* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Analysis and Simulation of Bus Loading conditions on Voltage Sag
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
History of electromagnetic theory wikipedia , lookup
Ground (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Public address system wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
War of the currents wikipedia , lookup
Electric power system wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Electric machine wikipedia , lookup
Wireless power transfer wikipedia , lookup
Distributed generation wikipedia , lookup
Distribution management system wikipedia , lookup
Hendrik Wade Bode wikipedia , lookup
Control system wikipedia , lookup
Anastasios Venetsanopoulos wikipedia , lookup
Electric motorsport wikipedia , lookup
Amtrak's 25 Hz traction power system wikipedia , lookup
General Electric wikipedia , lookup
Electrification wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Telecommunications engineering wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Power engineering wikipedia , lookup
Electrical engineering wikipedia , lookup
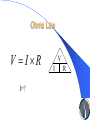
AEEE 170– Freshman Electrical Engineering Programme of Studies:BSc in Electrical Engineering Entrance requirements: None Number of ECTS credits:5 (Average student working time: 125 hours) Lecturer: Dr. Alexis Polycarpou, Frederick University, Cyprus Telecommunications Telecommunication is the transmission of messages, over significant distances. In the modern age, telecommunications has typically involved the use of electric means such as the telegraph, thetelephone, and the teletype, the use of fiber optics and their associated electronics, and/or the use of the internet.. These systems of communications all required the use of conducting metal wires Control Systems Engineering Applies control theory to design systems with predictable behaviors. The practice uses sensors to obtain measurements used to give feedback to the input actuators that can make corrections toward desired performance When a device is designed to perform without the need of human inputs for correction it is called automatic control. Electronics Engineering Uses the scientific knowledge of the behavior and effects of electrons to develop components, devices, systems, or equipment Power Engineering Deals with the generation, transmission and distribution of electric power as well as the electrical devices connected to such systems including generators, motors and transformers. Concerned with the problems of three-phase AC power and conversion between AC and DC power as well as the development of specialized power systems such as those used in aircraft or for electric railway networks. Basic Quantities Voltage is a representation of the electric potential energy per unit charge.. In other words, it is a measurement of the energy contained within an electric field, or an electric circuit, at a given point Electrical current is a measure of the amount of electrical charge transferred per unit time. It represents the flow of electrons through a conductive material. Electrical resistance of an object is a measure of its opposition to the passage of a steady electric current. An object of uniform cross section will have a resistance proportional to its length and inversely proportional to its cross-sectional area, and proportional to the resistivity of the material. Prefixes: Number Prefix Symbol 10 -1 deci- 10 -2 centi- c 10 -3 milli- 10 -6 micro- 10 -9 nano- n 10 -12 pico- 10 -15 femto- f 10 -18 atto- 10 -21 zepto- z 10 -24 yocto- y d m p a Rarely used Number Prefix Symbol 10 1 deka- da 10 2 hecto- h 10 3 kilo- 10 6 mega- M 10 9 giga- G 10 12 tera- T 10 15 peta- P 10 18 exa- E 10 21 zeta- Z 10 24 yotta- Y k Ohms Law V I R I=? V I R Questions?