* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Recall Last Lecture
Power inverter wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Ground loop (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Signal-flow graph wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative circuit wikipedia , lookup
Integrating ADC wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Voltage regulator wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Wien bridge oscillator wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Two-port network wikipedia , lookup
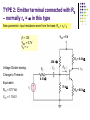
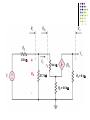
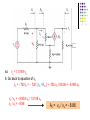
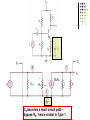
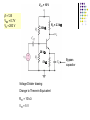
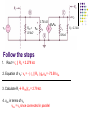
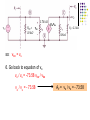
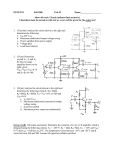
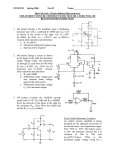
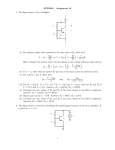
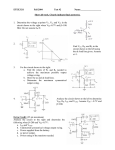
Recall Last Lecture Introduction to BJT Amplifier Small signal or AC equivalent circuit parameters Have to calculate the DC collector current by performing DC analysis first Common Emitter-Emitter Grounded TYPE 2: Emitter terminal connected with RE – normally ro = in this type New parameter: input resistance seen from the base, Rib = vb / ib β = 120 VBE = 0.7V VA = VCC = 5 V RC = 5.6 k 250 k Voltage Divider biasing: Change to Thevenin 0.5 k Equivalent RTH = 57.7 k VTH = 1.154 V 75 k RE = 0.6 k Perform DC analysis to obtain the value of IC BE loop: 57.7 IB + 0.7 + 0.6 IE – 1.154 = 0 IE = 121 IB 57.7 IB + 0.7 + 0.6 (121IB) – 1.154 = 0 IB = 0.454 / (72.6 + 57.7) = 0.00348 mA IC = βIB = 0.4176 mA Calculate the small-signal parameters r = 7.46 k , ro = and gm = 16.06 mA/V 0.5 k + 7.46 k vb 57.7 k RC = 6 k RE = 0.6 k - STEPS OUTPUT SIDE 1. Get the equivalent resistance at the output side, ROUT 2. Get the vo equation where vo = - ib ROUT INPUT SIDE 3. Calculate Rib = vb / ib : KVL at loop (extra step) 4. Calculate Ri 5. Get vb in terms of vs – eg: using voltage divider. 6. Go back to vo equation and calculate the voltage gain 1. Rout = RC = 6 k 2. Equation of vo : vo = - ib RC = - 720 ib 3. Calculate Rib using KVL: ib r + ie RE - vb = 0 but ie = (1+ ) ib = 121 ib so: ib [ 121(0.6) + 7.46 ] = vb Rib = 80.06 k 4. Calculate Ri RTH||Rib = 33.53 k 5. vb in terms of vs use voltage divider: vb = [ Ri / ( Ri + Rs )] * vs = 0.9853 vs vs = 1.0149 vb so: vs = 1.0149 vb 6. Go back to equation of vo vo = - 720 ib = - 720 [ vb / Rib ] = -720 vb / 80.06 = - 8.993 vb vo / vs = - 8.993 vb / 1.0149 vb vo / vs = - 8.86 AV = vo / vs = - 8.86 Current Gain RS = 0.5 k vs Ri = 33.53 k RC = 6k Output side: io = vo / RC = vo / 6 Input side: ii = vs / (RS + Ri ) = vS / 33.53 Current gain = io / ii = vo (33.53) = -8.86 * 5.588 vs (6) = - 49.5 TYPE 3: With Emitter Bypass Capacitor, CE Circuit with Emitter Bypass Capacitor ● There may be times when the emitter resistor must be large for the purpose of DC design, but degrades the small-signal gain too severely. ● An emitter bypass capacitor can be used to effectively create a short circuit path during AC analysis hence avoiding the effect RE vO vS RTH vbe gmvbe CE becomes a short circuit path – bypass RE; hence similar to Type 1 RC VCC = 10 V β = 125 VBE = 0.7V VA = 200 V 20 k RC = 2.3 k 20 k 5 k Voltage Divider biasing: Change to Thevenin Equivalent RTH = 10 k VTH = 5 V Bypass capacitor β = 125 VBE = 0.7V VA = 200 V Perform DC analysis to obtain the value of IC BE loop: 10 IB + 0.7 + 5 IE – 5 = 0 IE = 126 IB 10 IB + 0.7 + 5 (126 IB) – 5 = 0 IB = 1.8 / (10 + 630) = 0.00672mA IC = βIB = 0.84 mA Calculate the small-signal parameters r = 3.87 k , ro = 238 k and gm = 32.3 mA/V 3.74 k vS RTH = vbe 10 k vO gmvbe Follow the steps 1. Rout = ro || RC = 2.278 k 2. Equation of vo : vo = - ( ro || RC ) gmvbe= -73.58 vbe 3. Calculate Ri RTH||r = 2.79 k 4. vbe in terms of vs vbe = vs since connected in parallel RC = 2.3 k 238 k 3.74 k RTH = vbe 10 k vS vO gmvbe RC = 2.3 k 238 k so: vbe = vs 6. Go back to equation of vo vo / vs = -73.58 vbe / vbe vo / vs = - 73.58 AV = vo / vs = - 73.58 Current Gain vs Ri = 2.79 k Output side: io = vo / RC = vo / 2.3 Input side: ii = vs / Ri = vS / ( 2.79) Current gain = io / ii = vo (2.79) = -73.58 * 1.213 vs (2.3) = - 89.25 RC = 2.3 k