* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Key review sheet
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Atrial septal defect wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
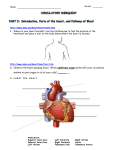
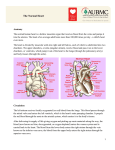
Unit 4: heart, circulation, blood pressure review page 1 1. a. Name: Your heart is the size of --. a. a grown man's fist Unit 4: the heart review Roster # Date: b. 2007 your fist 2. True/ False The apex of the heart rests on the diaphragm at the level of the 5th intercostal space 3. True/ false the top of the heart is located at the angle of Louis 4. True /false 2/3rd of the heart is located just to the right of the midline of the sternum 5. True /false the heart rests on its side , rather than on its apex 6. True /false blood never leaves the circulation; only substances carried in the blood enter and leave the circulation by diffusion through the capillary walls. 7. The systemic circulation is the circulation to: a. The lung to feed it b. To the lung to pick up 02 c. To the liver, kidneys and other organs d. All of these 8. The pulmonary circulation is the circulation to the: a. The lung to feed it b. To the lung to pick up 02 c. To the liver, kidneys and other organs 9. The bronchial circulation is the circulation to the: a. The lung to feed it b. To the lung to pick up 02 c. To the liver, kidneys and other organs 10. The coronary circulation is the circulation to the: a. The lung to feed it b. To the lung to pick up 02 c. To the liver, kidneys and other organs d. to the heart to feed it 11. The upper chambers of the heart: a. Receive blood b. Have thin walls c. Create a lot of blood pressure d. A, b only e. A, b and c 12. There are four: a. Heart chambers b. Intake valves c. Ventricular valves d. All of these 13. true/false Blood that leaves the right heart via an artery carries desaturated blood. 14. true/false Blood that leaves the left side of the heart via an artery carries desaturated blood. 5/9/20177:03:29 PM 1 Unit 4: heart, circulation, blood pressure review page 2 15. The venous blood from the rest of the body enters the heart at the: a. right atrium b. left atrium c. right ventricle d. left ventricle 16. The blood leaving the heart to go to the pulmonary bed leaves the: a. right atrium b. left atrium c. right ventricle d. left ventricle 17. The blood that comes back from the pulmonary bed is full of 02 now and it goes to the: a. right atrium b. left atrium c. right ventricle d. left ventricle 18. The blood that goes to the rest of the body leaves the heart via the: a. right atrium b. left atrium c. right ventricle d. left ventricle 19. A blood vessel that carries blood to the heart is called a[n]: a. Artery b. Vein c. Capillary 20. A blood vessel that carries blood away from the heart is called a[n]: a. Artery b. Vein c. Capillary 21. The two atrial chambers of the heart : a. Pump in sequence b. Pump at the same time c. Push their blood into the ventricles d. A and c e. B and c 22. While the heart muscle is contracted, the chamber is smaller which raises?/lowers? the blood pressure in the chamber. 23. While the heart muscle is relaxed, the chamber is larger so that the chamber can: a. Send blood out to the next chamber b. Receive the blood from the chamber upstream 24. The two Atrial/ventricular valves open: a. In sequence b. At the same time c. Making the "lub" sound of the "lub dub" of the heart beat d. A and c e. B and c 25. Systole is: 5/9/20177:03:29 PM 2 Unit 4: heart, circulation, blood pressure review page 3 a. b. Cardiac muscle contraction Cardiac muscle relaxation 26. Diastole is: a. Cardiac muscle contraction b. Cardiac muscle relaxation 27. When the Right Atrium is in systole: a. The left atrium is in diastole b. The right ventricle is in diastole c. The left atrium is in systole d. A and b e. B and c 28. The ventricular outflow valve on the right side of the heart is called the: a. Pulmonary valve b. Aortic valve c. Mitral valve 29. During atrial diastole, the right atrium: a. the right atrium accepts blood from the inferior vena cava and superior vena cava b. the right atrium accepts blood from the aorta c. sends blood to the right ventricle 30. During atrial systole, the left atrium: a. sends blood into the left ventricle b. sends blood into the aorta c. receives blood from the pulmonary veins 31. During atrial systole: a. Both right and left atria are contracting b. Both right and left atria are relaxing 32. The atria and the ventricles are separated by a fibro-skeleton: a. This structure electronically isolates atria from ventricles b. It contains all the support for all 4 valves on a slanted plane c. It acts as a bone for the cardiac muscles to pull against d. A, b only e. A, b and c 33. The intra-atrial septa: a. separates the atria from one another b. separates the atria from the ventricles 34. true/false Contraction of the myocardium results in a squeezing and wringing type of movement much like that used to wring out a wash rag. 35. A ventricular septal defect [VSD] would be: a. hole in the wall between the ventricles and the atria b. hole in the wall between the two atria c. hole in the wall between the two ventricles 36. The inferior vena cava [IVC] drains blood from the: a. Legs and abdomen b. Right and left side of the brain 37. The superior vena cava [SVC] drains blood from the: 5/9/20177:03:29 PM 3 Unit 4: heart, circulation, blood pressure review page 4 a. b. Legs and abdomen Right and left side of the brain 38. The right jugular vein drains blood from the: a. Right chest and arm b. The right side of the head 39. Which major vein comes goes through a hole in the diaphragm? a. Inferior vena cava b. Superior vena cava c. Trans-diaphramtium 40. The right subclavian vein drains blood from the: a. Right side of the abdomen b. Right arm, shoulder and chest wall 41. The left subclavian vein drains into the: a. Superior vena cava b. Inferior vena cava c. Right atrium directly d. left atrium directly 42. The first portion of the artery that leaves the left ventricle is called the: a. Ascending aorta b. Arch of the aorta c. Descending aorta d. Thoracic aorta 43. Blood from the aorta would get to the brain via the: a. the right brachiocephalic artery b. left common carotid artery c. both feed the head and brain 44. The main pulmonary artery takes blood to: a. right pulmonary artery b. the left pulmonary artery c. both 45. If the pulmonary blood vessels follow the bronchial tree, what is the name of the pulmonary vessel that carries blood to right lower lobe? a. right pulmonary artery b. the right lower lobar pulmonary artery c. the right lower lobar pulmonary vein d. the right lower lobar bronchial vein 46. At what point do the pulmonary arteries turn into arterioles? a. Segmental level b. Bronchiole level c. Capillary level 47. When the pulmonary capillaries leave the alveolar area, they: a. Contain more 02 because of diffusion from the alveoli b. Contain less 02 because gas moved into the hungry tissue of the lung 48. True/ false At every step, the pulmonary veins follow the course of the airways, increasing in diameter while decreasing in numbers. 5/9/20177:03:29 PM 4 Unit 4: heart, circulation, blood pressure review page 5 49. True/ false there are about 18-20 pulmonary veins entering the Left atrium. 50. In the bronchial circulation, the blood going to the lungs comes from: a. Abdominal aorta b. Thoracic aorta c. Main pulmonary artery d. Mammary arteries e. b and d f. a and d 51. true / false As the arteries of the bronchial circulation branch off, they move into the pari-bronchial sheath to feed the larger airways. 52. When the pulmonary and the bronchial vessels merge: a. 30% of the bronchial blood returns via bronchial veins to return to the systemic system b. 60% of the of the bronchial blood flow merges into the pulmonary blood vessels c. it creates part of the anatomical shunt d. a and c e. b and c f. a, b and c 53. The myocardium is fed: a. from the root of the aorta b. via the coronary circulation c. with the first 5% of the entire cardiac output d. all of these 54. Decreased blood flow to any part of the myocardium causes decreased 02 levels at the myocardial tissue: a. This is felt as pressure on the carotid artery b. This is felt as angina pain 55. There are five coronary arteries: a. Right coronary artery b. Posterior descending coronary artery c. Left coronary artery d. [Left] Circumflex e. [Left] Anterior descending f. All of these are coronary arteries 56. Which would be worse? a. Obstruction of the right coronary artery b. Obstruction of the [left] anterior descending coronary artery c. They are equally bad 57. Contraction of the myocardium interferes with myocardial perfusion so that most of this feeding of the heart muscle occurs during: a. Diastole b. Systole 58. While hypotension is defined as a blood pressure of less than 90/60 mmHg, there is a dangerous level of diastolic pressure in which the myocardium is no longer getting perfused. a. 55 mmHg b. 50 mmHg c. 45 mmHg 5/9/20177:03:29 PM 5 Unit 4: heart, circulation, blood pressure review page 6 d. 40 mmHg 59. Part of the anatomical shunt occurs because much of the coronary venous return is into the: a. Thebesian veins into the two left chambers [as well as the 2 right chambers] b. Right atrium 60. The normal anatomical shunt due to the bronchial merging and the coronary blood return to the left of the heart is ---. Anything higher is pathological: a. 1%-3% b. 2%-5% c. 5%-8% d. 10% to 15% ………………Blood pressure…………………………………. 1. The right atrial pressure is -- mmHg: a. 2 b. 8 c. 25 d. 130 2. The left atrial pressure is-- mmHg: a. 2 b. 8 c. 25 d. 130 3. The blood pressure in the right ventricle is-- mmHg: a. 2 b. 8 c. 25 d. 130 4. The blood pressure in the left ventricle is-- mmHg: a. 2 b. 8 c. 25 d. 130 5. The blood pressure in the pulmonary bed is-- mmHg: a. 2 b. 8 c. 15 d. 25 6. Arterioles: a. Branch off arteries b. have strong sphincter muscles to control blood flow. c. Both 7. Pre-capillary sphincters: a. control blood flow out of a capillary bed b. control blood flow into a capillary bed c. control perfusion to a selective tissue d. a and c e. b and c 5/9/20177:03:29 PM 6 Unit 4: heart, circulation, blood pressure review page 7 8. Diffusion of gases, nutrients and water occurs here: a. Arteriole level b. Pre-capillary level c. Capillary level 9. As the blood moves into smaller and smaller vessels, the pressure -- at each step. a. Drops b. Rises 10. The first condition necessary for good circulation is: a. Initial blood pressure coming out of the right ventricle b. Initial blood pressure coming out of the left ventricle 11. Immobility effects the circulation because: a. Smooth muscle action on the veins moves the blood back to the heart b. Skeletal muscle action on the veins moves the blood back to the heart 12. TRUE/FALSE As blood advances along the deep veins, it moves in one direction because of one-way valves in the larger veins. 13. As smaller blood vessels open into larger ones, there is less: a. Compliance b. airway resistance c. Friction, thus resistance to blood flow 14. [see above question] Due to the situation above, there is an – in the flow rate [velocity] of blood as the smaller vessels empty into larger ones. a. Increase b. Decrease 15. If there is only +5 mmHg blood pressure in the inferior vena cava below the diaphragm, how can we expect a driving pressure of 10 to move the blood against gravity into the right atrium? a. There is a pressure of -5 in the chest b. There is a pressure of +5 in the chest 16. If your heart rate is 100 bpm and your stroke volume is 70 ml. What is the Cardiac output? a. 7000 ml b. 7 lpm c. 7000 liters 17. Would the person in the above question have a Cardiac Output within normal limits? a. Yes b. No 18. There can be no perfusion at the arteriole level because: a. The arteriole has complete control over the lumen of the vessel b. The arteriole has walls that are too thick for molecular movement c. Both 19. TRUE /FALSE There can be perfusion at the capillary level because the wall is only a single cell thick at this point. 20. TRUE/FALSE Local control over perfusion is made possible by pre-capillary sphincters that open when the pH of the tissue rises. 5/9/20177:03:29 PM 7 Unit 4: heart, circulation, blood pressure review page 8 21. TRUE/FALSE Local control over perfusion is made possible by pre-capillary sphincters that open when the C02 in the tissue rises. 22. Identify the advantage of local control over perfusion. a. Conservation of energy b. No capillary bed gets extra blood that it doesn't need c. Both 23. During the fight or flight reaction, the local control over perfusion is over ridden by secretions of catecholamines [such as adrenalin and nor-epinephrine] that result in the following: a. Widespread vasodilatation of skeletal muscles b. Widespread vasoconstriction of abdominal vessels c. Vasoconstriction of myocardium d. a, b & c e. b & c only f. a & b 24. What is the effect of widespread vasoconstriction when combined with increased heart rate? a. Work of the heart increases b. Work of the heart decreases 25. What happens to the blood pressure, if there is widespread vasoconstriction in the body? a. Blood pressure rises b. Blood pressure falls 26. How does the body react to hypovolemic shock [bleeding]? a. Heart rate increases to raise cardiac output b. Widespread vasoconstriction except for brain and lungs c. Widespread vasodilation except for brain and lungs d. a & b e. a & c …………………..Conduction………………… 1. TRUE/FALSE When there is a voltage gradient it results in a flow of electrons. This flow of electrons results in muscle relaxation. 2. Ions are: a. Positively charged particles b. Negatively charged particles c. Electrically charged particles 3. TRUE/FALSE The two ions concerned with all muscle contraction and relaxation are the Na++ and the K+ 4. Na++ ions is: a. The dominate extracellular electrolyte, b. The dominant intracellular electrolyte. 5. K+ ions are the: a. The dominate extracellular electrolyte, b. The dominant intracellular electrolyte. 6. To depolarize a muscle cell, one must --- the cell membrane’s permeability to Na++ ions. a. Increase b. Decrease 5/9/20177:03:29 PM 8 Unit 4: heart, circulation, blood pressure review page 9 7. As the Na++ ions rush into the cell, the overwhelming intracellular charge is more. a. Positive b. Negative 8. Depolarization of a muscle cell causes that cell to –: a. Relax b. Contract 9. The act of returning the cell to its previous balance is called: a. depolarization b. polarization c. repolarization 10. During this phase of muscle action there is no movement and charges are in balance. a. depolarization b. polarization c. repolarization 11. During this phase of muscle action, the muscle cannot receive more stimuli to contract. a. depolarization b. polarization c. repolarization 12. Repolarization is considered a --- period : a. Negative b. Refractory c. Absolute 13. The atrial must be in systole while the ventricles are in : a. Diastole b. Systole 14. The sino-atrial node a. Is the primary pacemaker of the heart b. Is the secondary pacemaker of the heart c. Has an intrinsic rate of 60-100 bpm d. A and c e. B and c 15. The sino-atrial node is located in the: a. posterior wall of the right atrium b. anterior wall of the right ventricle c. just below the opening from the Superior vena cava d. a and c 16. When the cardiac output needs to be increased, the SA node will be raised by the stimulation of the: a. Sympathetic nervous system b. Parasympathetic nervous system 17. TRUE/FALSE The SA node would normally tend to beat in the upper end of the normal range. 5/9/20177:03:29 PM 9 Unit 4: heart, circulation, blood pressure review page 10 18. Those stimuli that cause the heartrate to increase generally via the sympathetic stimulation are called: a. Positive chrontropic effects b. Negative chronotropic effects 19. The pathway between the right and left atrium are called the: a. Intra-atrial pathways b. Bundle of His c. Intra-ventricular pathways d. Purkinje fibers 20. The pathway between the atria and the ventricles must go through the: a. SA node b. AV node c. AV junction d. A & c e. B & c 21. In addition to crossing the fibro-skeleton, the AV node has the job of: a. Holding the impulse long enough for blood to leave the atria and get into the ventricles b. Establish a back up heart rate c. Both 22. The intrinsic rate of the AV node is: a. 60-100 b. 40-60 c. less than 40 23. The pathway downstream from the AV node is called the : a. Intra-atrial pathways b. Bundle of His c. Intra-ventricular pathways d. Purkinje fibers 24. The bundle of His divides into the: a. Purkinje fibers b. Right and left bundle branches c. Intra-ventricular pathways 25. On the EKG, the P wave represents: a. Atrial polarization b. Atrial depolarization c. Atrial repolarization d. None of these 26. On the EKG, the QRS wave represents: a. Ventricular polarization b. Ventricular repolarization c. Ventricular depolarization d. None of these 27. On the EKG, the PR Interval represents: a. Atrial depolarization b. Ventricular depolarization c. The time spent in the atria and in the junction d. Atrial polarization 5/9/20177:03:29 PM 10 Unit 4: heart, circulation, blood pressure review page 11 28. On the EKG, the T wave represents the: a. Ventricular polarization b. Ventricular repolarization c. Ventricular depolarization d. None of these 29. Atrial repolarization is lost in the: a. PRI b. QRS c. ST segment ……………..The Blood…………. 1. Blood transports: a. gases of metabolism b. nutrients from digestive tract to the tissues c. nerve impulses between the CNS and the heart d. a, b only e. a, b and c 2. TRUE/FALSE Hormones secreted by a gland have greater effect because they are transferred through out the body via the circulatory system. 3. The blood steam regulates: a. Acid base balance b. Temperature c. Water content d. All of these 4. TRUE/FALSE The blood protects the body by distributing the immune cells 5. TRUE/FALSE the blood protects the body by clotting. 6. Respiratory gases are carried in the plasma where they – a. Cling to hemoglobin b. Exist as gases with measurable pressures c. Both d. None 7. Osmotic pressure is: a. pulling force through a membrane such as a capillary wall b. pushing force through a membrane such as a capillary wall 8. Hydrostatic pressure is created by: a. The concentration of substances such as proteins or NaCl b. The blood pressure pushing blood through the capillaries 9. Osmotic pressure rises as: a. Concentration of NaCl drops b. Concentration of NaCl rises 10. As water leaves a capillary, the osmotic pressure of the blood inside the capillary will: a. Rise b. Drop 11. [refer to the above question] When the osmotic pressure changes due to water leaving, the solids will now: 5/9/20177:03:29 PM 11 Unit 4: heart, circulation, blood pressure review page 12 a. Push more water out b. Pull water back until the osmotic and hydrostatic pressure equilibrate 12. Substances that create osmotic pressure: a. Proteins b. Albumin c. Colloids d. Na Cl e. All of these f. All but b 13. The yellow-colored plasma makes up about--- % of the blood volume. a. 35% b. 45% c. 55% d. 60% 14. The solids in the blood includes both white and red blood cells, and is collectively called the: a. Hemoglobin b. Hematocrit c. RBC 15. The vast majority of cells in the blood are: a. Red blood cells b. Epithelial cells c. Immune cells 16. Adult males and children of both sexes have a normal hematocrit of --. a. 35% b. 42% c. 45% d. 55% e. 60% 17. Adult females have a normal hematocrit of --. a. 35% b. 42% c. 45% d. 55% e. 60% 18. A person with a hematocrit of 45 would have an estimated Hb of a. 12 b. 15 c. 18 d. 20 19. A full 33% of the weight of the RBC is made up of: a. 02 molecules b. C02 molecules c. Hemoglobin molecules d. None of these 20. The color of blood comes from the: a. Color of the hemoglobin’s protein portion b. Color of the hemoglobin's iron portion 5/9/20177:03:29 PM 12 Unit 4: heart, circulation, blood pressure review page 13 c. Color of the RBC d. a & c e. b and c 5/9/20177:03:29 PM 13