* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Energy - Riverside Local Schools
Potential energy wikipedia , lookup
Efficient energy use wikipedia , lookup
Kinetic energy wikipedia , lookup
William Flynn Martin wikipedia , lookup
Open energy system models wikipedia , lookup
Energy subsidies wikipedia , lookup
100% renewable energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy storage wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative brake wikipedia , lookup
Low-Income Home Energy Assistance Program wikipedia , lookup
Public schemes for energy efficient refurbishment wikipedia , lookup
Zero-energy building wikipedia , lookup
World energy consumption wikipedia , lookup
Low-carbon economy wikipedia , lookup
Energy Charter Treaty wikipedia , lookup
Alternative energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of Australia wikipedia , lookup
Internal energy wikipedia , lookup
International Energy Agency wikipedia , lookup
Energy returned on energy invested wikipedia , lookup
Distributed generation wikipedia , lookup
Energy efficiency in transport wikipedia , lookup
Energy harvesting wikipedia , lookup
Life-cycle greenhouse-gas emissions of energy sources wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of Finland wikipedia , lookup
Conservation of energy wikipedia , lookup
Negawatt power wikipedia , lookup
Energy in the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of the European Union wikipedia , lookup
United States energy law wikipedia , lookup
Energy efficiency in British housing wikipedia , lookup
Energy Independence and Security Act of 2007 wikipedia , lookup
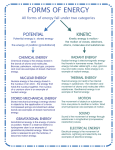
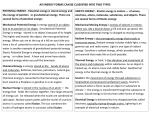
Instructions With your partner, sort the cards on your lab table into groups based on the idea of “energy”. You may have as many or as few groups as you like. Be able to explain your reasoning for the groups. Each group must contain more than one card. All the cards must be used. Record which cards you placed in which groups on a piece of paper! Instructions: Part 2 With your partner, re-sort the cards on your lab table into groups based on the seven types of energy. Use the definitions below to help you sort the cards. All cards must be used. Mechanical Energy: related to the movement of an object or its position in gravity. Sound Energy: Energy that travels in waves through a substance (solid, liquid, or gas). Chemical Energy: related to the potential energy stored in the bonds between atoms in a molecule. Radiant (Light) Energy: Electromagnetic energy traveling in waves. Electrical Energy: related to the movement or flow of electrons. Thermal (Heat) Energy: related to the motion of atoms or molecules in a substance. Nuclear Energy: energy stored within the nucleus of an atom. Introduction to Energy Types of Energy: A. Potential Energy: Energy due to position. 1. Chemical Energy: The energy stored in the bonds between atoms in a molecule. 1. Examples: food, gas 2. Gravitational Energy: The stored energy in an object due to its height. (Higher objects=more energy) 3. Nuclear Energy: Energy stored within the nucleus of an atom. When a nucleus in an atom splits (fission), this energy is released. Introduction to Energy Types of Energy: B. Kinetic Energy: Energy due to motion. 1. Electrical Energy: Energy from the flow or movement of electrons. 2. Radiant Energy: Electromagnetic energy that travels in waves. Examples: light, radio waves, x-rays… 3. Thermal Energy: Energy from the motion of atoms or molecules in a substance. =Heat. 4. Sound Energy: Energy that travels in waves through a substance (solid, liquid, or gas). Introduction to Energy Law of Conservation of Energy: Energy cannot be created or destroyed, it can only change form. Examples: Radiant Energy Chemical Energy Kinetic Energy (Sun) (Plants-food) (running to class) Chemical Energy Thermal Energy Radiant Energy (Wood) (Heat from fire) (Light from fire) Chemical Energy Electrical Energy Thermal Energy (Coal) (Electricity) (Heat from stove)