* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
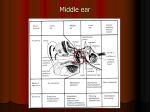
Bio 30 Ear Anatomy Review Name: Define & describe the function of the following anatomical parts using your notes & textbook: Outer Ear – Pinna: Auditory Canal: Tympanic membrane: Questions: 1) How are a musical instrument drum and ear drum similar? 2) Why is it dangerous to use a Q-tip to clean your ears and why would you use one in the first place? 3) Why is you pinna shaped the way it is? Describe a reasonable hypothesis for the convoluted shape of the pinna. Middle Ear – identify the main function of the following anatomical parts Ossicles: Oval Window: Eustachion tube: Questions: 1) Give the anatomical and nickname of the 3 ossicles. 2) Is the oval window soft or hard? Explain the advantage to your answer. 3) Explain why a person with a sore throat may end up with a middle ear infection. Inner Ear – describe the function of each part. Cochlea: Organ of Corti: Semicircular canals: Vestibule: Round Window: Auditory Nerve: Questions: 1) The ear serves two different purposes. What are they? 2) Why would a punctured eardrum prevent you from hearing? 3) Why do you have a hard time clearing your ears out when you go up in an airplane? 4) What part of the ear would be buzzing after attending a rock concert? 5) Describe 3 possible ways a person may be deaf. (Think of all the anatomy involved! The Human Ear – Nervous System – Work Sheet Place the correct terms listed below in the proper spaces provided below, (you may use more than once): Pinna – Cochlea – Ceruminous Glands – Eustachion tube – Ossicles – Oval Window – Tympanic membrane – Auditory Canal – Organ of Corti – Round Window – Semicircular Canals – High – Low – Temporal – Basilar The outer ear is composed of the following parts: 1. ______________ These are flaps of skin & cartilage that collect sound & funnel it to the ear. 2. ______________ This is the channel that leads to the tympanic membrane. 3. ______________ These glands secrete a waxy substance to lubricate & protect the ear drum. 4. ______________ Faint vibrations can push on the stretched membrane causing it to move a billionth of a centimetre resulting in sound transmission. This membrane collects vibrations & then has them sent to another membrane deeper in the ear called the ______________ window which is much smaller. The difference in size between the OVAL window and the tympanic membrane acts to AMPLIFY the SOUND intensity by 23 DECIBELS. The middle ear is an air-filled cavity in the head that contains the following parts: 5. ______________ These are the smallest bones in the body called the MALLEUS (hammer), INCUS (anvil) & STAPES (stirrup). They function to AMPLIFY the vibrations from the TYMPANIC 22 times (3 decibel increase). 6. ______________ This is a small membrane that transmits sound vibrations into the inner ear. 7. ______________ This is a channel that connects the throat to the middle ear. It is needed to EQUALIZE AIR PRESSURE from the middle to outer part of the ear. Often throat infections lead to middle ear infections because the bacteria can travel up this path. The inner ear resides in the hardest bone of the body the skull. It is fluid filled and is composed of the following parts: 8. ______________ This is a snail-shaped hearing device that contains the ORGAN of CORTI. 9. ______________ This is a sensitive membrane that has microscopic hairs that detect sound vibrations & convert them into nerve impulses. Hairs at the base near the oval window detect ______ frequency sound (20,000 Hz), shorter hairs at the opposite end respond to ______ frequency sounds. 10. ______________ This is a membrane that is responsible equalization of fluid pressure in the inner ear. It allows the fluid inside the cochlea to vibrate once the oval window is compressed. 11. ______________ These fluid-filled chambers are responsible for detection of motion & balance. 12. There are more than 30,000 nerve pathways or circuits that lead from the ORGAN of CORTI to form into a large CRANIAL NERVE that leads directly to the ______________ lobe of the brain. Label the diagram 1. _________________________________ 6. _________________________________ 2. _________________________________ 7. _________________________________ 3. _________________________________ 8. _________________________________ 4. _________________________________ 9. _________________________________ 5. _________________________________ 10. _________________________________