* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Worksheet 2
Automated airport weather station wikipedia , lookup
Severe weather wikipedia , lookup
Air quality law wikipedia , lookup
Marine weather forecasting wikipedia , lookup
Cold-air damming wikipedia , lookup
Lockheed WC-130 wikipedia , lookup
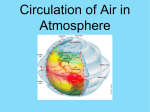
Atmospheric circulation wikipedia , lookup
Atmospheric convection wikipedia , lookup
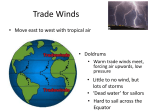
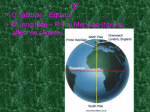
Earth Science Chapter 12 Worksheet 2 Name ____________________________ Block ____________________________ In the space to the left, write true if the statement is true, if the statement is false, change the underlined word to make it true __________________ 1. Meteorology is the study of atmospheric phenomena __________________ 2. Weather is the current state of the lithosphere __________________ 3. Long-term variations in weather for a particular area make up the climate of the area 4. The tropics are hotter than the poles because the sun strikes this area of Earth more indirectly __________________ Circle the letter that corresponds to the correct answer 5. A large parcel of air that takes on the characteristics of the area over which it forms is a(n) a. Cloud b. Air mass c. Source region d. Wind 6. An air mass takes on its source region’s a. Temperature and humidity b. Landforms c. Clouds and wind d. Elevation 7. Maritime air masses originate over a. Clouds b. Oceans c. Glaciers d. Mountains 8. When an air mass travels over land or water that has different characteristics than those of its source region, it undergoes a. Air source change b. Air mass modification c. Air pressure modification d. Temperature inversion Circle T if the statement is true or F if the statement is false T T T T T F F F F F 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. An isopleth is a line that connect points of equal or constant values Lines of equal pressure are called isobars Isobars that are far apart indicate a small difference in pressure and light winds Contour lines are lines of equal temperature Isotherms are used to identify temperature gradients and, consequently, frontal systems Use the words in the table below to complete the passage intertropical convergence zone trade winds southwest low pressure Prevailing westerlies rotation polar jet stream polar easterlies North America Coriolis effect northeast jet streams The (14) _______________________ deflects moving air to the right in the northern hemisphere and to the left in the southern hemisphere. The cause of this is Earth’s (15) __________________. Each hemisphere has three basic wind systems. The first, at 30O latitude north and south, is known as the (16) ________________________. There, air sinks, warms, and moves toward the equator from northeast to southwest in the northern hemisphere and from southeast to northwest in the southern hemisphere. When the air reaches the equator, it rises, then moves back toward 30O to start the cycle again. These winds from both hemispheres converge at the equator. They are forced upward, creating an area of (17) __________________. This area near the equator is called the (18) ____________________________. The second wind system, called the (19) __________________, flows between 30O and 60O latitude north and south of the equator. Its circulation pattern is opposite that of the wind system discussed above. These winds are responsible for the movement of many weather systems across much of (20) _____________________________. The third wind system, the (21) _________________________ lies between the poles and 60O latitude. In the northern hemisphere, these winds flow from the (22) ____________________ to the (23) ________________. They flow in the opposite direction in the southern hemisphere. Narrow bands of fast, high altitude, westerly winds called (24) ___________________ flow at the boundaries between wind zones in the middle latitudes. These bands of wind steer weather systems in the middle latitudes. The most important one, the (25) ___________________, separates the polar easterlies from the prevailing westerlies. Complete the table by filling in the type of weather system described Description Weather System 26. Cold, dense air that displaces warm air, forcing the warm air up ______________________ 27. Narrow region separating two air masses of different densities ______________________ 28. Advancing warm air that displaces cold air ______________________ 29. Low-pressure system that heavily influences weather in the middle latitudes 30. Cold air mass that moves rapidly and overtakes a warm front ______________________ 31. Two air masses that meet and do not advance ______________________ ______________________ Complete the table by checking the correct column for each statement High-pressure System Statement 32. 33. 34. 35. 36. 37. 38. 39. Low-pressure System Characterized by sinking air Characterized by rising air Air flows toward the center Air flows away from the center Air moves clockwise in the northern hemisphere Air moves counterclockwise in the northern hemisphere Associated with fair weather Associated with clouds and precipitation Match the terms to the correct definition ____ ____ ____ 40. An instrument that measures the height of cloud layers and estimates cloud cover 41. An instrument that measures wind speed and direction 42. An instrument that measures temperature b. barometer c. anemometer ____ 43. An instrument that measures air pressure d. hygrometer ____ 44. A balloon-borne package of sensors that gathers upper-level weather data 45. An instrument that measures relative humidity e. ceilometer ____ a. thermometer f. radiosonde Use the terms below to complete the passage digital forecast short term long term analog forecast There are two major types of weather forecasts. A(n) (46) ______________________ relies on numerical data. It is the main method used in modern weather forecasting. Another type of forecast, the (47) ____________________, involves comparing current weather patterns to patterns that took place in the past. Regardless of the forecasting method, all forecasts are more reliable in the (48) ______________________. Forecasts become less reliable as they attempt to predict (49) _______________________ weather changes.