* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Potential energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of the European Union wikipedia , lookup
Energy efficiency in transport wikipedia , lookup
Kinetic energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy Independence and Security Act of 2007 wikipedia , lookup
Conservation of energy wikipedia , lookup
Negawatt power wikipedia , lookup
Photoelectric effect wikipedia , lookup
Energy in the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetic radiation wikipedia , lookup
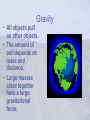
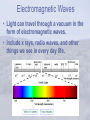
Review Notes #10 Motion and Energy Forces • A force is either push or pull. • Can stop an object, change its speed or cause it to change directions. • Exs. Balanced(top picture) and Unbalanced (bottom Picture) forces Gravity • All objects pull on other objects. • The amount of pull depends on mass and distance. • Large masses close together have a large gravitational force. Motion • Velocity is how fast an object is moving and in which direction. • Also the change in distance over a certain time • Acceleration is how fast an object speeds up or slows down. • Slowing down is negative acceleration. • Change in Velocity over a certain time. Newton’s Laws • 1st law – Law of inertia. An object in motion stays in motion, object at rest stays at rest unless acted on by an outside force. • 2nd law – F = ma • 3rd law – For every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction. Work and Machines • Work – a force moves an object a distance. • A machine can do work. • A machine puts in effort force to overcome resistance force. • No machine is 100% efficient. • Simple Machines – screw, lever, pulley, inclined plane, wheel and axle, wedge. Energy • Energy is the ability to do work. • Potential energy is stored. A certain height. • Kinetic energy is energy because an object is moving. • Energy can’t be created or destroyed only change forms. • Mechanical, sound, chemical, electrical, nuclear, light, heat. Waves • Light and sound travel in waves. • Longitudinal waves push and pull. • Transverse waves go up and down, • High amplitude, large volume • High frequency, high pitch. Sound • Produced by a vibrating object. • Doppler effect is what you hear when an object approaches and passes you. • The denser the medium the faster sound travels. • Temperature can also influence speed of sound. Heat • The vibrating motion of molecules. • Increase heat, molecules speed up and spread out. • Conduction – transfer by touch • Convections – transfer by warm rising and cool sinking • Radiation – transfer by waves through space. Magnetism • Magnets have north and south poles. • Poles are where the magnets are strongest. • Opposite poles attract. • Similar poles repel Electricity • Like charges repel and opposites attract. • Conductors, let electricity pass • Insulators prevent electricity from flowing. • Circuits – Need energy source, path, and energy user. • Series – one goes out they all go out, add one user and the rest get dimmer. • Parallel – wired like your house. Light • Light travels in straight paths called rays. • Light is 1,000,000 times faster than sound. • Light can be absorbed, reflected, or transmitted. • Light can be bent or refracted. Electromagnetic Waves • Light can travel through a vacuum in the form of electromagnetic waves. • Include x rays, radio waves, and other things we see in every day life.