* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 30.1 Respiratory and Circulatory Functions
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Jatene procedure wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
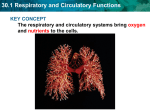
30.1 Respiratory and Circulatory Functions KEY CONCEPT The respiratory and circulatory systems bring oxygen and nutrients to the cells. 30.1 Respiratory and Circulatory Functions The respiratory and circulatory systems work together to maintain homeostasis. • The circulatory system transports blood and other materials. – brings supplies to cells – carries away wastes – separates oxygen-poor and oxygen-rich blood Oxygen-rich blood Oxygen-poor blood 30.1 Respiratory and Circulatory Functions • The respiratory system is where gas exchange occurs. – picks up oxygen from inhaled air – expels carbon dioxide and water sinus nose mouth epiglottis trachea lungs 30.1 Respiratory and Circulatory Functions The respiratory system moves gases into and out of the blood. • The lungs contain the bronchi, bronchioles, and alveoli. • Millions of alveoli give the lungs a huge surface area. • The alveoli absorb oxygen from the air you inhale. alveoli bronchiole 30.1 Respiratory and Circulatory Functions • Breathing involves the diaphragm and muscles of the rib cage. • Air flows from areas of high pressure to low pressure. Air inhaled. Air exhaled. Muscles and rib cage relax. Muscles contract and rib cage expands. Diaphragm flattens and moves downward. Diaphragm relaxes and rises. 30.1 Respiratory and Circulatory Functions The circulatory system moves blood to all parts of the body. • The system includes the heart, arteries, veins, and capillaries. – heart pumps blood throughout body – arteries move blood away from heart – veins move blood back to heart – capillaries get blood to and from cells arteries veins 30.2 Respiration and Gas Exchange Respiratory diseases interfere with gas exchange. • Lung diseases reduce airflow and oxygen absorption. – Emphysema destroys alveoli. – Asthma constricts airways. – Cystic fibrosis produces sticky mucus. 30.2 Respiration and Gas Exchange • Smoking is the leading cause of lung diseases. 30.3 The Heart and Circulation KEY CONCEPT The heart is a muscular pump that moves the blood through two pathways. 30.3 The Heart and Circulation The tissues and structures of the heart make it an efficient pump. • Cardiac muscle tissue works continuously without tiring. NORMAL HUMAN HEART 30.3 The Heart and Circulation • The heart has four chambers: two atria, two ventricles. • Valves in each chamber prevent backflow of blood. pulmonary valve aortic valve left atrium right atrium mitral valve left ventricle tricuspid right ventricle septum • Muscles squeeze the chambers in a powerful pumping action. 30.3 The Heart and Circulation • Blood flows through the heart in a specific pathway. – oxygen-poor blood enters right atrium, then right ventricle – right ventricle pumps blood to lungs – oxygen-rich blood from lungs enters left atrium, then left ventricle – left ventricle pumps blood to body 30.3 The Heart and Circulation • Blood pressure is a measure of the force of blood pushing against artery walls. – systolic pressure: left ventricle contracts – diastolic pressure: left ventricle relaxes • High blood pressure can precede a heart attack or stroke.