* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
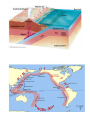
12th grade – APRIL 22, 2016 *all late/makeup work & corrections must be completed before April 29 for credit. Math tests are MONDAYS Science tests are FRIDAYS Quizzes are any days TESTS may need to be moved if we are not quite ready… but that is the exception. You need to check the weebly every night BEFORE you start your HW!!!!! PHYSICAL SCIENCE **TAKE NOTES IN YOUR SCIENCE SPIRAL CH 26 RQ 1-10 REVIEW QUESTIONS 1. How do P-waves travel through Earth’s interior? P-waves are longitudinal; they compress and expand rock as they move through it. P-waves can travel through any type of material—solid, liquid, or gas. They are the fastest of all seismic waves and the first to register on a seismograph. 2. How do S-waves travel through Earth’s interior? S-waves are transverse—they vibrate the particles of their medium up and down and side-to-side. S-waves can travel only through solids. They are the second to register on a seismograph. 3. Can S-waves travel through liquids? No. S-waves can travel only through solids. 4. Name the two types of surface waves and describe the motion of each. Rayleigh waves and Love waves. Rayleigh waves move in an up-and-down, rolling motion. Love waves move in a side-toside, whip like motion. Both of these surface-waves travel at lower speeds than P- and S-waves and so are the last to register on a seismograph. 5. What was Andrija Mohorovicic’s major contribution to Earth science? Mohorovicic discovered the crust-mantle boundary. 6. How did seismic waves contribute to the discovery of Earth’s core? Both P- and S-waves are strongly refracted at the core-mantle boundary, causing a wave shadow. The reflection and refraction of P-waves through the core identified the solid inner core. 7. What is the evidence that Earth’s inner core is solid? The reflection and refraction of P-waves through the core identified the solid inner core. 8. What is the evidence that Earth’s outer core is liquid? S-waves cannot travel through liquids. The presence of the Swave shadow—no S-waves are found in this zone—indicates that the outer core is liquid. 9. In what ways are the asthenosphere and the lithosphere different from each other? The upper mantle, extending from the crust-mantle boundary down to a depth of about 700 kilometers, has two zones: The lower zone is the plastic-like asthenosphere, which flows due to convection. The upper zone (above the asthenosphere) is the lithosphere. The lithosphere includes the entire crust and the uppermost part of the mantle. It is relatively rigid and brittle and resists deformation. The mobile lithosphere is, in a sense, floating on top of the asthenosphere. 10. How does continental crust differ from oceanic crust? They differ in density, composition, and thickness. Oceanic crust is thin and compact (about 10 km thick) and composed of dense basaltic rocks. Continental crust is between 20 and 60 kilometers thick and composed of less dense granitic rocks. 11. Why does continental crust stand higher on the mantle than oceanic crust? The continental crust stands higher than oceanic crust because it is less dense. 12. What happens to rock when stress exceeds a rock’s elastic limit? Rocks are an elastic material—they can return to their original form after the imposed stress is removed. However, when stress exceeds the rock’s elastic limit, the rock permanently loses its original form. The rock either breaks— brittle deformation, or it flows—plastic deformation. 13. Are folded rocks primarily the result of compressional or tensional forces? Compressional force. 14. Distinguish between anticlines and synclines. An anticline folds upward like an arch. The rocks in the core of an anticline are the oldest, and as you move horizontally away from the axis, the rocks get younger. A syncline folds downward—it sags. The rocks in the core of a syncline are the youngest, and as you move horizontally away from the axis, the rocks get older. 15. What is the difference between reverse faults and normal faults? Reverse faults are created by compressional forces. The hanging wall is pushed upward along the fault plane relative to the footwall. Normal faults are created by tensional forces. The hanging wall drops downward along the fault plane relative to the footwall. 16. Which kind of fault forms primarily from tension in Earth’s crust? Primarily from compression? Tension creates normal faults. Compression creates reverse faults. 17. Where does most of an earthquake’s damage generally occur? The focus is the point where the rock actually breaks. Directly above the focus is the epicenter. The epicenter is the point on Earth’s surface where most of the earthquakes energy does its damage. 18. Where do most of the world’s earthquakes occur? Most earthquakes (about 80%) are found in the area of the Pacific Rim that encircles the Pacific Ocean. 19. What device do scientists use to measure an earthquake? Ground movement is recorded on a machine called a seismograph (seismometer). Charles Richter used seismograph data to develop a magnitude scale to quantify the amount of energy released by an earthquake. So, the magnitude scale is used to measure an earthquakes size and amount of energy released; and the Mercalli intensity scale measures the earthquakes degree of damage on the local environment. 20. What is the source of a tsunami’s huge amount of energy? A massive underwater disturbance, such as an earthquake, a volcanic eruption, an underwater landslide, or an explosion. BANDA ACEH EARTHQUAKE & TSUNAMI: ================================================ http://www.conceptualacademy.com/textbook/conceptual-physical-science I HAVE SOME HW 4 U 4/19 HW = RATS READINESS ASSURANCE TEST (RAT) 1a, 2d, 3a, 4b, 5c, 6b, 7d, 8b, 9d, 10b Grade: write corr letter then tonite go and write the corr words… Any rats questions? 9…page 625 2…d…page 617…our little mouse… More elastic rocks = More speed waves 3…a…page 624 fig 26.9 5…c…page 618 p3 ‘primary waves’ are the fastest…first to reach the seismograph… 6…b…page 627 last parag… Page 629 first 3 parag Friday – review for test on Monday 9. In what ways are the asthenosphere and the lithosphere different from each other? The upper mantle, extending from the crust-mantle boundary down to a depth of about 700 kilometers, has two zones: The lower zone is the plastic-like asthenosphere, which flows due to convection. The upper zone (above the asthenosphere) is the lithosphere. The lithosphere includes the entire crust and the uppermost part of the mantle. It is relatively rigid and brittle and resists deformation. The mobile lithosphere is, in a sense, floating on top of the asthenosphere. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=fArB5Jz2wos#t=691.641 PreCalculus Glogs due Monday…ELSE = 0…BEGINNING MARCH 14, 2016. HW WAS: WS FRAC & DEC Turn this in now to me… Remember – FOR ALL CLASSES – to note every 30 minutes!!! option 1 = do 30 min on each class hw - start with math then you must move on to another class…then come back if you need to… option 2 = there is no option 2. YOU NEED TO SET A TIMER FOR 30 MIN. Precalc = 4/19 = cw = hw = ws “EVALUATING FUNCTIONS” not a boring ws and yet your must do it!! You must SAW for each problem in your spiral…no work = no credit. No help at all except textbook & calculator. Precalc = 4/20 = hw = order of operations worksheet = = saw No help at all except textbook & calculator. Precalc = 4/21 = hw = fractions & decimals worksheet = = saw No help at all except textbook & calculator. ====================================== OTHER 12th grade HW IS LISTED BELOW: LIT = LONE RANGER & TONTO = READ CH & GIVE RESPONSE ON WEEBLY TONIGHT US HISTORY = read ch 24c RELIGION = pray & rice box ECON = STUDY VOCAB … watch video and take notes Spanish – SPANISH AUTHOR PROJECT = ½ OF FINAL EXAM SEE ABOVE FILE FOR MATH AND SCIENCE!!! Science = test Monday ch 26 Math = ws linear equations do all saw MATEO SAYS: DO ALL OF YOUR HW AND DO IT WELL!!!