* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Lesson 2 Beginning of exploration (SEARCH)
Nanban trade wikipedia , lookup
Spanish expeditions to the Pacific Northwest wikipedia , lookup
Voyages of Christopher Columbus wikipedia , lookup
Portuguese India wikipedia , lookup
European maritime exploration of Australia wikipedia , lookup
Conquistador wikipedia , lookup
Portuguese India Armadas wikipedia , lookup
Portuguese discoveries wikipedia , lookup
History of Portugal (1415–1578) wikipedia , lookup
Treaty of Tordesillas wikipedia , lookup
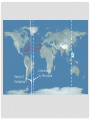
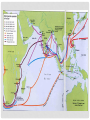
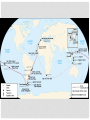
UNIT 3 AGE OF EXPLORATION LESSON 2 BEGINNING OF EXPLORATION (SEARCH) LESSON 2 BEGINNING OF EXPLORATION (SEARCH) Learning Target Students can explain the series of cause and effect events leading to European Exploration LESSON 2 BEGINNING OF EXPLORATION (SEARCH) Introduction and Background During the 1300s and 1400s, Arab merchants bought goods like silks and spices in China and India. Then they carried these goods overland to the eastern end of the Mediterranean Sea. There, they loaded the goods on Italian ships and sold them to the Italian city-states The overland journey was slow and hard. But once on the sea, the journey was fast and easy. Soon, the goods arrived in the Italian city-states. Then Italian merchants sold the goods at high prices to other European states. Italian city-states like Venice grew wealthy from the eastern trade. For many years, these city-states controlled the trade routes to the East. But other countries wanted to become wealthy too. So they began to look for new trade routes. During the 1400s, Portugal began its SEARCH. LESSON 2 BEGINNING OF EXPLORATION (SEARCH) S – Starts with the Portuguese • Bartholomew Dias sailed around the southern tip of Africa to find a new route to India and China • The west coast of Africa was called the “gold coast” and the southern tip was named the “Cape of Good Hope” • Led to the trade in the east for slaves, gold, and spices • This route was dangerous and was very time consuming LESSON 2 BEGINNING OF EXPLORATION (SEARCH) E – Eventually the Spanish begin exploring • Christopher Columbus believed he knew a better way to reach Asia • In 1492, Columbus convinced King Ferdinand and Queen Isabella of Spain to finance his voyage • Columbus thought he had reached the East Indies islands (he had actually reached the Caribbean islands) LESSON 2 BEGINNING OF EXPLORATION (SEARCH) A – A line of Demarcation is created • In the 1450’s the pope had given control to Portugal over all African trade and exploration • In 1493, the pope drew a line down a map and divided the world into two parts • The Portuguese demanded the line be moved(Treaty of Tordesillas) • Spain controlled all the lands to the west • Portugal controlled all the lands to the east Treaty of Tordesillas Line drawn by the pope LESSON 2 BEGINNING OF EXPLORATION (SEARCH) R – A Route to India is found • Portugal still wanted to reach India by sailing south and eastward • In 1497, Vasco da Gama rounded the Cape of Good Hope and reached India • Da Gama’s ships returned full of spices, jewels, and other goods • He sold his goods for 1000’s % profit LESSON 2 BEGINNING OF EXPLORATION (SEARCH) C – Control of the East Indies • The Portuguese controlled the spice trade in the East Indies • As years passed they traded with China and Japan (Asians feared westernization) • However they did not trust the Europeans and would only allow limited access to the country • Eventually the Dutch, French, and English joined the Portuguese in establishing trading companies in the East LESSON 2 BEGINNING OF EXPLORATION (SEARCH) H – Hope of Circumnavigation • Ferdinand Magellan set sail to find a western route to India that Columbus had failed to find • Set sail with five ships and 265 men • Explored the coast of South America, across the Pacific Ocean, to the Philippines, and back via South Africa • Three year voyage, I ship remained with 18 sailors who had circumnavigated the globe