* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Preview of Period 3: Electromagnetic Waves – Radiant Energy II
Retroreflector wikipedia , lookup
Thomas Young (scientist) wikipedia , lookup
Photonic laser thruster wikipedia , lookup
Photoacoustic effect wikipedia , lookup
Rutherford backscattering spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
Ultrafast laser spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Nonlinear optics wikipedia , lookup
X-ray fluorescence wikipedia , lookup
Upconverting nanoparticles wikipedia , lookup
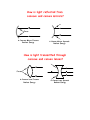
Preview of Period 3: Electromagnetic Waves – Radiant Energy II 3.1 Radiant Energy from the Sun How is light reflected and transmitted? What is polarized light? 3.2 Energy Transfer with Radiant Energy How can electromagnetic waves transfer energy and information? 3.3 Radio and Television Broadcasts What is the difference between AM and FM broadcasts? 3-1 Solar Cells and the Photoelectric Effect Solar cells use the photoelectric effect to produce electricity. ♦ When electrons absorb photons of electromagnetic radiation, some electrons have enough energy to escape from their atom and form an electric current. ♦ Only photons with wavelengths equal to or shorter than visible light have enough energy per photon to produce a current. 3-3 Activity 3.1.d: Mirrors and Lenses How does light reflect off of a plane mirror? Light box Mirror ♦ Place a sheet of white paper under the mirror. ♦ Mark the position of the mirror on the paper with a straight line. ♦ Draw lines on the paper showing the path of the light beams at they strike the mirror and reflect off the mirror. ♦ Use a protractor to compare the angle of incidence and the angle of reflection of light striking a mirror. ♦ How are these angles related? How is light reflected from concave and convex mirrors? Focus A Concave Mirror Focuses Radiant Energy A Convex Mirror Spreads Radiant Energy How is light transmitted through concave and convex lenses? Focus A Concave Lens Focuses Radiant Energy A Convex Lens Spreads Radiant Energy An Atom Flourescing Fluorescence is the absorption of radiant energy and the re-emission of radiant energy at longer wavelengths. Photon 1 Electron Nucleus Time 1: An ultraviolet light photon is absorbed by an electron. Photon 2 Time 3: The electron drops down one one energy level and emits one photon of visible light. Time 2: The electron moves up two energy levels. Photon 3 Time 4: The electron drops down one more energy level and emits a second photon. 3-6 Information Transfer Communication is the transfer of information Transferring information requires ….. ♦ a source of information (a person or device) ♦ a signal (the information) ♦ a receiver ♦ modulation (changing) of the signal Encoding Information ♦ Information must be encoded for transfer. ♦ Encoding modulates the signal in a way meaningful to the sender and receiver. ♦ Examples of encoded information: Spoken and written language Computer languages Sign language Morse Code 3-7 Signal to Noise ratio SNR = average energy in the signal average energy in the noise A large signal to noise ratio is better (Example) If the average energy in the noise of a signal is 250 joules and the average energy in the signal is 750, what is the signal to noise ratio? SNR = average energy in the signal = 750 J = 3 average energy in the noise 250 J 3-8 Total Internal Reflection of Light in an Optical Fiber Lower Index of Refraction Higher Index of Refraction Wire Many of these optical fibers are combined into a cable. Electromagnetic Radiation Traveling in a Coaxial Cable Electromagnetic Radiation Coaxial Cable Central Wire Metal Sheath 3-9 Information Transfer Radio and TV broadcasts use a carrier wave that is modulated to encode information. ♦ AM modulates the amplitude (the height) of the carrier wave. ♦ FM modulates the frequency of the carrier wave. Amplitude Modulation – AM Radio AM radio operates on the principle of encoding by modulating the amplitude of the carrier wave. Figure 3.6 illustrates a carrier wave whose amplitude has been modulated to encode the signal of a complex sound wave. Amplitude Modulation Frequency Modulation