* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download heart
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
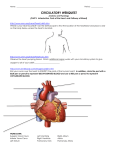
Circulatory system and the blood Chapters 5 and 6 Circulatory system PREVENTS CELLS FROM SUFFOCATING BRINGS CELLS OXYGEN AND NUTRIENTS Also called the cardiovascular system PATHWAYS HEART- PUMPS BLOOD ARTERIES- CARRY BLOOD AWAY FROM THE HEART VEINS- CARRY BLOOD TOWARD THE HEART CAPILLARIES- TINY VESSELS THAT REACH SINGLE CELLS- THE SITE WHERE EXCHANGE OCCURS ARTERIES WALL- have 3 LAYERS INNER- simple squamous epithelium + connective tissue= endothelium Middle- smooth muscle Outer- loose and fibrous connective tissue Arterioles- tiny arteries Capillaries Nourish individual cells can be closed when muscles in precapillary sphincter are contracted an arteriovenous shunt is a vessel allows the blood to bypass the capillaries and move on to a venule while the precapillary sphincter is closed Veins Venules- tiny veins that drain capillary beds 3 layers, but less muscle and connective tissue Have one way valves to prevent blood from staying in the legs Vein walls can expand- 70% of all the blood is in the veins Heart Cone shaped, fist sized Myocardium- the cardiac muscle Pericardium- the thick sac around the heart Septum- the internal wall that separates the right and left halves Upper 2 chambers- atria Lower 2- ventricles Valves Chordae tendineae- strings that prevent one way valves from opening backwards Atrioventricular valves- separate upper and lower chambers Right- tricuspid Left- bicuspid or mitral Semilumar valves- downstream of ventricles pulmonary- right aortic- left Major vessels Right half source of blood- from superior and inferior vena cavae Right blood output- to Pulmonary arteries Left blood input- from pulmonary veins Left output- to Aorta HEART RIGHT SIDE- PUMPS OXYGEN POOR BLOOD FROM BODY (VENA CAVA) TO LUNGS (PULMONARY ARTERY) LEFT SIDE- PUMPS OXYGEN RICH BLOOD FROM LUNGS (PULMONARY VEIN) TO THE REST OF THE BODY (AORTA) The Left side works harder Cardiac cycle Systole- period of muscle contraction Diastole- resting period Lub dub- sound of heart valves slamming shut Murmur- caused by leaky valves SA node- the heart’s pacemaker- located on the right atrium, creates the electrical impulse AV node- below right atrium- electrical impulse passes through on its way to Perkinje fibers- conducts the impulses to the muscle cells that cause contraction of ventricles Control of heart rate 1 Medulla oblongata- nerve impulses from brain stem 2. Endocrine hormones from adrenal glands- epinephrine and nor epinephrine Defibrillation- an electrical shock to reestablish ventricular rhythm given to persons with heart problems HEART ATTACK BLOCKAGE OF A CORONARY ARTERY which supplies the heart muscle with oxygen and nutrients PART TO HEART MUSCLE SUFFOCATES IF ENOUGH MUSCLE TISSUE STOPS WORKING THEN THE HEART CAN’T PUMP BLOOD (massive heart attack) Other Problems/Treatments Aneurysm- ballooning of weakened artery, can burst and cause massive internal bleeding Treatments for clogged vessels Nitroglycerine- dilates blood vessels Clot dissolving drugs- to treat heart attack Angioplasty- balloon inflated inside a partially clogged artery to expand it BLOOD PRESSURE THE FORCE THAT BLOOD EXERTS AGAINST THE WALLS OF OUR BLOOD VESSELS CONTRACTION OF VENTRICLES= HIGH PRESSURE- SYSTOLE PRESSURE DROPS MOMENTARILYwhen the heart relaxes- DIASTOLE BLOOD PRESSURE SYSTOLE/DIASTOLE MEASURED WITH A STETHOSCOPE AND PRESSURIZED CUFF CUFF CUTS OFF BLOOD AT A HIGH ENOUGH PRESSURE SYSTOLIC- 110-140 = NORMAL BELOW 100- LOW HYPERTENSION- 140/90 or greater Other Problems Hypertension= High blood pressure Atheriosclerosis- cholesterol under endothelium of arteries Blood clots may form on the irregular artery walls Thrombus- attached clot- embolus- free clot which is moving through the vessels Stroke- burst or blockage of brain arteriole Veins Weak one way valves- causes swelled veins (spider veins and varicose veinsusually in the legs/feet) Hemorrhoids- swelled veins of rectum Phlebitis- inflammation of veins