* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Survey
Document related concepts
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Atrial fibrillation wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
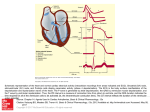
http://www.medicine-on-line.com ECG – A Pictorial Primer: 26/44 Second Degree Heart Block When transmission of the depolarizing impulse from the sinus node through the AV conduction system of the heart is interrupted intermittently, P wave of atrial contraction is no longer followed by a QRS complex of ventricular contraction in the interrupted beat. This is second degree heart block. There are 2 types of second degree heart block: Mobitz type I & Mobitz type II. In Mobitz type I block there is progressive prolongation of the PR interval, indicating increasing delay in AV conduction, before it fails altogether. When failure in AV conduction occurs, the P wave of atrial contraction is not followed by a QRS complex. After this missed ventricular beat, the PR interval returns to its shorter duration and the cycle of progressive PR prolongation and missed ventricular beat repeats itself. In Mobitz Type II block, a non-conducted P wave not followed by a QRS complex occurs suddenly without progressive prolongation of the PR interval. That is, the PR interval, which can be normal or prolonged, is constant before the non-conducted beat materializes. Mobitz type II second degree heart block indicates more serious disease of the conduction system in regions below the AV node and can progress to total failure of AV conduction (third degree heart block) without warning.