* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 16
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
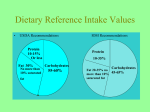
Chapter 16 Food Chemistry Carbohydrates Review: Types of carbohydrates All sugars and digestible carbohydrates are broken down to glucose in our bodies “Blood Sugar” Glucose undergoes catabolism CO2 and H2O Are “low carb” diets really low carb? Saccharin vs. Aspartame Saccharin: oldest artificial sweetener Stable at high temperatures Bitter metallic aftertaste Aspartame Breaks down at high temp 180 times sweeter than sugar No calories because of low concentration! Splenda® (Sucralose) Chlorination of sucrose molecule 600 times sweeter than table sugar No calories because of low concentration Fats Review: Types of fats Dietary fats = triglycerides Fat storage Adipose tissue Around vital organs Under the skin Are fats good? Source: http://www.seeingscience.cclrc.ac.uk/Activity/Light;SECTION=5243 The Skinny on Fat Saturated Unsaturated Monounsaturated Polyunsaturated Trans The body’s fat transporters VLDL: triglyceride (dietary fat) LDL: carry cholesterol to cells HDL: carry cholesterol to liver Olestra 8 fatty acid tails (attached to sucrose molecule) rather than the usual 3 Too large to be digested Fatty acids bind fat-soluble vitamins The “bottom” line Too much fat Heart disease Obesity Atherosclerosis Too little fat Diet deficiencies/imbalances Cancer Heart Disease Source: http://whyquit.com/whyquit/LinksJBlood.html Proteins Dietary proteins broken down to amino acids Most complete sources: meat & dairy Vegetarians Combine foods to get necessary nutrients Cereal grain + legume Brain growth Minerals Inorganic (no C or H) Vital! Iodine: thyroid function Iron: oxygen transport Sodium & chlorine: cellular transport Phosphorus: energy exchange Calcium: bones, heartbeat, coagulation Vitamins Water-soluble B-complex, C Excess are excreted Lower content in cooked food Fat-soluble A, D, E, K Build up a storage in fat cells Fiber Soluble May lower cholesterol Remove fat-digesting enzymes Control blood sugar: delay stomach emptying Insoluble No calories: not absorbed Texture, low fat, low calories Bulky: feel full Prevent constipation: G.I. health Food Enzymes Catabolism: break down molecules Most end in –ase Amylase Pepsin (Peptidase) Protease Bile (pre-processing fat) Nuclease Pancreatic amylase Lipase Lactase Water Recommended 1.5-2L daily Body = up to 75% water Brain = 85% water Dehydration Back pain Kidney damage Migraines Joint pain Temperature regulation Stomach pain and ulcers Low energy, disorientation Excess body fat Poor muscle tone, size and function Poor digestive and organ function Water retention Build-up of toxins in blood Food Additives Substances not found in natural foods Regulated by the FDA Thousands! Improve storage, handling, retard spoilage, add color, flavor, sanitize, texture Additives for Nutrition Iodine Thiamine, niacin, riboflavin, folic acid Vitamin C Vitamin D Vitamin A Fiber Additives for Taste Sweeteners Flavors Sugar, corn syrup Saccharin, NutraSweet, Splenda Polyhydroxyl alcohols (sorbitol, xylitol) Salt Spices & herbs Esters (vanilla, mint, almond) Enhancers MSG Source: http://www.zenithpumps.com/images/food.jpg) MSG Triggers newly-identified taste buds: umami Respond to glutamic acid the same way “sweet” taste buds respond to sugar Augment meaty/savory flavors Additives for Storage Spoilage inhibitors Sorbic acid, benzoic acid, propionic acid Sodium nitrite Vitamin C Sulfur dioxide Antioxidants BHT, BHA Source: http://www.cleevemh.co.uk/i/silo-01.jpg Additives for Color “Natural” β-carotene, Beet juice, Saffron, Annatto, Caramel, Turmeric, chlorella Artificial Food colors “FD&C” Dye vs. Lake Are they dangerous? Source: http://www.sugarcraft.com/catalog/coloring/colormist.jpg Food Poisons Carcinogens Charbroiled meat (3,4-benzopyrene) Cinnamon & nutmeg (safrole) Biologicals Aflatoxins (mold on peanuts & grains) Botulism Salmonella Source: http://www.nature.com/news/2001/011025/images/salmonella_160.jpg Source: http://www.scenta.co.uk/_db/_images/botulism140.jpg Growing Your Food: Fertilizers Nitrogen: Proteins Fixation N2 in the air usable nitrates by lightning Bacteria in the soil Legumes Genetically modified crop plants Fertilizers Manure Ammonia & urea Source: http://www.noble.org/Ag/Soils/InSeasonResponse/Figure1.jpg Growing Your Food: Fertilizers Phosphorus: DNA & RNA Ancient Sources Bone Fish meal Guano Modern Sources Phosphate ores (concentrated deposits) Manufactured calcium dihydrogen phosphate Create serious pollution during production Environmental imbalance Growing Your Food: Fertilizers Potassium: Fluid balance KCl is the main source In fertilizers: potassium oxide Uptake of potassium leaves soil acidic Non-renewable resource! Source: http://waupacasoilblenders.com/images/EV_51010.JPG Growing Your Food: Pests Chemical Control DDT: chlorinated hydrocarbons Organic phosphorus pesticides Persistent in the environment Nerve poisons, concentrate in fatty tissue Not as persistent in the environment Biological Control Insect-specific viruses Sterilization Juvenile hormones Specific predators Source: http://www.imba.missouri.edu/artwork/cornbor2.gif You Are What You Eat What you eat literally becomes part of YOU Current FDA recommendations Depends on height, weight, activity level, special needs Men 19-30yr Women 19-30yr <2900 <2200 Carbs 45-65% 45-65% Fat 20-35% 20-35% Protein 10-35% 10-35% Fiber 38g / day 25g / day Water 3.7L / day 2.7L / day Calories You Are What You Eat Source: http://www.bakersfederation.org.uk/images/healthy%20eating%20plate%20small.jpg Final Thoughts D&C Section 89: The Word of Wisdom V. 16: “All grain is good for the food of man; as also the fruit of the vine; that which yieldeth fruit, whether in the ground or above the ground” V. 12: “Yea, flesh also of beasts and of the fowls of the air, I, the Lord, have ordained for the use of man with thanksgiving; nevertheless they are to be used sparingly” V. 11: “Every herb in the season thereof, and every fruit in the season thereof; all these to be used with prudence and thanksgiving” WE ARE SO BLESSED! Source: http://images.google.com/url?q=http://everyone.is.not.theuseless.com/archives/2003_09.html Review What are each of the following broken down into in our bodies: carbohydrates, protein, fat Be able to label parts of a trigylceride molecule Be able to recognize saturated vs. unsaturated fatty acids Know the omega- designations of fatty acids Name one mineral and what it does in our bodies Name the 3 essential plant nutrients, sources of each and what each does in the plant Name one type of chemical and one type of biological pest control, and discuss pros and cons of each What are some symptoms of dehydration? Name each of the body’s fat transporters and what they do Discuss soluble and insoluble fiber What do the 3 numbers on a bag of fertilizer represent? Name one food additive and what it’s used for. Name some common food enzymes, what they digest, and where they are produced in the body. Food poisons: name one biological and one carcinogen we discussed.