* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
Eradication of infectious diseases wikipedia , lookup
Maternal physiological changes in pregnancy wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Hygiene hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Epidemiology of metabolic syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Fetal origins hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Epidemiology wikipedia , lookup
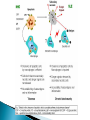
Naomi Sen Aim ◦ To give an outline of the diagnosis and management of SLE Objectives ◦ To describe signs and symptoms of SLE ◦ To outline relevant investigations ◦ To describe management of SLE Pathogenesis Epidemiology and risk factors Presentation Investigations Associated illnesses Management Pregnancy and fertility Prognosis Summary SLE is a heterogeneous, inflammatory, multisystem autoimmune disease in which antinuclear antibodies occur. heterogeneous, inflammatory, multisystem autoimmune disease in which antinuclear antibodies occur. SLE is a Failure to clear apopetic material efficiently Anti-Ro and Anti–La widespread vasculitis Prevalence : 50-100/100000 Peak onset 20-40y Female : Male 9:1 Chinese, Southeast Asian (1 in 1000) and Afro-Caribbean (1 in 500) most common Least common in Northern European origin (1 in 2800) Genetic ◦ HLA-B8 and DR3 in caucasians, (DR2 in Japanese) Complement ◦ Defective C4 gene Environmental ◦ EBV ◦ UV light ◦ Drugs: Chlorpromazine Methyldopa Hyrdalazine Isoniazid d-penicillamine Minocycline Relapsing and remitting Non-specific ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ Fatigue Malaise Arthralgia Lymphadenopathy Fever Joints and Muscles ◦ Most common clinical feature ◦ Symmetrical small joint arthralgia Clinically normal examination Skin ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ Butterfly erythema Vasculitic lesions on fingertips and nail folds Purpura and urticaria 1/3 - photosensitivity Lungs ◦ Pleurisy ◦ Recurrent pleural effusions (exudate) Cardiovascular Pericarditis Mild myocarditis =/- arrhythmias Raynaud’s Arterial and venous thromboembolism – antiphospholipid syndrome ◦ Atherosclerotic disease ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ Kidneys ◦ glomerulonephritis CNS ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ Depression Epilepsy Migraine Hemiplegia Ataxia Psychosis Demyelinating syndromes Eyes ◦ Retinal vasculitis hard exudates and haemorrhages ◦ Episcleritis/conjunctivitis/optic neuritis GI ◦ Mouth ulcers ◦ Abdominal pain – mesenteric vasculitis inflammation perforation or infarction DOPAMINE RASH – 4 out of 11 ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ Discoid Rash Oral Ulcers Photosensitivity Arthritis Malar rash Immunological – anti ro, la, smith, dsDNA Neurological changes Elevated ESR Renal involvement ANA +ve Serositis (plurisy and pericarditis) Haematological (haemolytic anaemia, ↓WCC↓plt) Bloods ◦ FBC Leucopenia/ Lymphopenia Thrombocytopenia Anameia –AI haemolysis ◦ ESR Raised, CRP normal ◦ ANA Positive ◦ RF +ve – 25% ◦ Complement levels Reduced ◦ Antiphospholipid antibodies Anticardiolipn Anti B2-glycoprotein Lupus anticoagulant ◦ Immunoglobulins Raised Polyclonal IgG and IgM Histology ◦ Skin biopsies ◦ Renal biopsies Imaging ◦ CT ◦ MRI Antiphospholipid syndrome Overlap syndromes: scleroderma, polymyositis, rheumatoid arthritis and Sjögren's syndrome Prone to other autoimmune conditions such as thyroiditis Higher incidence of drug allergy Increased risk of infection Increased risk atherosclerosis, hypertension, dyslipidaemias, diabetes, osteoporosis, avascular necrosis and malignancies (especially nonHodgkin's lymphoma) Individual counselling Avoid sun exposure , use sunscreen Analgesia – caution with NSAIDs Corticosteroids – effecitive – but s/e Hydroxychloroquine Cyclphosphamide – life threatening Azothioprine – steroid sparing Methotrexate Barrier methods of contraception -safest Oestrogens can exacerbate lupus Lowest dose COCP can be used with caution if no ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ Migraines Thrombosis Hypertension Anticardiolipin antibodies are negative Increased risk of thrombosis – needs to be counselled. Fertility is normal Pregnancy is safe in mild or stable disease In severe lupus – disease should be controlled prior to pregnancy Morbidity - ↑if antiphospholipid antibodies ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ Recurrent miscarriage Pre-eclampsia IUGR Premature delivery Thrombosis Worsening or renal disease and hypertension LMWH and low dose aspirin treatment of choice Improved with earlier recognition and improved management. ◦ Morbidity and mortality – higher in patients with extensive multisystem disease and multiple auto antibodies ◦ Renal involvement poorer prognosis ◦ Drug induced lupus usually subsides when the drug is discontinued. heterogeneous, inflammatory, multisystem autoimmune disease in which antinuclear antibodies occur. SLE is a More common in females in their 20-40s More common in Asian and Afro-Caribbean populations Relapsing remitting Diagnosis – 4 out of 11 “DOPAMINE RASH” Multiple systems – most common – joint pain Initial investigations – Bloods - FBC, ESR, CRP, Complement, ANA, RF, Immunoglobulins, Antiphospholipid antibodies Management ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ Individual Sunscreen Analgesia Steroids and immunosuppression if severe Contraception if severe Barrier – fewer risks than hormonal ◦ If antiphospholipid LMWH and aspirin in pregnancy www.patient.co.uk Kumar and Clarke Also Wikipedia and Dr Google!