* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Powerpoint file (2 slides per page)
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
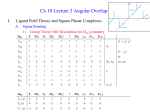
Isomerism & Crystal Field Theory Chapter 24 – Lecture 3 Chemistry 123 Spring 2008 Dr. Woodward Isomers Different ligands make bonds to the metal Ligands bond to the metal through different atoms Ligands have different (ligand) neighbors Molecules are nonsuperimposable mirror images 1 Linkage Isomers Geometric Isomers 2 Optical Isomers IntraIntra-atomic (d to d) excitations MnSO4 FeSO4 CoSO4 NiSO4 CuSO4 ZnSO4 In these complexes the color comes from absorption of light that leads to excitation of an electron from one d-orbital to a different d-orbital on the same metal cation. 3 [M(H2O)6]n+ Complex ions M MO6 Octahedron Crystal Field Splitting (Octahedron) dz2 & dx dx2-y2 orbitals (e (eg) Energy H2O • Point directly at the ligands • Stronger (repulsive) interaction with the ligands dxy, xy, dyz & dxz orbitals (t2g) dz2 dx2-y2 dyz dxz • Point between the ligands • Weaker (repulsive) interaction with the ligands dxy Electrons in d-orbitals are repelled from the electrons in the ligands. The repulsion is stronger for electrons in d-orbitals pointing directly at the ligands. 4 Energy Levels of d-orbitals in an octahedron Energy dz2 Δ dxy dyz dxz dz2 dx2x2-y2 Cr3+ ion with a spherical crystal field dxy dx2x2-y2 dyz dxz dz2 dxy dyz dxz Cr3+ ion in an octahedral crystal field dx2x2-y2 Free Cr3+ ion Energy Electronic Excitation dx2-y2 dz2 dx2-y2 dz2 eg Δ = Crystal Field Splitting Energy light (photon) t2g dxy dyz dxz dxy dyz dxz 5 [Cr3+(H2O)6]3+ Absorption Spectra Antibonding (σ*) Metal-Ligand MO’s 0.6 0.5 Absorbance 0.4 Δoct 0.3 0.2 Nonbonding Metal d MO’s 0.1 0.0 250 300 350 400 450 500 550 600 650 700 750 Wavelength (nm) 6