shoulder, back fascial sheath of shoulder Into tissue space of lateral triangle of neck, into infraspinous osseous- fibrous sheath, into subdeltoid tissue space Into inguinal fossa, infrascapula osseous- fibrous sheath, infraspinous and supraspinous fossas, back and front sheath of shoulder, subpectoral space !What is situated in infrascapula osseous- fibrous sheath? M.subscapularis, гiлки a.subscapularis, n.subscapularis #M.supraspinatus, a.suprascapularis, v.suprascapularis, n.suprascapularis M.infraspinatus, a.suprascapularis, v.suprascapularis, n.suprascapularis, а.circumflexa scapulae, r.profundus a.transversae colli M.teres minor, m.teres major, a.suprascapularis, a.circumflexa scapulae, r.profundus a.transversae colli !What is front prescapula gap limited by? Chest and m.serratus anterior #M.subscapularis and m.serratus anterior M.latissimus dorsi and m.trapezius M.teres minor and m.teres major 1) chest and !What is back prescapula gap limited by? M.subscapularis and m.serratus anterior # Chest and m.serratus anterior M.latissimus dorsi and m.trapezius M.teres minor and m.teres major !What incisions are made for draining front and bach prescapula gap? Paravertebral incision along the medial margo of scapula, by horizontal incision of Sozon-Yaroshevich #By incision along lateral margo of scapula, incision along front and back margo of m. deltoideus According to Boychev-Chaklin, by Langenback’s incision Back medistinotomy, intercostal toracotomy !Which arteries form arterial ring of scapula? A.suprascapularis, a.circumflexa scapulae, r.profundus a.transversae colli #A.subscapularis, а.axillaris, а.thoracodorsalis, а.thoracica lateralis Truncus costocervicalis, a.thoracoacromialis, a. cervicalis dorsalis A. axillaries, a. circumflexa humeri posterior, r.profundus a.transversae colli !What goes through subcutaneous tissue of deltoid area? V.cephalica, n.n.supraclaviculares, n.cutaneus brachii lateralis superior, n.cutaneus brachii medialis #V. basilica, n.cutaneus brachii lateralis inferior, n.cutaneus brachii posterior, n.axillaris V.jugularis externa, n.accessorius, n.n.supraclaviculares, a.et v.cervicalis superficialis A.et v.suprascapularis, a.et v.subclavia, plexus brachialis !What is subdeltoid tissue space limited by? M.deltoideus, by capsule of shoulder joint #M.teres minor and m.teres major M.subscapularis and m.serratus anterior Chest and m.serratus anterior !What is situated in tissue of subdeltoid space? Sinews of muscles, synovial bursas, a. et v.circumflexae humeri anterior et posterior, n.axillaris #V.cephalica, n.n.supraclaviculares, n.cutaneus brachii lateralis superior, n.cutaneus brachii medialis V. basilica, n.cutaneus brachii lateralis inferior, n.cutaneus brachii posterior, n.axillaris Bursa subdeltoidea, bursa subacromialis, bursa subtendinea m.subscapularis, vagina synovialis intertubercularis !Which synovial bursas are situated in subteltoid space? Bursa subdeltoidea, bursa subacromialis, bursa subtendinea m.subscapularis, vagina synovialis intertubercularis #Bursa suprapatellaris, bursa infrapatellaris profunda, bursa subcutanea prepatellaris, recessus subpopliteus Bursa ischiadica m. glutei maximi, bursa trochanterica, bursa intermusculares m.m. gluteorum, bursa m. piriformis Vagina synovialis intertubercularis, bursa m.subscapularis subtendinea, recessus axillaris !Name the projection of nervovascular fascicle of subdeltoid space? Middle of back margo of m. deltoideus #Under acromion process Under coracoid process Middle of front margo of m. deltoideus !What is observed with patients with damage of n. axillaris? Atrophia of deltoid muscle, inability to bring shoulder up in frontal plane to horizontal level #Atrophia of big round muscle, inability to bring arm up higher than horizontal level, anesthesia of internal area of tissue Inability to extend hand and fingers, drophand, inability to abduct thumb, hand looks like “seal foot” Inability to flex IV and V fingers, inability to adduct IV and V fingers, hand looks like “clawhand” , fingers are extension loss, others are flexed. !Name the possible ways of pus spreading from subdeltoid space: Into inguinal fossa, infrascapula osseous- fibrous sheath, infraspinous and supraspinous fossas, back and front sheath of shoulder, subpectoral space #Into tissue space of lateral triangle of neck, into infraspinous osseous- fibrous sheath, into subdeltoid tissue space Into tissue of inguinal fossa, front prescapula gap, back prescapula gap Into supraspinous osseous- fibrous sheath formed, tissue of inguinal fossa, subdeltoid tissue space !Which incisions are used to open phlegmons of subdeltoid space? Incision along front and back margo of deltoid muscle #Paravertebral incision along the medial margo of scapula By incision along lateral margo of scapula By horizontal incision of Sozon-Yaroshevich !Name the weak places of capsole of shoulder joint: Vagina synovialis intertubercularis, bursa m.subscapularis subtendinea, recessus axillaris #Vagina synovialis intertubercularis, bursa subdeltoidea, bursa subacromialis Bursa suprapatellaris, bursa infrapatellaris profunda, bursa subcutanea prepatellaris, recessus subpopliteus Bursa ischiadica m. glutei maximi, bursa trochanterica, bursa intermusculares m.m. gluteorum, bursa m. piriformis !Name ligaments that strengthen shoulder joint: Lig.coracohumerale, lig.glenohumerale superius, lig.glenohumerale inferius, lig.glenohumerale medius #Lig.transversum scapulae, lig.coracoacromiale, lig. acromioclaviculare, lig. coracoclaviculare Lig.collaterale radiale, lig.collaterale ulnare, lig.anulare radii, lig.quadratum Lig.glenohumerale superius, lig.glenohumerale inferius !Which muscles strengthen shoulder joint from the front? M.subscapularis, m.coracobrachialis, caput breve m.biceps brachii, m.pectoralis major, m.deltoideus #M.supraspinatus, m.infraspinatus, m.teres minor M.deltoideus, m.pectoralis major M.teres major, m.latissimus dorsi, m.pectoralis major !Which muscles strengthen shoulder joint from the back? M.supraspinatus, m.infraspinatus, m.teres minor #M.subscapularis, m.coracobrachialis, caput breve m.biceps brachii, m.pectoralis major, m.deltoideus M.deltoideus, m.pectoralis major M.teres major, m.latissimus dorsi, m.pectoralis major !Which muscle strengthen shoulder joint externally? M.deltoideus #M.supraspinatus M.subscapularis M.teres major !Which arteries furnish circulation of shoulder joint? A.circumflexa humeri anterior, а.circumflexa humeri posterior, а.thoracoacromialis #A.thoracodorsalis, а.thoracica lateralis, а.axillaris, а.thoracoacromialis A.thoracica suprema, a.thoracica lateralis, a.subscapularis, a.circumflexa humeri anterior et posterior A.circumflexa scapulae, a.thoracodorsalis !What is shoulder joint innervated by? N.axillaris, n.suprascapularis #N.thoracodorsalis, n.n.supraclaviculares N.cutaneus brachii lateralis superior, n.cutaneus brachii medialis N.cutaneus brachii lateralis inferior, n.cutaneus brachii posterior !Name the external marks of the place of needle puncture when puncture of shoulder joint is done from the back: Under acromion, between back margo of deltoid muscle and lower margo of supraspinous muscle #Coracoid process of scapula, middle of back margo of deltoid muscle and lower margo of supraspinous muscle Along the lower margo of clavicula Down from acromion process !Name the external marks of the place of needle puncture when puncture of shoulder joint is done from the front: Coracoid process of scapula #Ander acromion, between back margo of deltoid muscle and lower margo of supraspinous muscle Down from acromion process Middle of front margo of deltoid muscle !Name the external marks of the place of needle puncture when puncture of shoulder joint is done from the side: Down from acromion process #Coracoid process of scapula Under deltoid muscle Towards tuber major ossis humeri !Name the direction of soft tissues cut for arterothomy of shoulder joint according to Langenbeck: From acromion process, along the front margo of deltoid muscle, along sulcus deltoideopectoralis #From coracoid process of scapula, along the external margo of deltoid muscle, along spina scapulae From acromion process, along external surface of deltoid muscle, along lateral margo of scapula Incision along front and back margo and deltoid muscle !Which muscles are splited up by hooks for arterothomy of shoulder joint according to Langenbeck? M.pectoralis major, m.deltoideus, caput breve et longum m.biceps brachii, m.coracobrachialis #M.teres major, m.latissimus dorsi, caput longum m.biceps brachii, m.coracobrachialis M.pectoralis major, m.pectoralis minor, m.deltoideus, m.subscapularis, m. brachialis M.pectoralis major, m.pectoralis minor !Which compartment of shoulder joint capsule is cut for arterothomy according to Langenbeck? Vagina synovialis intertubercularis #In the area of anatomical neck of humeral bone In the area of tuber minor ossis humeri In the area tuber major ossis humeri !What is front wall of cavum axillare formed by? M.pectoralis major, m.pectoralis minor #M.subscapularis, m.latissimus dorsi, m.teres major M.deltoideus, m.subscapularis M.pectoralis major, m.deltoideus, caput breve et longum m.biceps brachii, m.coracobrachialis !What is back wall of cavum axillare formed by? M.subscapularis, m.latissimus dorsi, m.teres major #M.pectoralis major, m.pectoralis minor Vagina synovialis intertubercularis Humeral bone, m.coracobrachialis, caput breve m.biceps brachii !What is medial wall of cavum axillare formed by? Side surface of chest, m.serratus anterior #Vagina synovialis intertubercularis Humeral bone, m.coracobrachialis, caput breve m.biceps brachii M.trapezius !What is lateral wall of cavum axillare formed by? Humeral bone, m.coracobrachialis, caput breve m.biceps brachii #M.pectoralis major, m.deltoideus, caput breve et longum m.biceps brachii, m.coracobrachialis M.subscapularis, m.latissimus dorsi, m.teres major Caput longum m.biceps brachii !Which triangles are projected to the front wall of axilla? Trigonum clavipectorale, trigonum pectorale, trigonum subpectorale #Trigonum omoclaviculare, trigonum omotrapezoideum, trigonum omotracheale Trigonum submandibularis, Pirogov’s triangle, scalenovertebral triangle Trigonum clavipectorale, Pirogov’s triangle !What is foramen quadrilaterum limited by from above? M.subscapularis, m.teres minor #M.teres major M.latissimus dorsi Caput longum m.triceps brachii !What is foramen quadrilaterum limited by from beneath? M.teres major #M.subscapularis, m.teres minor M.latissimus dorsi Caput longum m.triceps brachii !What is foramen quadrilaterum limited by laterally? By surgical neck of shouder #Caput longum m.triceps brachii M.subscapularis, m.teres minor M.brachialis !What is foramen quadrilaterum limited by medially? Caput longum m.triceps brachii #M.subscapularis M.teres major By surgical neck of shouder !What is foramen trilaterum limited by from above? M.subscapularis, m.teres minor #M.teres major M.latissimus dorsi M.deltoideus !What is foramen trilaterum limited by from laterally? Caput longum m.triceps brachii # By surgical neck of shouder M.coracobrachialis M.latissimus dorsi !What is foramen trilaterum limited by from beneath? M.teres major #M.teres minor Caput longum m.triceps brachii M.pectoralis major !Where is nervovascular fescical of axilla situated? Near interior margo of m. coracobrachialis #In sulcus bicipitalis medialis Between m.biceps brachii and m.brachialis In sulcus bicipitalis lateralis !What does go through the foramen trilaterum? A. et v.circumflexa scapulae #N.axillaris A. et v.circumflexae humeri posterior A. et v.circumflexae humeri anterior !What does go through the foramen quadrilaterum? A. et v.circumflexae humeri posterior, n.axillaris #A. et v.circumflexae humeri anterior, n.axillaris A. et v.circumflexae scapulae N.cutaneus brachii medialis !What is situated in trigonum subpectorale below, more medial and more superficial from a. axillaris? V.axillaris #N.medianus N.cutaneus brachii medialis N.ulnaris, n.cutaneus antebrachii medialis, n.cutaneus brachii medialis !What is situated in trigonum subpectorale more lateral from a. axillaris? N.musculocutaneus #V.axillaris N.radialis N.ulnaris !What is situated in trigonum subpectorale at the front of a. axillaris? N.medianus #V.axillaris N.ulnaris, n.cutaneus antebrachii medialis, n.cutaneus brachii medialis V.basilica !What is situated in trigonum subpectorale medially from a. axillaris? N.ulnaris, n.cutaneus antebrachii medialis, n.cutaneus brachii medialis #V.axillaris N.axillaris N.musculocutaneus !What is situated in trigonum subpectorale behind a. axillaris? N.axillaris, n.radialis #N.ulnaris, n.musculocutaneus N.cutaneus antebrachii posterior N.ulnaris, n.cutaneus antebrachii medialis, n.cutaneus brachii medialis !What arteries branch out of a. axillaris to trigonum subpectorale? A.circumflexa humeri anterior et posterior, a.subscapularis #A.thoracoacromialis, a.thoracica lateralis, a.circumflexa scapulae A.thyreoidea inferior, a.cervicalis ascendens, a.cervicalis superficialis, a.suprascapularis A.thoracica interna, a.vertebralis, a.transversa colli !Name the projecting line of a. axillaris: Along the front margo of hair growing, on the border between front and middle third of width of axilla #Through the middle of width of axilla On the border between middle and back third of width of axilla From the point situated on the border between front and middle third of width of axilla, to the middle of antecubital fossa !Where is the incision made to expose a. axilaris? 1 cm in front of projecting line, through vagina of m. coracobrachialis #Along projecting line, between m. coracobrachialis and m. biceps brachii In the middle of distance between m. pectoralis major and m. latissimus dorsi Behind projection line of a. axillaris !Where is the incision done for phlegmona of axilla? Behind projection line of a. axillaris, in the middle of distance between m. pectoralis major and m. latissimus dorsi #Along projectional line of a. axillaris In the middle of distance between m. pectoralis major and m. latissimus dorsi 1 cm in front of projecting line, through vagina of m. coracobrachialis !Which incisions are made to open pyogenic abscess in axilla according to Voyno-Yasentsky? Supraclavicular, infraclavicular, axillar #From acromion process, along front margo of deltoid muscle, along sulcus deltoideopectoralis From coracoid process of scapula, along back margo of deltoid muscle, along spina scapulae Incision along front and back margo of deltoid muscle !Which nerves branch out of back fascicle of brachial plexus? N.axillaris, n.radialis #N.ulnaris, n.cutaneus antebrachii medialis, n.cutaneus brachii medialis N.musculocutaneus, part of n.medianus N.cutaneus brachii medialis !Which nerves branch out of lateral fascicle of brachial plexus? N.musculocutaneus, part of n.medianus #N.ulnaris, n.cutaneus brachii medialis, n .cutaneus antebrachii medialis, part of n.medianus N.axillaris, n.radialis N.radialis !Which nerves branch out of medial fascicle of brachial plexus? N.ulnaris, n.cutaneus brachii medialis, n .cutaneus antebrachii medialis, part of n.medianus #N.musculocutaneus, part of n.medianus N.radialis N.axillaris !Name branches of a. axillaris: A.thoracica suprema, a.thoracica lateralis, a.thoracoacromialis, a.subscapularis, a.circumflexa humeri anterior et posterior #A.circumflexa scapulae, a.thoracodorsalis A.thoracoacromialis, a.thoracica lateralis, a.circumflexa scapulae A.thyreoidea inferior, a.cervicalis ascendens, a.cervicalis superficialis, a.suprascapularis !What artery is important for development of collateral circulation when occlusion of a. axillaris happens? A.subscapularis #A.thoracoacromialis A.circumflexa scapulae A.thoracodorsalis !Where is better to legate a. axillaris? Above the origin of a. subscapularis #Below the origin of a. subscapularis Above the origin of a. thoracodorsalis Above the origin of a. circumflexa scapulae